Calcium isotope signature: new proxy for net change in bone volume for chronic kidney disease and diabetic rats†
Abstract
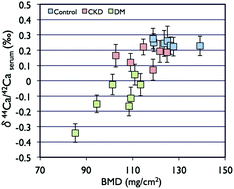
Herein, we measure the Ca isotope ratios (44Ca/42Ca and 43Ca/42Ca) in serum and bone samples collected from rats with chronic kidney disease (CKD) or diabetes mellitus (DM). For the serum samples, the isotope ratios are lower for the CKD (δ44Ca/42Caserum = 0.16 ± 0.11‰; 2SD, n = 6) and the DM (δ44Ca/42Caserum = −0.11 ± 0.25‰; 2SD, n = 7) rats than that for the control rats (δ44Ca/42Caserum = 0.25 ± 0.04‰; 2SD, n = 7). Bone samples from two distinct positions of 20 rats in total, namely, the center and proximal parts of the tibial diaphysis, are subject to Ca isotope analysis. The resulting δ44Ca/42Ca values for the bone of the proximal part are about 0.3‰ lower than that for the serum samples from the same rats. The larger isotope fractionations between the serum and bone are consistent with previously reported data for vertebrate animals (e.g., Skulan and DePaolo, 1999), which suggests the preferential incorporation of lighter Ca isotopes through bone formation. For the bones from the control and CKD rats, there were no differences in the δ44Ca/42Ca values between the positions of the bone. In contrast, the δ44Ca/42Ca values of the bone for the DM rats were different between the positions of the bone. Due to the lower bone turnover rate for the DM rats, the δ44Ca/42Ca for the middle of the diaphysis can reflect the Ca isotopes in the bone formed prior to the progression of DM states. Thus, the resulting δ44Ca/42Ca values show a clear correlation with bone mineral density (BMD). This can be due to the release of isotopically lighter Ca from the bone to the serum. In the present study, our data demonstrate that the δ44Ca/42Ca value for serum can be used as a new biomarker for evaluating changes in bone turnover rate, followed by changes in bone volume.
- This article is part of the themed collections: Metallomics Recent HOT articles and Metallomics in Japan


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...