The development of a biomimetic enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay based on the molecular imprinting technique for the detection of enrofloxacin in animal-based food
Abstract
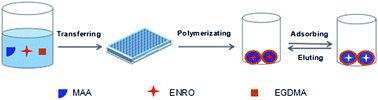
In this study, a direct competitive biomimetic enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (BELISA) method using molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) as artificial antibodies was developed to detect enrofloxacin (ENRO) in animal-based food. The MIPs were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy, adsorption kinetic experiments and isothermal adsorption experiments. The results showed that molecularly imprinted polymers were successfully synthesized with a fast adsorption rate and high adsorption. Under the optimum conditions, the sensitivity (IC50) and limit of detection (IC15) of the established BELISA method were 85.7 ng mL−1 and 1.1 ng mL−1, respectively. The method was applied to the determination of ENRO in spiked beef and shrimp samples, and recoveries ranged from 74.4 to 86.8% with relative standard deviations (for n = 3) between 3.3 and 8.0%. The results correlated well with those obtained using ELISA and high performance liquid chromatography methods.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...