3D multi-energy deconvolution electron microscopy†
Abstract
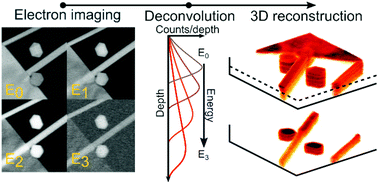
Three-dimensional (3D) characterization of nanomaterials is traditionally performed by either cross-sectional milling with a focused ion beam (FIB), or transmission electron microscope tomography. While these techniques can produce high quality reconstructions, they are destructive, or require thin samples, often suspended on support membranes. Here, we demonstrate a complementary technique allowing non-destructive investigation of the 3D structure of samples on bulk substrates. This is performed by imaging backscattered electron (BSE) emission at multiple primary beam energies – as the penetration depth of primary electrons is proportional to the beam energy, depth information can be obtained through variations in the beam acceleration. The detected signal however consists of a mixture of the penetrated layers, meaning the structure's three-dimensional geometry can only be retrieved after deconvolving the BSE emission profile from the observed BSE images. This work demonstrates this novel approach by applying a blind source separation deconvolution algorithm to multi-energy acquired BSE images. The deconvolution can thereby allow a 3D reconstruction to be produced from the acquired images of an arbitrary sample, showing qualitative agreement with the true depth structure, as verified through FIB cross-sectional imaging.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...