Tuning the aggregation/disaggregation behaviours of ZnSe quantum dots for high-sensitivity fluorescent rutin sensors†
Abstract
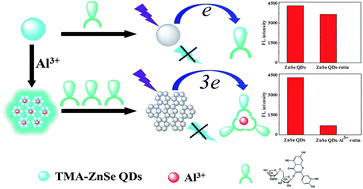
The design of quantum dots as a new sensing platform is very important for developing high-sensitivity fluorescent sensors. However, achieving a new strategy is still a great challenge. Here, a new strategy for fabricating water-dispersible thiol malic acid modified ZnSe quantum dots (TMA-ZnSe QDs) is presented in aqueous solution. The characteristics of the modified TMA-ZnSe QDs and the interactions between TMA-ZnSe QDs, Al3+ and rutin were investigated by atomic force microscopy, energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, fluorescence spectrometry, resonance Rayleigh scattering, UV-vis absorption spectroscopy and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. A new high-sensitivity fluorescent sensor based on tuning the aggregation/disaggregation behavior of TMA-ZnSe QDs by structure-switching for the detection of rutin was developed. The results confirmed that the detection sensitivity was greatly improved by the aggregation of TMA-ZnSe QDs with Al3+ because rutin effectively quenched the FL of TMA-ZnSe QDs–Al3+via the photoinduced electron transfer process. Under optimum conditions, the decrease in the FL intensity was linear to the rutin concentration from 0.02 μg mL−1 to 9 μg mL−1 and the detection limit for rutin was 0.02 μg mL−1. The proposed method offered a new possibility for rutin detection in real samples owing to its low cost, simplicity, high sensitivity and good stability. The present work provides a new strategy for improving sensitivity by tuning the aggregation/disaggregation behavior of TMA-ZnSe QDs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...