Ultrafast dynamics and solvent-dependent deactivation kinetics of BODIPY molecular rotors†
Abstract
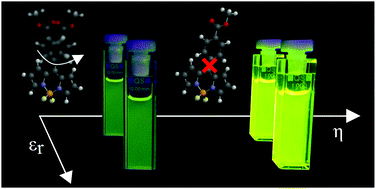
Molecular rotors based on meso-substituted boron-dipyrromethane (BODIPY) are widely recognized fluorescent viscosity sensors. The viscosity dependence of their fluorescence arises from an efficient excited-state deactivation process that can only occur when molecular-scale motion is not hindered. Here, we use visible and IR pump–probe spectroscopies combined with TD-DFT calculations to show that this fluorescence deactivation takes place through a fast and irreversible process which does not involve intermediate electronic states. Our data indicate that nonradiative excited-state deactivation of BODIPY molecular rotors is practically independent of solvent polarity, but strongly governed by viscoelastic/free volume properties of the local environment in both low- and high-viscosity regimes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...