Novel Fe–Mn–Si–Pd alloys: insights into mechanical, magnetic, corrosion resistance and biocompatibility performances†
Abstract
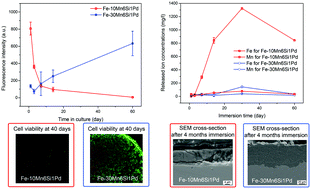
Two new Fe-based alloys, Fe–10Mn6Si1Pd and Fe–30Mn6Si1Pd, have been fabricated by arc-melting followed by copper mold suction casting. The Fe–30Mn6Si1Pd alloy mainly consists of ε-martensite and γ-austenite Fe-rich phases whereas the Fe–10Mn6Si1Pd alloy primarily contains the α-Fe(Mn)-ferrite phase. Additionally, Pd-rich precipitates were detected in both alloys. Good mechanical response was observed by nanoindentation: hardness values around 5.6 GPa and 4.2 GPa and reduced Young's moduli of 125 GPa and 93 GPa were measured for the as-prepared Fe–10Mn6Si1Pd and Fe–30Mn6Si1Pd alloys, respectively. Both alloys are thus harder and exhibit lower Young's modulus than 316L stainless steel, which is one of the most common Fe-based reference materials used for biomedical applications. Compared with the ferromagnetic Fe–10Mn6Si1Pd alloy, the paramagnetic Fe–30Mn6Si1Pd alloy is more appropriate to be used as an implant since it would be compatible for nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) analyses. Concerning biocompatibility, the more hydrophilic Fe–10Mn6Si1Pd alloy shows improved cell adhesion but its pronounced ion leaching has a negative effect on the proliferation of cells. The influence of immersion in a simulated body fluid on the composition, microstructure, mechanical and magnetic properties of both alloys is assessed, and the correlation between microstructure evolution and physical properties is discussed.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...