Combined toxicity of Fe3O4 nanoparticles and cadmium chloride in mice
Abstract
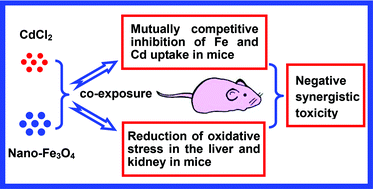
Nanomaterials have been widely used in diverse areas. Heavy metals are ubiquitous environmental pollutants. In spite of the real risk of humans’ co-exposure to nanoparticles and heavy metals, their combined toxicity has received little attention. We have reported that silica nanoparticles and CdCl2 have a positive synergistic toxicity in mice. Here, we demonstrate that Fe3O4 nanoparticles (nano-Fe3O4) and CdCl2 have a negative synergistic toxicity in mice. Nano-Fe3O4 showed low toxicity in mice. In contrast, CdCl2 caused significant oxidative damage mainly in the liver as indicated by severe liver dysfunction and histopathological abnormalities. Co-exposure to nano-Fe3O4 and CdCl2 significantly attenuated CdCl2-induced damage in the liver through reduction of oxidative stress. Nano-Fe3O4 and CdCl2 had negative cooperative effects on the biodistributions of Fe and Cd in mice due to mutually competitive inhibition of Fe and Cd uptake. The reduction of Cd accumulation in tissues and the inhibition of Cd-induced deprivation of tissue Fe by nano-Fe3O4 played two key roles in the protective effect of nano-Fe3O4 on CdCl2-induced oxidative damage.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...