Effect of bimetallic iron:zinc nanoparticles on collagen stabilization†
Abstract
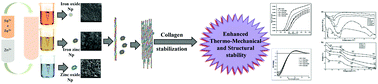
The ability of metallic nanoparticles to facilitate crosslinking of collagen by binding to side chain moieties has been studied for some time. The current study is mainly focused on understanding the effect of bimetallic iron:zinc nanoparticles on the stability of collagen. The results showed that the bimetallic nanoparticle was able to efficiently stabilize collagen, which is reflected by the enhanced fibril formation kinetics, viscosity, mechanical and thermal stability of the collagen molecule crosslinked with bimetallic nanoparticles. Contrary to the inhibitory effects on these properties exhibited by individual nanoparticles, in combination as bimetallic nanoparticles they showed superior collagen crosslinking properties. It was observed that the physico-chemical properties of the individual nanoparticles drastically change when they are combined with other metal nanoparticles and these properties are entirely different from the properties they exhibit individually. Circular dichroism analysis confirmed no structural disparity in collagen despite the superior physicochemical properties suggesting the significance of bimetallic iron:zinc nanoparticle mediated crosslinking. The ability of the bimetallic iron:zinc nanoparticles to crosslink collagen molecules suggested that the bimetallic iron:zinc nanoparticles apart from their application in tissue engineering could find use in tanning of leather. Superior stabilization of collagen by bimetallic Fe:Zn nanoparticles when compared to chrome tanning therefore may reduce the amount chromium used in leather tanning process. The present study is the first report on the application of a bimetallic nanoparticle as crosslinker for stabilisation of collagen and its application as an ecofriendly tanning agent in the leather industry. This study gives new scope for the application of bimetallic nanoparticle-based strategies for the development of alternative crosslinking agents for tissue engineering applications.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...