Unravelling the solvent polarity effect on the excited state intramolecular proton transfer mechanism of the 1- and 2-salicylideneanthrylamine. A TD-DFT case study†
Abstract
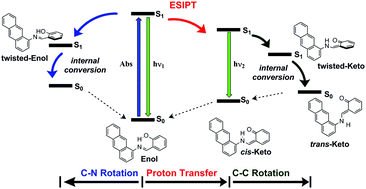
Time dependent density functional theory has been used to investigate the photochemical and photophysical processes involved in the excited states relaxation of 1- and 2-salicylideneanthrylamine in different solvent environments. This investigation reveals that the pathways involved in the relaxation of the first excited state depend on the solvent polarity. The emission spectrum in acetonitrile and methanol is dominated by the cis-keto tautomers, while in cyclohexane, the spectrum is dominated by the fluorescence emission of the locally excited trans-enol form. Our results showed that, for each compound, two nearly isoenergetic trans-enol conformers can coexist in equilibrium, which upon photoexcitation, can relax by two competitive processes: rotation about the azomethine N![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C bond leading to the twisted-enol conformer, and the excited state intramolecular proton transfer leading to the fluorescent cis-keto tautomer, which can undergo a cis–trans isomerization producing the trans-keto photochromic product. The TD-DFT relaxed potential energy profiles for the ESIPT show that the effect of changing the solvent from polar to nonpolar solvents results on an increment of the energy barrier, and therefore, the ESIPT become kinetically less favoured. In constrast, this change favours the relaxation of the excited trans-enol form towards the twisted conformers, in both the enol and keto regions.
C bond leading to the twisted-enol conformer, and the excited state intramolecular proton transfer leading to the fluorescent cis-keto tautomer, which can undergo a cis–trans isomerization producing the trans-keto photochromic product. The TD-DFT relaxed potential energy profiles for the ESIPT show that the effect of changing the solvent from polar to nonpolar solvents results on an increment of the energy barrier, and therefore, the ESIPT become kinetically less favoured. In constrast, this change favours the relaxation of the excited trans-enol form towards the twisted conformers, in both the enol and keto regions.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Celebrating Latin American Talent in Chemistry


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...