Influence of transition metal doping on the electronic and optical properties of ReS2 and ReSe2 monolayers
Abstract
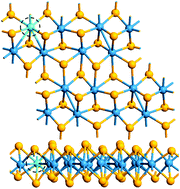
We investigate the structural, electronic and optical properties of transition metal doped triclinic monolayered rhenium disulfide and diselenide (ReS2 and ReSe2) by means of quantum mechanical calculations. The calculated electronic band gaps for ReS2 and ReSe2 monolayers are 1.43 eV and 1.23 eV, respectively, with both having a non-magnetic ground state. The calculated dopant substitutional energies under both Re-rich and X(S or Se)-rich conditions show that it is possible to experimentally synthesize transition metal doped ReX2 (where X is S or Se) monolayer systems. We found that the presence of dopant ions (such as V, Cr, Mn, Fe Co, Nb, Mo, Ta and W) in the ReS2 and ReSe2 monolayers significantly modifies their electronic ground states with consequent introduction of defect levels and modification of the density of states profile. However, it was found that Mn doped structures show a very minute reduction of the electronic band gap. We found that a ferro- or a non-magnetic ground state configuration was obtained depending on the choice of dopant ions in ReS2 and ReSe2 monolayers. Cr, Fe and Co doping result in a ferro-magnetic ground state configuration of the ReX2 structures. The calculated absorption and reflectivity spectra show that this class of dopants causes a general increase in the absorption spectral peaks but only a minute influence on the reflectivity. Optical anisotropy was observed depending on whether the direction of polarization in the xy-plane is either parallel or perpendicular.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...