Design, synthesis and preliminary antimicrobial evaluation of N-alkyl chain-tethered C-5 functionalized bis-isatins†
Abstract
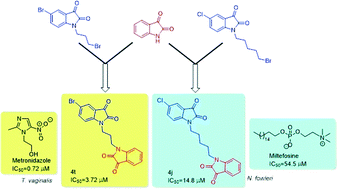
A series of N-alkyl-tethered C-5 functionalized bis-isatins were synthesized and evaluated for their antimicrobial activity against pathogenic microorganisms. The preliminary evaluation studies revealed compound 4t, with an optimal combination of a bromo substituent at the C-5 position of the isatin ring and a propyl chain linker, being the most active among the synthesized series exhibiting an IC50 value of 3.72 μM against Trichomonas vaginalis while 4j exhibited an IC50 value of 14.8 μM against Naegleria fowleri, more effective than the standard drug miltefosine. Compound 3f with an octyl spacer length was the most potent among the series against Giardia lamblia with an IC50 of 18.4 μM while 3d exhibited an IC50 of 23 μM against Entamoeba histolytica. This library was also screened against the fungal pathogen Aspergillus parasiticus. A number of the compounds demonstrated potency against this fungus, illustrating a possible broad-spectrum activity. Furthermore, an evaluation of these synthesized compounds against a panel of normal flora bacteria revealed them to be non-cytotoxic, demonstrating the selectivity of these compounds. This observation, in combination with previous studies that found isatin to be non-toxic to humans, presents a new possible scaffold for drug discovery against these important protozoal pathogens of humans and animals.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...