Selective voltammetric sensors based on composites of chitosan polyelectrolyte complexes with cyclodextrins for the recognition and determination of atenolol enantiomers†
Abstract
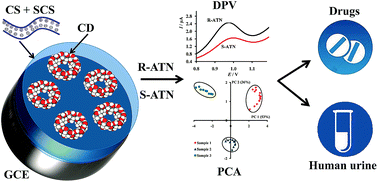
Voltammetric sensors based on glassy carbon electrodes (GCEs) modified with composites of polyelectrolyte complexes of chitosan (CS) and chitosan succinamide (SCS) with cyclodextrins (CDs) for the enantioselective recognition and determination of atenolol (ATN) enantiomers were studied using cyclic voltammetry and differential pulse voltammetry. The films of the polyelectrolyte complexes of CS and SCS, as well as composites with α-, β- and γ-CDs, are stable in aqueous solutions and their properties do not change over a long period of time. The analytical characteristics of the sensors, the conditions of voltammogram registration and the capabilities for the recognition and determination of ATN enantiomers were studied. It was shown that the recognition of ATN enantiomers by registering voltammograms on three GCEs modified with composites of polyelectrolyte complexes of CS and SCS with CDs, followed by chemometric treatment of the principal component analysis, resulted in a significant increase in the percentage of correctly recognised samples, in comparison with the registration of voltammograms on only one electrode. The proposed sensory system was successfully applied to the recognition and determination of ATN enantiomers in pharmaceutical formulations and human urine and to establish the manufacturers of pharmaceuticals.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...