Interfacial behavior of nonionic Tween 20 surfactant at oil–water interfaces in the presence of different types of nanoparticles
Abstract
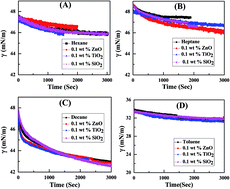
In this paper, we have studied the effect of three different types of nanoparticles (NPs) (e.g. SiO2, TiO2, and ZnO) on the interfacial tension (IFT) of different oil–water systems (e.g. oil: n-hexane, n-heptane, n-decane, toluene). The IFT of different oil–water systems, at variable concentrations of a nonionic surfactant, Tween 20, in the absence and presence of three different NPs was examined. As expected, the presence of Tween 20 surfactant effectively reduces the initial as well as final IFT of the n-hexane–water system. However, inclusion of NPs, irrespective of charge, alters the efficacy of Tween 20 surfactant in further reducing the IFT. In order to investigate the retarding efficiency of NPs on Tween 20 surfactant, the surface excess concentration of surfactants in the presence of 0.1 weight% of different NPs was also inspected along with apparent diffusion coefficients (Da). It has been found that the surface excess of surfactants at the interface decreases in the presence of NPs. Also increasing the concentration of Tween 20 surfactant increases the Da, leading to a higher adsorption rate. However, similar to a surface excess of surfactant, Da values are less in the presence of NPs compared to the particle free system.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...