N-Doped hollow carbon nanosheet supported SnO2 nanoparticles
Abstract
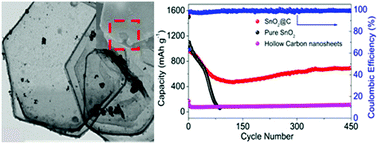
For the first time, we design and synthesise a novel structure of hollow carbon nanosheets with MgAl-layered double hydroxide (MgAl-LDH) as the template and poly-dopamine (PDA) as the carbon source via a facile method. To reveal the significance of hollow carbon nanosheets, buffering large strains during the lithium de-intercalation cycle and prolonging the cycle life, SnO2@C nanocomposites as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) are prepared. As a result, the structure of hollow carbon nanosheets contributes to the improvement of the capacity and stability of the SnO2 anode material. The capacity of hollow SnO2@carbon nanosheets remains 693 mA h g−1 after 450 cycles with the current density of 0.5 A g−1 far better than that of pristine SnO2.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers HOT articles for 2017


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...