Towards ionic liquids with tailored magnetic properties: bmim+ salts of ferro- and antiferromagnetic Cu II3 triangles†
Abstract
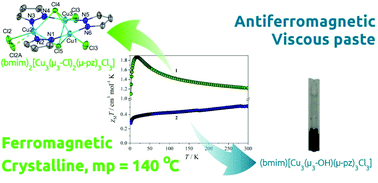
Complexes (bmim)2[Cu3(μ3-Cl)2(μ-pz)3Cl3] (1), (bmim)[Cu3(μ3-OH)(μ-pz)3Cl3] (2) and (bmim)2[Cu3(μ3-OH)(μ-Cl)(μ-pz)3Cl3] (3) were synthesized (bmim+ = 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium, pz− = pyrazolato anion). Dianionic complexes 1 and 3 were obtained as crystalline solids, whereas the monoanionic complex 2 was obtained as a viscous paste. Magnetic susceptibility and X-band EPR studies revealed intramolecular ferromagnetic interactions for 1 with small magnetoanisotropy in its ground state (D3/2 ∼ 10−3 cm−1) and intramolecular antiferromagnetic interactions for 2 and 3 (−285 and −98 cm−1 average J, respectively) with important magnetic anisotropy in their ground states stemming from a combination of low magnetic symmetry and antisymmetric exchange interactions. Thermal studies revealed a clear melting point of 140 °C for 1, which is lower than that of its PPN+ and Bu4N+ analogues (1PPN and 1Bu4N, respectively, PPN+ = bis(triphenylphosphine)iminium). Upon cooling, 1 remains molten down to 70 °C. Mixtures of the salts 1, 1PPN and 1Bu4N, exhibited modified melting behaviours, with the mixtures exhibiting lower melting points than those of either of their pure components.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...