A reduced graphene oxide/mixed-valence manganese oxide composite electrode for tailorable and surface mountable supercapacitors with high capacitance and super-long life†
Abstract
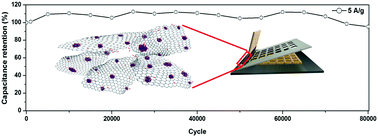
Developing supercapacitor electrodes with an ultra-long cycle life and a high specific capacitance is critical to the future energy storage devices. Herein, we report a scalable synthesis technology of mixed-valence manganese oxide nanoparticles anchored to reduced graphene oxide (rGO/MnOx) as the high-performance supercapacitor electrodes. First, 2-dimensional (2D) δ-MnO2 nanosheets are formed on a graphene oxide (GO) template, which is then in situ reduced by hydrazine vapour to mixed-valence manganese oxide nanoparticles evenly distributed on a rGO conductive network. The obtained rGO/MnOx electrode material exhibits a high specific capacitance of 202 F g−1 (mass loading of 2 mg cm−2), a large areal specific capacitance of 2.5 F cm−2 (mass loading of up to 19 mg cm−2), and a super-long-life stability of 106% capacitance retention after 115 000 charge/discharge cycles. By using an ionic liquid electrolyte and an activated carbon anode, asymmetric supercapacitors (AScs) are also constructed and can be packaged into a high performance miniaturized energy storage component in either a tailorable or surface mountable configuration. Our ASc shows superior performance characteristics, with typical figures of merit including maximum energy densities of 47.9 W h kg−1 at 270 W kg−1 and 19.1 W h kg−1 at the maximum power density of 20.8 kW kg−1. The capacitance retention of the ASc is 96% after 80 000 charge/discharge cycles, which is the most excellent stability performance in an ionic liquid electrolyte as compared with the recently reported pseudo-supercapacitors. This technology may find vast applications in future miniaturized portable and wearable electronics.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...