Consecutive reactions of small, free tantalum clusters with dioxygen controlled by relaxation dynamics†
Abstract
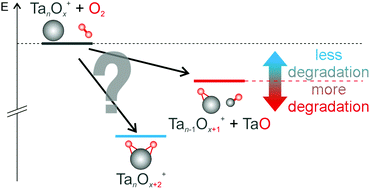
The reaction of small cationic tantalum clusters (Tan+, n = 4–8) with molecular oxygen is studied under multi-collision conditions in the gas phase, and the reaction kinetics are analyzed in order to elucidate underlying mechanisms. Reaction pathways as well as relevant apparent rate constants are reported. Two principal pathways in the consecutive oxidation reaction are present in this size regime: solely oxidative degradation (loss of a TaO fragment) in the beginning followed by parallel intact oxidation of certain intermediate species. Selected product structures and energies are subsequently determined via density functional theory calculations. The branching between oxidative fragmentation and intact oxidation is related to the corresponding relaxation dynamics.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...