Catalytic effects of electrode material on the silicon tetrachloride hydrogenation in RF-arc-discharge
Abstract
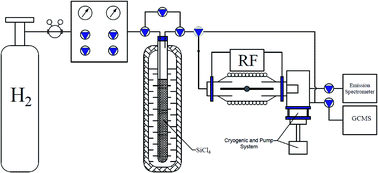
A silicon tetrachloride reduction in RF-arc-discharge (40.86 MHz) has been experimentally studied. The electrode material significantly affects the composition of the chlorosilanes in the gas phase at the outlet of the reactor which may be attributed to high and at the same time different catalytic activity of Cu, Ni, Nb, and Zr metals belonging to the transition of d-elements and W f-elements of the periodic table. The corrosion has been observed on the electrodes with the formation of chlorides of Cu, Ni, Nb, Zr, and W metals. In the system formed by two electrodes and plasma there are three main reactive regions in which the recovery of silicon tetrachloride by hydrogen at different flows is conducted independently from each other. The analysis of exhaust gases, chemically active plasma and condensed phase by emission-spectroscopy and GCMS spectrometry made it possible to propose the mechanism of formation of observed intermediate species and final products. On the basis of the obtained results we can conclude that this type of RF-plasma discharge includes two mechanisms of plasma chemical reactions: one with the participation of active particles formed in plasma and one initiated by the catalytically-active surface of the electrode.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...