Three-dimensional fusiform hierarchical micro/nano Li1.2Ni0.2Mn0.6O2 with a preferred orientation (110) plane as a high energy cathode material for lithium-ion batteries†
Abstract
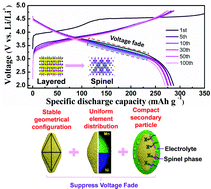
Layered Li-rich cathode materials have a series of severe issues which limit their commercialization, such as sharp voltage fading, poor rate performance and bad cycling stability, among which voltage drop is a serious barrier for the successful practical application of Li-rich cathode materials because it will lead to a serious energy fading of batteries. To solve this problem, we design a new-type of three-dimensional fusiform hierarchical micro/nano Li-rich Li1.2Ni0.2Mn0.6O2 cathode material synthesized through a hydrothermal method. The as-prepared sample presents high capacity, superior rate capability and good cycling stability as a cathode material for lithium ion batteries. After 100 cycles at 0.1C, the voltage plateau of this cathode material has almost no decline, and the capacity retention reaches up to 94%. At a high rate of 5C, the initial discharge capacity of the sample is 166.8 mA h g−1. The excellent electrochemical performance can be ascribed to both peculiar architecture and preferred orientation growth of the (110) plane. Therefore, Li1.2Ni0.2Mn0.6O2 with three-dimensional fusiform hierarchical micro/nano morphology and preferred orientation active plane (110) is a promising cathode material for lithium ion batteries.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...