Poly(fluoroacrylate)s with tunable surface hydrophobicity via radical copolymerization of 2,2,2-trifluoroethyl α-fluoroacrylate and 2-(trifluoromethyl)acrylic acid†
Abstract
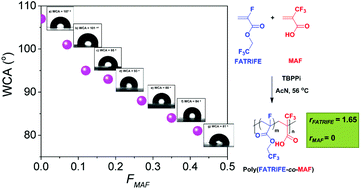
The synthesis of poly(fluoroacrylate)s with tunable wettability and improved adhesion for potential application as functional coatings was achieved via radical copolymerization of 2,2,2-trifluoroethyl α-fluoroacrylate (FATRIFE) with 2-(trifluoromethyl)acrylic acid (MAF), an adhesion-promoting monomer. These copolymerizations, initiated by tert-butyl peroxypivalate at varying comonomer feed ([FATRIFE]0/[MAF]0) ratios led to a series of poly(FATRIFE-co-MAF) copolymers with different molar compositions in fair to good conversions (32–87%) depending on the MAF feed content. The microstructures of the synthesized poly(FATRIFE-co-MAF) copolymers were determined by 19F NMR spectroscopy. Even at MAF feed contents higher than 50%, MAF incorporation into the copolymers was lower than 50%, since MAF does not undergo any homopolymerization under radical polymerization conditions. The reactivity ratios of the (FATRIFE; MAF) monomer pair were also determined (rFATRIFE = 1.65 ± 0.07 and rMAF = 0 at 56 °C) evidencing the formation of statistical copolymers. Initiation involving a highly branched perfluorinated radical that released a ˙CF3 radical enabled the demonstration of the regioselective attack of the latter radical onto the CH2 of FATRIFE. The resulting poly(FATRIFE-co-MAF) copolymers exhibited various glass transition temperatures (Tgs) depending on their compositions. Tg values increased with increasing MAF contents in the copolymer. In addition, their thermal stability (the temperature for 10% weight loss in air, Td10%) increased with increasing FATRIFE content in the copolymer and reached 348 °C (for that containing 93 mol% FATRIFE). Finally, a high copolymer MAF content led to both a good adhesion onto metal substrates and to improved hydrophilicity, as revealed by the decrease of the water contact angle from 107° (for a reference PFATRIFE homopolymer) to 81° (for a copolymer containing 42 mol% MAF).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...