Evaluation and optimization of reduction and alkylation methods to maximize peptide identification with MS-based proteomics†‡
Abstract
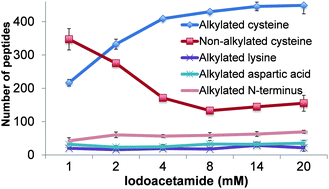
Mass spectrometry (MS) has become an increasingly important technique to analyze proteins. In popular bottom-up MS-based proteomics, reduction and alkylation are routine steps to facilitate peptide identification. However, incomplete reactions and side reactions may occur, which compromise the experimental results. In this work, we systematically evaluated the reduction step with commonly used reagents, i.e., dithiothreitol, 2-mercaptoethanol, tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine, or tris(3-hydroxypropyl)phosphine, and alkylation with iodoacetamide, acrylamide, N-ethylmaleimide, or 4-vinylpyridine. By using digested peptides from a yeast whole-cell lysate, the number of proteins and peptides identified were very similar using four different reducing reagents. The results from four alkylating reagents, however, were dramatically different with iodoacetamide giving the highest number of peptides with alkylated cysteine and the lowest number of peptides with incomplete cysteine alkylation and side reactions. Alkylation conditions with iodoacetamide were further optimized. To identify more peptides with cysteine, thiopropyl-sepharose 6B resins were used to enrich them, and the optimal conditions were employed for the reduction and alkylation. The enrichment resulted in over three times more cysteine-containing peptides than without enrichment. Systematic evaluation of the reduction and alkylation with different reagents can aid in a better design of bottom-up proteomic experiments.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...