Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleLoss channels in triplet–triplet annihilation photon upconversion: importance of annihilator singlet and triplet surface shapes†
Victor
Gray
 a,
Ambra
Dreos
a,
Paul
Erhart
a,
Ambra
Dreos
a,
Paul
Erhart
 b,
Bo
Albinsson
b,
Bo
Albinsson
 a,
Kasper
Moth-Poulsen
a,
Kasper
Moth-Poulsen
 a and
Maria
Abrahamsson
a and
Maria
Abrahamsson
 *a
*a
aDepartment of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Chalmers University of Technology, 412 96 Gothenburg, Sweden. E-mail: abmaria@chalmers.se
bDepartment of Physics, Chalmers University of Technology, 412 96 Gothenburg, Sweden
First published on 5th April 2017
Abstract
Triplet–triplet annihilation photon upconversion (TTA-UC) can, through a number of energy transfer processes, efficiently combine two low frequency photons into one photon of higher frequency. TTA-UC systems consist of one absorbing species (the sensitizer) and one emitting species (the annihilator). Herein, we show that the structurally similar annihilators, 9,10-diphenylanthracene (DPA, 1), 9-(4-phenylethynyl)-10-phenylanthracene (2) and 9,10-bis(phenylethynyl)anthracene (BPEA, 3) have very different upconversion efficiencies, 15.2 ± 2.8%, 15.9 ± 1.3% and 1.6 ± 0.8%, respectively (of a maximum of 50%). We show that these results can be understood in terms of a loss channel, previously unaccounted for, originating from the difference between the BPEA singlet and triplet surface shapes. The difference between the two surfaces results in a fraction of the triplet state population having geometries not energetically capable of forming the first singlet excited state. This is supported by TD-DFT calculations of the annihilator excited state surfaces as a function of phenyl group rotation. We thereby highlight that the commonly used “spin-statistical factor” should be used with caution when explaining TTA-efficiencies. Furthermore, we show that the precious metal free zinc octaethylporphyrin (ZnOEP) can be used for efficient sensitization and that the upconversion quantum yield is maximized when sensitizer–annihilator spectral overlap is minimized (ZnOEP with 2).
1 Introduction
As an energy source the Sun has enormous potential to provide mankind with large amounts of clean and renewable energy.1 Accordingly a great deal of research is focused on developing efficient ways of converting solar photons to usable and storable forms of energy.2–9 However, most direct ways of utilizing solar photons are limited to only the part of the solar spectrum that provides sufficient energy for driving the desired processes. One possibility to access the otherwise wasted, low-energy photons is through photon upconversion.Photon upconversion (UC) is a process that generates high energy photons from two, or more, low energy photons. A number of processes are capable of achieving this, with the two most relevant for solar energy applications being energy transfer in lanthanide ion-doped materials and triplet–triplet annihilation (TTA) in organic molecules.10,11 In the last decade there has been renewed interest in TTA-UC amongst chemists, biochemists and physicists as new and improved systems have been applied in e.g., bio-imaging,12–16 photo-dynamic therapy17,18 and solar energy applications.19–26 TTA is also important in OLEDs as it makes otherwise dark triplet states accessible.27
TTA is a bimolecular process that occurs between two molecules in their lowest triplet excited state, which form one higher excited singlet, triplet or quintet state.28 If the formed excited state is a singlet, the TTA process can result in delayed fluorescence as observed by Hatchard and Parker half a century ago.29–32 With proper design of the molecular system TTA can lead to anti-Stokes shifted delayed fluorescence,30,33,34 when two photons of low energy (long wavelength) are fused into one photon of high energy (short wavelength). The TTA-UC mechanism is described in detail in the ESI,† and Fig. S1.
Even though TTA-UC already has been incorporated in some technical applications and devices19,21,25,26,35,36 there are still many fundamental questions to be answered. For example TTA-UC systems working close to or at the maximum 50% quantum yield (two absorbed photons result in one emitted photon) are still to be realized. In order to design efficient TTA-UC systems, all possible loss mechanisms must be understood in detail. One loss mechanism, frequently invoked to explain efficiencies lower than 50%, is the so called spin factor which originates from the statistical probability of forming a singlet state when two triplets are combined. Initially, this spin-statistical factor was believed to limit a TTA-UC system efficiency to 5.5%‡ but this notion has since been dismissed, due to many reports of efficiencies well above that.23,37 Still, a full understanding of the impact of the spin-statistical factor as well as other loss mechanisms is missing. This makes it difficult to rationally design new annihilators for more efficient TTA-UC. In fact, the only explicitly formulated design parameters for the two involved species, the annihilator and the sensitizer, are based on a few basic requirements.35,38 The sensitizer should have;
• high absorption coefficient,
• close to quantitative triplet yield,
• long lived triplet state (>10 μs),
• small singlet–triplet splitting minimizes energy losses,
For the annihilator
• the triplet energy should be slightly lower than the triplet energy of the sensitizer to ensure efficient triplet energy transfer,
• two times the annihilator triplet state energy (2 × ET1) must be higher than the energy of the annihilator first excited singlet state (ES1). In other words eqn (1) must be fulfilled.
| 2 × ET1 ≥ ES1 | (1) |
• 2 × ET1 should optimally also be less than the energy of the first quintet (EQ1) state and second triplet state (ET2), eliminating the possibility of forming these parasitic states during the TTA process.
• Finally, the annihilator should have a high fluorescence quantum yield.
Besides these fundamental considerations it is important that the emitted light is not reabsorbed by the sensitizer, in other words there should be a small spectral overlap between the sensitizer absorption and annihilator emission. Ideally the sensitizer and annihilator should consist of cheap, non-toxic and abundant materials.
Even with all the above requirements fulfilled the overall UC quantum yield (ΦUC) might, however, be low. One example of such a case is the combination of 9,10-bis(phenylethynyl)anthracene (BPEA, 3) with the sensitizer meso-tetraphenyl-tetrabenzoporphyrin palladium (PdPh4TBP).16,39–41 To the best of our knowledge there has been no report of BPEA (3) with a ΦUC greater than 5% in low-viscosity solvents.16,39–41 This is surprising as the similar chromophore DPA (1) has successfully been used as an annihilator with ΦUC well exceeding 15%.23,42 This discrepancy between two chromophores that both appear to fulfill the basic requirements illustrates the limitations of the design strategy outlined above and so far most UC-pairs are based on a few similar molecular structures.26
Thus, we set out to do a detailed investigation of the differences between DPA (1, Fig. 1) and BPEA (3, Fig. 1) and ultimately understand the loss mechanisms involved in TTA. We synthesized a hybrid analogue similar to both 1 and 3 with one ethynyl spacer between the anthracene core and the phenyl side-group, 9-(4-phenylethynyl)-10-phenylanthracene (2, Fig. 1). We find that the shape of the excited state surfaces of the annihilator plays a key role for the overall efficiency. This is especially important for conformationally flexible annihilators, as in their relaxed triplet state, eqn (1) might not be fulfilled for the whole excited population. We argue that this loss channel can have an equal or larger influence than the spin-statistical factor.
This set of annihilators also allow for a systematic study of the effect of spectral overlap, and we demonstrate clearly that with a properly matched annihilator, the precious metal free sensitizer, zinc octaethylporphyrin (ZnOEP, Fig. 1), is as efficient as its platinum analogue (PtOEP, Fig. 1), previously unprecedented with precious metal free sensitizers. We observe that the highest upconversion quantum yield (ΦUC) is obtained in the system with the smallest spectral overlap, namely that consisting of 2 and ZnOEP.
2 Experimental details
2.1 Preparation of annihilators
9-(4-Phenylethynyl)-10-phenylanthracene (2) was directly synthesized from the commercially available 4-ethynylbenzene and the brominated derivative of 9-phenylanthracene in a Sonogashira cross-coupling reaction; full details and NMR spectra are provided in the ESI,† Fig. S2 and S3. 9,10-Diphenylanthracene (1) and 9,10-bis(phenylethynyl)anthracene (3) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich and used without further purification.2.2 Transient absorption spectroscopy
Transient absorption was used to study the annihilator triplet lifetimes, triplet energy transfer from ZnOEP to the annihilators and the TTA rate-constant in UC samples. Details of the setup and sample preparation can be found in the ESI.†2.3 Upconversion setup and measurement
UC samples were prepared in pairs in a glovebox and sealed in screw-cap quartz cuvettes, with optical path length 1 cm. The samples were excited at 532 nm with a Millenia Vs continuous laser from Spectra-Physics Lasers, the excitation intensity was varied using a neutral density filter and the intensity measured using a power-meter from Starlite Ophir. The laser spot diameter was determined to 2.5 mm using laser alignment paper. The emission was recorded at 90° angle using a Spex1681 (YJ Horiba) monochromator and a Photo-Multiplier Tube detector.The upconversion quantum yield (ΦUC) was determined by relative actionometry using Cresyl Violet in methanol (fluorescence quantum yield, Φr = 54%)43 as reference. The reference was measured at the maximum excitation intensity and ΦUC was calculated from eqn (2):
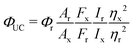 | (2) |
2.4 DFT calculations
Density functional theory (DFT) as well as time dependent DFT (TD-DFT) calculations at the B3LYP/6-311+G* level44–47 using the NWChem 6.5 software package were carried out to further elucidate the optical properties of the annihilator molecules.48 To evaluate the sensitivity of the results to the choice of the exchange–correlation functional, we also conducted calculations using the CAM-B3LYP functional,49 which yields similar results. For further details, see the ESI.†3 Results and discussion
3.1 Spectral characterization
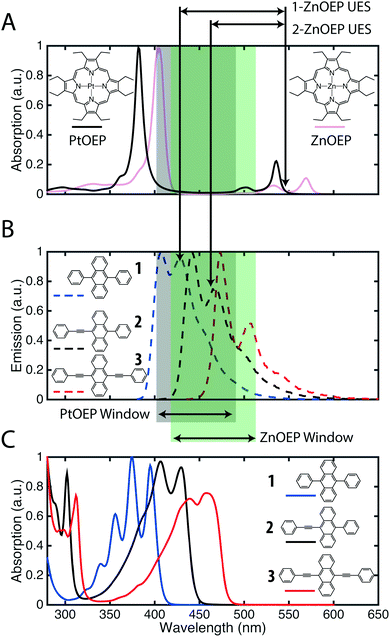
In Fig. 2 the absorption and emission spectra of the anthracene derivatives (1–3) in toluene are compared to the ZnOEP and PtOEP absorption spectra. The fraction of reabsorbed photons (α) is a function of sensitizer concentration (cS), path length (l) and wavelength (λ), as described by eqn (3).50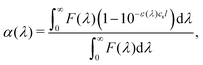 | (3) |
To compare the annihilator–sensitizer pairs we calculate the fraction of reabsorbed photons using the actual concentrations used in the UC samples (cS = 16 μM) and half of the cuvette path length (l = 0.5 cm). Under these conditions the combination of 2 with ZnOEP has the smallest fraction of reabsorbed photons (2.9%) whereas 1 and ZnOEP has the largest (35.8%), Table 1. To emphasize the spectral window where the sensitizer has minimal absorption the wavelength region is highlighted in Fig. 2.
| Compound | α ZnOEP (%) | α PtOEP (%) | k ZnOEPTET (M−1 s−1) | k PtOEPTET (M−1 s−1) | UESZnOEP (eV) | UESPtOEP (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Fraction of reabsorbed photons, calculated for cS = 16 μM and l = 0.5 cm. | ||||||
| 1 | 35.8 | 15.8 | 7.83 × 108 | 1.88 × 109 | 0.59 | 0.46 |
| 2 | 2.9 | 8.1 | 1.69 × 109 | 2.70 × 109 | 0.37 | 0.24 |
| 3 | 4.7 | 11.3 | 2.55 × 109 | 2.70 × 109 | 0.20 | 0.08 |
To the best of our knowledge there are only a few recent reports42,51,52 of zinc porphyrins as sensitizer for TTA-UC. Aulin et al. observed that, with 9,10-diphenylanthracene (1), ZnOEP was not as efficient as the precious metal analogues PdOEP and PtOEP.52 The authors invoked less efficient triplet energy transfer to 1 as a reason. This is a consequence of the first excited triplet state (T1) being lower in energy for ZnOEP compared to PtOEP and PdOEP, resulting in a reduced driving force for triplet energy transfer to 1. This can, however, be overcome by use of high annihilator concentrations (vide infra).
We recently reported that, at low sensitizer concentrations and high annihilator concentrations, ZnOEP was efficient in sensitizing 1.42 These contradicting observations can be explained by the relatively large spectral overlap between the ZnOEP absorption and the emission from 1, Fig. 2. A small spectral overlap is particularly important when using high concentrations of the sensitizer, which e.g., is necessary in thin solid films where a high concentration is needed to absorb the majority of the photons.
3.2 Triplet energy transfer to the annihilators
The triplet energy transfer (TET) from sensitizer to annihilator follows Stern–Volmer kinetics (Fig. S4, ESI†). Even though ZnOEP has a triplet state energy of 1.78 eV53–55 (Fig. 3), which is lower than that of PtOEP (1.91 eV, determined from phosphorescence at 650 nm in degassed toluene), they both efficiently sensitize the triplet states of 2 and 3. The diffusion limited bimolecular quenching constants (kTET) are presented in Table 1. The more blue-shifted annihilator 1 is not as efficiently sensitized by ZnOEP, (kTET = 7.83 × 108 M−1 s−1) because 1 has a triplet state higher in energy compared to 2 and 3, thus decreasing the driving force of TET from ZnOEP to 1. This is not surprising as both 2 and 3 have red-shifted absorption compared to 1 which is paralleled by the triplet state energies as shown by the calculations, vide infra (Fig. 3). At sufficiently high annihilator concentration the TET from ZnOEP to 1 can, however, still be close to quantitative (ΦTET > 97% for concentrations [1] >0.35 mM, see Fig. S5, ESI†) and should therefore not limit the UC process at these concentrations.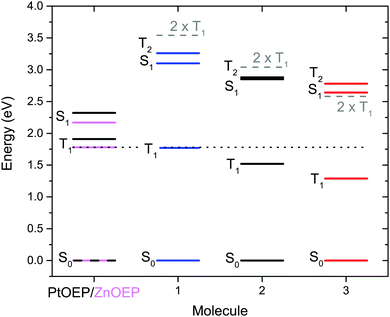 | ||
| Fig. 3 Energy level diagram of the studied molecules. ES1 of 1–3 are the experimentally determined 0–0 transition. ET1 and ET2 are obtained from TD-DFT calculations while ES1 and ET1 energies for PtOEP as well as the ES1 energy of ZnOEP are experimentally obtained. ZnOEP ET1 is from ref. 50–55. Dotted line is at 1.78 eV, the triplet energy of ZnOEP, and dashed lines are at 2 × ET1 for the annihilators. | ||
The experimental findings are in good agreement with our TD-DFT calculations, where the T1–S0 excitation energies (ET1) calculated at the singlet ground state structure are 1.76 eV, 1.51 eV and 1.28 eV for 1, 2 and 3, respectively. The calculated energies for 2 and 3 are also very close to that previously reported.56 The calculated energies are summarized in Fig. 3 and further details can be found in the ESI.† The calculated ET1 for 1 (1.76 eV) is in excellent agreement with that determined experimentally (1.77 eV).57 Based on experimental data, the ET1 energy of 3 has been estimated to lie in the range 1.36–1.82 eV,58 slightly above the calculated value (1.28 eV). Our experiments, however, strongly suggest that the upper limit of this interval must be substantially lower as ZnOEP (ET1 = 1.78 eV) efficiently sensitizes 3. Furthermore, the calculated S1–S0 excitation energy (ES1) of 1 (3.10 eV) is identical to the experimental 0-0 transition determined from the absorption and fluorescence of 1. ES1 of 2 (2.74 eV) and 3 (2.44 eV) are slightly underestimated compared to the experimental 0–0 transitions which are 2.85 eV and 2.64 eV for 2 and 3 respectively. Therefore, we use the experimentally determined ES1 energies in Fig. 3.
A reduction in the triplet state energy of the annihilator leads to a more efficient triplet energy transfer from sensitizer to annihilator. However, as mentioned above there is a requirement that the triplet energy of the annihilator (ET1) must be more than half of the singlet energy (ES1) as described in eqn (1). Comparing the experimentally determined ES1 energy to the calculated ET1 energy the margin to fulfilling eqn (1) decreases from 1 to 2 and for 3 2 × ET1 is very close to ES1 but slightly lower, as seen in Fig. 3. As TTA-UC is still observed for 3, there must be circumstances under which eqn (1) is fulfilled (vide infra).
A lower singlet energy leads to a smaller anti-Stokes shift of the upconverted emission if the same sensitizer is used. In Table 1 the anti-Stokes shift or upconverted energy shift (UES) is shown for the different sensitizer annihilator pairs. The UES is calculated from the average integral weighted center points of the absorption and emission spectra of the sensitizer absorption and annihilator emission, respectively, in an upconverting sample as previously described.26 Quantum yields and fluorescence lifetimes of the annihilators are reported in Table S1 (ESI†).
3.3 Triplet–triplet annihilation photon upconversion
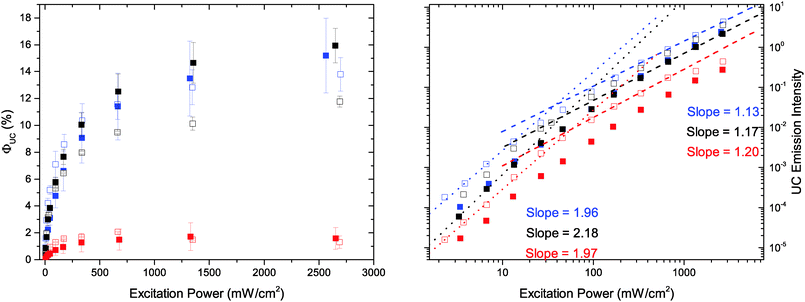
To study the upconversion capabilities samples containing 0.5 mM annihilator and 15.5 μM sensitizer were prepared as described in Experimental details. To the left in Fig. 4 the upconversion quantum yield (ΦUC) as a function of excitation power is displayed. To the right in Fig. 4 the UC emission intensity shows the expected initial quadratic, followed by a linear, excitation power dependency.59ΦUC of 1 and 2 is high when the linear region is reached. 1 has an average ΦUC of 15.2 ± 2.8% and 13.8 ± 1.3% when sensitized by ZnOEP and PtOEP, respectively. 13.8 ± 1.3% is close to that observed by Monguzzi et al. at similar concentrations of 1 and PtOEP.60 It is somewhat surprising that the combination of 1 and ZnOEP which has a larger spectral overlap compared to 1 and PtOEP displayed a higher upconversion quantum yield. This is also in direct contrast to what was previously reported where ZnOEP was found to be an inefficient sensitizer to 1.52 However, in that study a ∼10 times higher sensitizer concentration was used and at high concentrations the reabsorption of the UC emission would be more significant, furthermore the excitation source was a ns pulsed Nd:YAG laser. Thus, considering the high triplet-yield of ZnOEP (∼90%61,62) and close to quantitative TET (vide supra), UC from ZnOEP and 1 would be expected to be similar, but slightly lower, compared to the case with PtOEP at low sensitizer concentrations, where reabsorption is not as substantial.As we observe a greater ΦUC in the case of ZnOEP there must be another factor influencing the UC process. To preclude that this originates from the heavy atom in PtOEP having a negative effect on the annihilator triplet lifetime through increased spin–orbit coupling, we determined the triplet lifetime of 2 in presence of low (0.5 μM) and high (50 μM) ZnOEP and PtOEP concentrations, respectively. The triplet state lifetimes, at low PtOEP concentrations, of 2 and 3 was determined to 2.41 ± 0.12 ms and 0.50 ± 0.03 ms, respectively (Fig. S6 and S7, ESI,† respectively), shorter than that previously determined for 1, 8.6 ms.63 A larger decrease in the lifetime of 2 was observed for high ZnOEP concentrations, compared to PtOEP and therefore the heavy-atom hypothesis was rejected. For full details see the ESI† and Fig. S6–S10.
For 2, ΦUC is maximized when combined with ZnOEP corresponding to the annihilator–sensitizer pair with the smallest spectral overlap. The combination of 2 with ZnOEP shows an average ΦUC of 15.9 ± 1.3% exceeding that of 1, which has larger spectral overlap with the sensitizer. ΦUC of 3 with either ZnOEP or PtOEP is low, 1.6 ± 0.8 and 1.3 ± 0.5%, respectively, which is in the same range as reported previously.16,39–41 This can be understood in terms of the small TTA-UC excess energy (eqn (1)) and large difference in the singlet and triplet excited state surfaces, as will be discussed below.
The kinetics of the TET and TTA is dependent on concentration of the sensitizer and annihilator and we have previously shown that the triplet–triplet annihilation rate-constant kTTA can be determined for 1 and other diphenyl-substituted anthracenes by solving the differential rate equations governing the system and fitting the results to the TA signals using kTTA as one of the fitting parameters (Table 2).63 Similar values of kTTA for 1 were obtained compared to what we reported previously.63 The rate-constants of annihilation for 2 and 3, 4.91 × 109 M−1 s−1 and 4.43 × 109 M−1 s−1, respectively, are slightly higher than for 1, 3.14 × 109 M−1 s−1. The value for 3 is also close to that previously determined for 2-chloro-bis-phenylethynylanthracene.64
| Molecule | τ T (ms) | k TTA (M−1 s−1) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8.6163 | 3.14 × 109 |
| 2 | 2.41 ± 0.12 | 4.91 × 109 |
| 3 | 0.50 ± 0.03 | 4.43 × 109 |
3.4 Loss mechanisms in triplet–triplet annihilation upconversion
The large difference of the upconversion quantum yields between the annihilators 1 and 3 suggests that there are fundamental differences and that a detailed analysis can provide valuable information about the loss mechanisms. The upconversion quantum yield depends on the efficiencies of all the involved processes as described in eqn (4):| ΦUC = fΦISCΦTETΦTTAΦAF, | (4) |
As the quantum yields in eqn (4) can be determined from individual experiments f is usually determined as the factor to equate the measured ΦUC to the product of the process efficiencies. This implies that any other loss mechanism would incorrectly be included in the spin-statistical factor. For example, ΦISC is 90% and 100% for ZnOEP and PtOEP respectively, and in the current UC samples ΦTET was determined to 100% for 3 (Fig. S5, ESI†) with both sensitizers. At an excitation power of about 2600 mW cm−2ΦTTA can be calculated to 46% and 48% for 3 with ZnOEP and PtOEP, respectively (see the ESI† for derivation and calculations of ΦTTA, Table S2). Also, the fluorescence quantum yield of 3 was determined to 85% (Table S1, ESI†) in degassed toluene. With these efficiencies and the determined ΦUC values we calculate the spin-statistical factor to 5.0–5.6%. This is close to the previously suggested spin-statistical limit of 5.55%37,65 indicating that both the triplet and quintet channel would be accessible. We see no reason why the quintet states would be accessible in 3 but not in 1 and 2. Also, from our calculations 3 has the highest lying T2 state, actually far above 2 × ET1, compared to 1 and 2. Therefore, the low ΦUC of 3 cannot be primarily explained by the spin-statistical factor.
One major difference between 1 and 3 is the possibility of phenyl group rotation. In 1 there is a relatively large barrier for rotation,67 whereas for 3 rotation is almost barrier-free, resulting in many more possible conformations in an equilibrated ground state population68 (Fig. 6A). In order to understand the system better we calculated the singlet and triplet energies for 1–3 as a function of phenyl group rotation (Fig. 6 and Fig. S12, ESI†). Obviously, depending on whether the two phenyl groups are rotated individually or simultaneously and in the same or opposite direction(s), the results are different. The differences are, however, small and do not change the overall conclusions (Fig. S12, ESI†). For clarity Fig. 6 only shows the energies for the case when the two phenyl groups are rotated simultaneously in opposite directions, as shown in Fig. 6B and we define the angle Δθ as the angle of rotation away from the equilibrium state configuration (θ), i.e. Δθ = θ − 90° for 1 and Δθ = θ − 0° for 3 as illustrated in Fig. 6B.
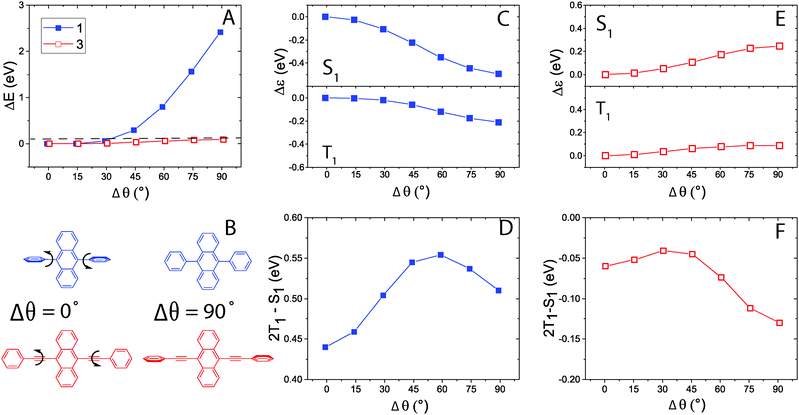 | ||
| Fig. 6 (A) Change in total energy of 1 (blue) and 3 (red) as a function of phenyl group rotation away from the equilibrium geometry (Δθ); dashed line corresponds to 4 × kBT = 0.1 eV at room temperature. (B) Schematic illustration of Δθ and corresponding phenyl group orientations. (C) Relative change in ES1 excitation energy (top) and ET1 (lower) for 1. (D) Change in the TTA energy balance (cf.eqn (1)) upon phenyl group rotation for 1. (E) Same as (C) for 3 and (F) same as (D) for 3. | ||
In the case of 1 with two single bonded phenyl rings, rotations away from the equilibrium geometry (θ = 90°) are restricted to a range of about Δθ = ±30° when allowing for an energy change of 0.1 eV (corresponding to 4 × kBT at room temperature) or less (Fig. 6A). The rotations cause a stronger coupling between the π-system of the phenyl rings and the extended π-conjugated system of the anthracene, leading to a red shift of both singlet (Fig. 6C, top) and triplet (Fig. 6C, bottom) excitations. Since the effect is less pronounced for the latter the TTA-UC energy excess, as described in eqn (1), becomes more positive with rotations (Fig. 6D).
The opposite behavior is true for 3, which features two phenylethynyl units. Here, an angular range of up to Δθ = ±90° is readily accessible within 4 × kBT at room temperature (Fig. 6A). In contrast to 1, rotations cause a less planar geometry for 3. This leads to a decrease in the extent of the conjugated π-system and correspondingly a blue shift of the excitation spectrum. Again singlet excitations (Fig. 6E, top) are found to be more sensitive to side-group rotations than triplet excitations (Fig. 6E, bottom). In the case of 3, however, this causes the TTA-UC energy excess to decrease at large angles (Fig. 6F). Due to the long lifetime of the triplet excited 3 an equilibrium population will have a relatively broad distribution of geometries and since 2 × ET1 is close to isoenergetic with ES1 at the planar geometry, only a small part of the triplet excited population likely fulfills eqn (1).§
In a recent study by Castellano and co-workers 3 was used to achieve an unprecedented ΦUC of 15.5% (based on a maximum of 50%).69 Their system studied therein consisted of a ∼100 times more viscous PEG solution (η = 55 mPa s) compared to toluene solutions (η = 0.59 mPa s) used here. According to another study, by Yokoyama et al., the viscosity affected the TTA efficiency of 1 and they found that there is an optimal viscosity where the TTA quantum yield is maximized.70 For 1 the optimal viscosity was found to be relatively low, 0.78 mPa s. In a high viscosity system diffusion is limited, resulting in fewer collisions between annihilators during a specific time. However, this would not dramatically affect the efficiency if the annihilator lifetime is long enough. On the other hand, the encounter complexes formed upon collision between two triplet excited annihilators would have a longer lifetime compared to the low viscosity systems. This could greatly benefit molecules such as 3, where only a few geometries result in successful annihilation, giving the annihilator time to adopt a conformation capable of singlet formation. To verify this explanation further experiments will be needed.
In summary we wish to sound a note of caution for the common practice of explaining unexplained losses by introducing the spin-statistical factor. More understanding of the effect of spin-statistics on a detailed photophysical level is definitely necessary, but one must also consider other loss channels as highlighted here. We explain the large difference in ΦUC between the similar annihilators DPA (1) and BPEA (3) not by spin-statistics, but by a loss channel originating from the difference in the excited triplet and singlet surfaces. The important differences arise from the softer rotations in the case of 3, which are readily accessible at room temperature, that give rise to stronger changes in the excitation energies than in the case of 1 and ultimately lead to a reduction in the driving force for TTA.
4 Conclusions
We have studied a series of annihilators, including the efficient annihilator DPA (1), the less efficient annihilator BPEA (3) and an intermediate anthracene analogue with only one phenylethynyl substituent (2). The series showed a gradual redshift of the absorption and emission with an approximate shift of 40 nm per additional triple bond. These annihilators were combined with the precious metal free sensitizer ZnOEP and the platinum analogue PtOEP to obtain functioning TTA-UC systems. ZnOEP was found to perform better than the platinum analogue and the combination of ZnOEP and 2, the pair with the smallest spectral overlap, resulted in the most efficient system in this study with an average ΦUC of 15.9 ± 1.3%. The spectral overlap, however, was found to only play a minor role at the low sensitizer concentrations used here (15.5 μM) as also 1 together with ZnOEP showed a high ΦUC of 15.2 ± 2.8% despite the much larger spectral overlap. For all three annihilators the combination with ZnOEP resulted in the highest ΦUC. These results clearly demonstrate that the precious metal free sensitizer ZnOEP is efficient, especially when combined with an optimal annihilator. Our work here highlight the need for a detailed photophysical understanding of TTA-UC systems in order to design more efficient and sustainable materials.Furthermore, in accordance with previous studies,16,39–41 we also found that 3 with both sensitizers showed a low ΦUC of about 2%, even though inherent processes such as triplet energy transfer, triplet–triplet annihilation and annihilator fluorescence all are efficient in these systems. Previous studies have not addressed this issue and here we explain the low ΦUC with a, not previously considered, loss factor, namely that if the excited state singlet and triplet surfaces have very different shapes the energetic requirement 2 × ET1 > ES1 might not be fulfilled for the whole excited triplet population. Our results thereby demonstrate the sensitivity of not only the excitation spectra but the TTA-UC energy balance (eqn (1)) to thermal vibrations. In particular, the rotational motion of side groups has a sizable impact in this regard. These findings contribute to the overall understanding of the requirements for designing efficient TTA-UC systems and it illustrates that the understanding of the TTA process is still very incomplete and that simply explaining losses as arising from spin-statistics is an oversimplification that should be applied with caution.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge funding from the Swedish Energy Agency, the Swedish Research Council, Swedish Strategic Research council and Knut and Alice Wallenberg foundation.References
- N. S. Lewis and D. G. Nocera, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2006, 103, 15729–15735 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. J. Nozik, M. C. Beard, J. M. Luther, M. Law, R. J. Ellingson and J. C. Johnson, Chem. Rev., 2010, 110, 6873–6890 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Li, M. Liu, N. G. Pschirer, M. Baumgarten and K. Müllen, Chem. Rev., 2010, 110, 6817–6855 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. M. Clarke and J. R. Durrant, Chem. Rev., 2010, 110, 6736–6767 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. W. Hains, Z. Liang, M. A. Woodhouse and B. A. Gregg, Chem. Rev., 2010, 110, 6689–6735 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. V. Kamat, K. Tvrdy, D. R. Baker and J. G. Radich, Chem. Rev., 2010, 110, 6664–6688 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Hagfeldt, G. Boschloo, L. Sun, L. Kloo and H. Pettersson, Chem. Rev., 2010, 110, 6595–6663 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Chen, S. Shen, L. Guo and S. S. Mao, Chem. Rev., 2010, 110, 6503–6570 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. G. Walter, E. L. Warren, J. R. McKone, S. W. Boettcher, Q. Mi, E. A. Santori and N. S. Lewis, Chem. Rev., 2010, 110, 6446–6473 Search PubMed.
- J. de Wild, A. Meijerink, J. K. Rath, W. G. J. H. M. van Sark and R. E. I. Schropp, Energy Environ. Sci., 2011, 4, 4835–4848 CAS.
- J. C. Goldschmidt and S. Fischer, Adv. Opt. Mater., 2015, 3, 510–535 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Wohnhaas, A. Turshatov, V. Mailänder, S. Lorenz, S. Baluschev, T. Miteva and K. Landfester, Macromol. Biosci., 2011, 11, 772–778 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q. Liu, T. Yang, W. Feng and F. Li, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 5390–5397 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q. Liu, B. Yin, T. Yang, Y. Yang, Z. Shen, P. Yao and F. Li, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 5029–5038 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Wohnhaas, V. Mailänder, M. Dröge, M. A. Filatov, D. Busko, Y. Avlasevich, S. Baluschev, T. Miteva, K. Landfester and A. Turshatov, Macromol. Biosci., 2013, 13, 1422–1430 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- O. S. Kwon, H. S. Song, J. Conde, H.-I. Kim, N. Artzi and J.-H. Kim, ACS Nano, 2016, 10, 1512–1521 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. H. C. Askes, A. Bahreman and S. Bonnet, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2014, 53, 1029–1033 Search PubMed.
- S. H. Askes, M. Kloz, G. Bruylants, J. T. Kennis and S. Bonnet, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015, 17, 27380–27390 RSC.
- Y. Y. Cheng, B. Fückel, R. W. MacQueen, T. Khoury, R. G. C. R. Clady, T. F. Schulze, N. J. Ekins-Daukes, M. J. Crossley, B. Stannowski, K. Lips and T. W. Schmidt, Energy Environ. Sci., 2012, 5, 6953–6959 CAS.
- T. F. Schulze, Y. Y. Cheng, B. Fckel, R. W. MacQueen, A. Danos, N. J. L. K. Davis, M. J. Y. Tayebjee, T. Khoury, R. G. C. R. Clady, N. J. Ekins-Daukes, M. J. Crossley, B. Stannowski, K. Lips and T. W. Schmidt, Aust. J. Chem., 2012, 65, 480–485 CrossRef CAS.
- T. F. Schulze, J. Czolk, Y.-Y. Cheng, B. Fückel, R. W. MacQueen, T. Khoury, M. J. Crossley, B. Stannowski, K. Lips, U. Lemmer, A. Colsmann and T. W. Schmidt, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2012, 116, 22794–22801 CAS.
- J.-h. Kim and J.-h. Kim, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 17478–17481 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. S. Khnayzer, J. Blumhoff, J. A. Harrington, A. Haefele, F. Deng and F. N. Castellano, Chem. Commun., 2012, 48, 209–211 RSC.
- A. Nattestad, Y. Cheng, R. Macqueen, T. Schulze, F. Thompson, A. Mozer, B. Fu, T. Khoury, M. Crossley, K. Lips, G. Wallace and T. W. Schmidt, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2013, 4, 2073–2078 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Börjesson, D. Dzebo, B. Albinsson and K. Moth-Poulsen, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2013, 1, 8521–8524 Search PubMed.
- V. Gray, D. Dzebo, M. Abrahamsson, B. Albinsson and K. Moth-Poulsen, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2014, 16, 10345–10352 RSC.
- D. Y. Kondakov, Philos. Trans. R. Soc., A, 2015, 373, 20140321 CrossRef PubMed.
- N. J. Turro, V. Ramamurthy and J. Scaiano, Modern Molecular Photochemistry of Organic Molecules, University Science Books, 2010 Search PubMed.
- C. A. Parker and C. G. Hatchard, Philos. Trans. R. Soc., A, 1962, 269, 574–584 CrossRef.
- C. A. Parker and C. G. Hatchard, Proc. Chem. Soc., 1962, 386–387 CAS.
- C. A. Parker, Philos. Trans. R. Soc., A, 1963, 276, 125–135 CrossRef CAS.
- C. A. Parker and T. A. Joyce, Chem. Commun., 1967, 744–745 RSC.
- D. V. Kozlov and F. N. Castellano, Chem. Commun., 2004, 2860–2861 RSC.
- T. N. Singh-Rachford and F. N. Castellano, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2010, 254, 2560–2573 CrossRef CAS.
- T. F. Schulze and T. W. Schmidt, Energy Environ. Sci., 2015, 8, 103–125 CAS.
- Y. Y. Cheng, A. Nattestad, T. F. Schulze, R. W. MacQueen, B. Fückel, K. Lips, G. G. Wallace, T. Khoury, M. J. Crossley and T. W. Schmidt, Chem. Sci., 2015, 7, 559–568 RSC.
- Y. Y. Cheng, B. Fückel, T. Khoury, R. G. C. R. Clady, M. J. Y. Tayebjee, N. J. Ekins-Daukes, M. J. Crossley and T. W. Schmidt, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2010, 1, 1795–1799 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Zhao, S. Ji and H. Guo, RSC Adv., 2011, 1, 937–950 RSC.
- S. Baluschev, V. Yakutkin, T. Miteva, G. Wegner, T. Roberts, G. Nelles, A. Yasuda, S. Chernov, S. Aleshchenkov and A. Cheprakov, New J. Phys., 2008, 10, 013007 CrossRef.
- J. H. Kang and E. Reichmanis, Angew. Chemie - Int. Ed., 2012, 51, 11841–11844 Search PubMed.
- K. Moor, J.-H. Kim, S. Snow and J.-H. Kim, Chem. Commun., 2013, 49, 10829–10831 RSC.
- V. Gray, K. Börjesson, D. Dzebo, M. Abrahamsson, B. Albinsson and K. Moth-Poulsen, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2016, 120, 19018–19026 CAS.
- D. Magde, J. H. Brannon, T. L. Cremers and J. Olmsted, J. Phys. Chem., 1979, 83, 696–699 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Becke, J. Chem. Phys., 1993, 98, 5648–5652 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Lee, W. Yang and R. Parr, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys., 1988, 37, 785–789 CrossRef CAS.
- A. D. McLean and G. S. Chandler, J. Chem. Phys., 1980, 72, 5639–5648 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Krishnan, J. S. Binkley, R. Seeger and J. A. Pople, J. Chem. Phys., 1980, 72, 650–654 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Valiev, E. J. Bylaska, N. Govind, K. Kowalski, T. P. Straatsma, H. J. J. Van Dam, D. Wang, J. Nieplocha, E. Apra, T. L. Windus and W. A. De Jong, Comput. Phys. Commun., 2010, 181, 1477–1489 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Yanai, D. P. Tew and N. C. Handy, Chem. Phys. Lett., 2004, 393, 51–57 CrossRef CAS.
- IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology (the “Gold Book”), ed. A. D. McNaught and A. Wilkinson, Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, 2nd edn, 1997, p. 411 Search PubMed.
- X. Cui, J. Zhao, P. Yang and J. Sun, Chem. Commun., 2013, 49, 10221–10223 RSC.
- Y. V. Aulin, M. V. Sebille, M. Moes and F. C. Grozema, RSC Adv., 2015, 5, 107896–107903 RSC.
- O. Ohno, Y. Kaizu and H. Kobayashi, J. Chem. Phys., 1985, 82, 1779 CrossRef CAS.
- G.-Z. Wu, W.-X. Gan and H.-K. Leung, J. Chem. Soc., Faraday Trans., 1991, 87, 2933–2937 RSC.
- X. Liu, E. K. L. Yeow, S. Velate and R. P. Steer, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2006, 8, 1298–1309 RSC.
- F. Zhong and J. Zhao, Dyes Pigm., 2017, 136, 909–918 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Brinen and J. G. Koren, Chem. Phys. Lett., 1968, 2, 671–672 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Fang, J. Lin, R. Schneider, T. Yamada and A. L. Singer, Chem. Phys. Lett., 1982, 92, 283–287 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Haefele, J. Blumhoff, R. S. Khnayzer and F. N. Castellano, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2012, 3, 299–303 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Monguzzi, R. Tubino, S. Hoseinkhani, M. Campione and F. Meinardi, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012, 14, 4322–4332 RSC.
- A. Harriman, G. Porter and M.-C. Richoux, J. Chem. Soc., Faraday Trans. 2, 1981, 77, 833–844 RSC.
- J. Andréasson, H. Zetterqvist, J. Kajanus, J. Mårtensson and B. Albinsson, J. Phys. Chem. A, 2000, 104, 9307–9314 CrossRef.
- V. Gray, D. Dzebo, A. Lundin, J. Alborzpour, M. Abrahamsson, B. Albinsson and K. Moth-Poulsen, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2015, 3, 11111–11121 RSC.
- T. N. Singh-Rachford and F. N. Castellano, Inorg. Chem., 2009, 48, 2541–2548 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. W. Schmidt and F. N. Castellano, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2014, 5, 4062–4072 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Dick and B. Nickel, Chem. Phys., 1983, 78, 1–16 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Nikitin, H. Müller-Bunz, Y. Ortin, J. Muldoon and M. J. McGlinchey, Org. Lett., 2011, 13, 256–259 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Beeby, K. S. Findlay, A. E. Goeta, L. Porrés, S. R. Rutter and A. L. Thompson, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2007, 6, 982–986 CAS.
- C. Mongin, J. H. Golden and F. N. Castellano, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2016, 8, 24038–24048 CAS.
- K. Yokoyama, Y. Wakikawa, T. Miura, J.-I. Fujimori, F. Ito, T. Ikoma, K. Yokoyama, Y. Wakikawa, T. Miura, J.-I. Fujimori and F. Ito, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2015, 119, 15901–15908 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
Footnotes |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Experimental procedures and characterization of new compounds, spectroscopic data and transient absorption measurements as well as details about the DFT calculations. See DOI: 10.1039/c7cp01368j |
| ‡ Note that in this paper all upconversion quantum yields are referred to on the basis of a 50% maximum. |
| § We note that the calculations suggest that the 2 × ET1 energy difference in the case of 3 is actually negative regardless of the rotation angle (Fig. 6F), which would imply that the conversion is not favorable under any circumstances. This very small energy difference is, however, below the accuracy that can be reasonably expected from the present calculations. Rather we focus here on the relative changes to the energy balance due to the phenyl group rotations, which can be predicted with higher fidelity. |
| This journal is © the Owner Societies 2017 |