Solubility and interfacial segregation of salts in ternary polyelectrolyte blends†
Abstract
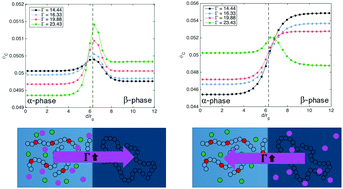
Solid Polymer Electrolytes (SPEs) consisting of ternary blends of charged polymer, neutral polymer, and plasticizer or salt have received much interest for their low volatility and high flexibility of polymers with ion-selective conductivity of the charge-carrying backbone. It has been shown that in these polyelectrolyte blends, where the dielectric constant is relatively low, ionic correlations can significantly influence the miscibility, inducing phase separation even at negative values of χN. Here we present a comprehensive study of phase behavior and interfacial segregation upon the addition of a tertiary component in blends of charged and neutral homopolymers. Using a hybrid of self-consistent field and liquid state theories (SCFT-LS), we investigate the bulk miscibility and the distribution of ions across the interface, looking at interfacial adsorption and selectivity of the minority component. We demonstrate that the competition between ionic correlations and ion entropy induces complex charge-dependent selectivity that can be tuned by the value of Γ, the ionic correlation strength. We show that charge interactions can have a pronounced effect on the interfacial width and tension, especially at low χN.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...