Photocatalytic nanomaterials for solar-driven bacterial inactivation: recent progress and challenges
Abstract
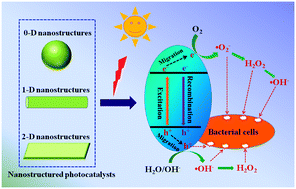
Nanostructured photocatalysts have attracted ever-growing research attention in the application of solar energy for water disinfection. Over the past few decades, various photocatalytic nanomaterials have shown superior bacterial inactivation activity to their bulk counterparts, due to their enhanced interfacial charge separation and large surface area providing more active sites. This review presents an overview of the current research activities that focus on the development of nanostructured photocatalysts for water disinfection, including 0D, 1D and 2D (low-dimensional) nanostructures. The synthesized methods, characterization and photocatalytic bacterial inactivation performances are systematically summarized and discussed. In particular, a new conceptual direction to develop naturally occurring materials is highlighted, especially for accelerating practical industrial application. Moreover, the photocatalytic bacterial inactivation process and mechanisms based on the role of reactive species are briefly reviewed from a tutorial point of view. Finally, future research opportunities and challenges associated with the development of highly efficient and cost-effective nano-photocatalysts for water disinfection using inexhaustible solar energy are also pointed out.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Environmental Science: Nano 2017 Most Downloaded Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...