DOI:
10.1039/C6RA18391C
(Paper)
RSC Adv., 2016,
6, 79910-79919
Feasible oxidation of 17β-estradiol using persulfate activated by Bi2WO6/Fe3O4 under visible light irradiation
Received
19th July 2016
, Accepted 8th August 2016
First published on 9th August 2016
Abstract
Bismuth tungstate magnetic composites (BTMCs, Bi2WO6/Fe3O4) were synthesized by a template-free hydrothermal process. The as-synthesized samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), UV-vis diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (DRS), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and using a vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM). The photocatalytic activities of BTMCs were evaluated to degrade 17β-estradiol (E2) under visible light irradiation in the presence of persulfate (PS). It was found that PS could enhance the photocatalytic efficiency of BTMCs and could be activated to promote the removal of E2 with sulfate and hydroxyl radicals. The persulfate concentration and catalyst dosage play important roles on the degradation of E2, which is significant in a wide pH range (3.0–9.0). Recycling experiments demonstrated that BTMCs could maintain strong photo-catalytic stability over five cycles. Moreover, a mechanism is proposed that contains adsorption and electron transfer for the interactions between BTMCs and PS under visible light with 9 intermediate products identified. This study provides a feasible way to degrade organic pollutants in water using BTMCs with PS under solar light.
1. Introduction
Semiconductor photocatalysis has been one of the most promising technologies in organic pollution control and water splitting due to its clean process, low operating cost and mild reaction conditions.1–3 Among various semiconductors, TiO2 (with a relatively large band gap of 3.0–3.2 eV) and its compounds have been widely studied for the cleanup of environmental organic pollutants through the activation of ultraviolet light (UV).4,5 However, it can only absorb less than 5% of the solar energy, with low quantum efficiency, which requires wavelengths less than 385 nm.5,6 Solar energy has been considered as a free, clean technology with great application potential, and efforts have been made to develop new photocatalysts which are active to visible light. Bismuth tungstate (Bi2WO6), a new kind of photocatalyst with a narrower band gap (2.6–2.8 eV) than TiO2, has a great photocatalytic capacity under simulated solar light and visible light.7–9 In order to further improve the photocatalyst activity of Bi2WO6, an effective technique is to dope Bi2WO6 with a noble metal, nonmetal material or metal oxide, which remarkably enhances photocatalytic performance by promoting the separation of photo-generated electron–hole pairs.10–12 However, due to its hydrophilic characteristics, it is difficult to separate Bi2WO6 from reaction solutions without using other means, like centrifugation or filtration.
Magnetite (Fe3O4) is an ideal magnetic material providing an effective way for utilizing and recycling by using an external magnetic field. Recently, researchers have paid much attention to composite materials based on magnetite. For instance, a 3D flower-like Bi2WO6/Fe3O4 hierarchical architecture was synthesized by way of hydrothermal synthesis, and achieved high degradation efficiency for RhB.13 The BiVO4/Fe3O4 composite was synthesized and the results demonstrate that this magnetic composite photocatalyst is beneficial for the efficient degradation of organic pollutants present in water and air under solar light.14
The advanced oxidation process (AOP) based on the sulfate radical ˙SO4− (2.6–3.1 V) has raised considerable attention in emerging compounds decontamination.15 Persulfate (PS) has been activated to generate sulfate radicals using several methods like thermolysis,16 transition metal ions,15,17,18 ultrasound,19 base,20 laser flash,21 UV,22 quinones,23 phenol and active carbon.24, Among these, photo-activated persulfate could provide a gentle and economic process to degrade target compounds. However, single visible light has limited potential in activating persulfate. According to a very recent study by Shan, the photocatalytic activity of the Bi2WO6/Fe3O4 magnetic composites (BTMCs) was improved under visible light in the presence of H2O2, while the detail mechanism and parameters are still not clear.25
However, to our best knowledge little research has been reported on the interactions between PS and bismuth tungstate magnetic composites under visible light. The purpose of this study represents the first investigation on the potential application of PS on the degradation of organic compounds using BTMCs under visible light irradiation. 17β-Estradiol (E2), a typical Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals (EDCs), was selected as the refractory micro-pollutant due to its endocrine disrupting function on environmental organisms and ubiquitous characteristics in aquatic system.26,27 Bi2WO6 and BTMCs were synthesized by a solvent-thermal process and the performance of PS for promoting the photochemical activity of BTMCs was evaluated. Moreover, critical impacting factors on the degradation of E2 were investigated and the interaction mechanism in the photo-catalysis system was proposed. Furthermore, the main intermediates formed in the reaction were analyzed by liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LC-MS). Our results demonstrated the great potential of PS for enhancing the removal of reluctant compounds the using vis-light catalysis process.
2. Materials and experimental methods
2.1 Reagents
17β-Estradiol (C18H24O2, E2, >98%) was purchased from J&K Scientific Ltd. (Beijing, China). Ferric(III) chloride hexahydrate (FeCl3·6H2O, AR) and sodium persulfate (Na2S2O8, AR) was purchased from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co. Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Methanol (MA, HPLC), isopropanol (IPA, HPLC) and tert-butanol (TBA, HPLC) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Shanghai, China). Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt (EDTA-2Na), potassium bromate (KBrO3) and other chemicals were analytical grade without further purification and obtained from Kelong Chemical Reagent Co. Ltd. (Chengdu, China). The water used for the preparation of the reagents and reaction system was purified by a Millipore Reverse Osmosis (RO) system.
2.2 Prepartion of bare Fe3O4, bare Bi2WO6 and Bi2WO6/Fe3O4
The Fe3O4 nanoparticles were synthesized using the solvent-thermal process reported in published papers.13 1.35 g of FeCl3·6H2O and 3.6 g sodium acetate were dissolved in 75 mL of glycol. After ultrasonic agitation for 30 min, the mixture was heated at 200 °C for 16 h in a 100 mL stainless-steel autoclave equipped with a Teflon lining. The black solid products were separately washed with deionized water and ethanol six times, sequentially, and then dried to constant weight in a vacuum oven at 60 °C for 20 h. The dried particles were stored in a vacuum desiccator.
The bare Bi2WO6 or BTMCs were prepared according to Shan's method.25 0.140 g of Fe3O4 nanoparticles were dissolved in 20 mL glycol and agitated for 30 min in an ultrasonic atmosphere. 10 mL of 79.02 g L−1 Bi(NO)3 solution (dissolved in 1 mol L−1 HNO3) was added into the Fe3O4 mixture solutions and magnetically stirred for 20 min. Then, 10 mL of 29.386 g L−1 Na2WO4 solution (dissolved in 1 mol L−1 NaOH) was mixed together with the former solution containing Fe3O4 and Bi(NO)3. The mixture was stirred vigorously for 10 min and sonicated for 30 min. After the pH was adjusted to 3.0 using 1 mol L−1 HCl, the suspension was transferred into a 100 mL stainless-steel autoclave equipped with a Teflon lining, and heated at 140 °C for 20 h. The black solid products were separately washed with deionized water and ethanol six times sequentially and then dried to constant weight at in a vacuum oven 60 °C for 20 h. According to the theoretical yield of Bi2WO6, the theoretical mass ratio of Bi2WO6 to Fe3O4 is 5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 in the as-prepared Bi2WO6/Fe3O4 compound. The bare Bi2WO6 was prepared by the same method without Fe3O4.
1 in the as-prepared Bi2WO6/Fe3O4 compound. The bare Bi2WO6 was prepared by the same method without Fe3O4.
2.3 Characterization
Scanning electron microscope (SEM) was carried out using JSM-7500F (JEOL, Japan). X-ray diffraction (XRD) was carried on a X'Pert Pro MPD diffractometer (Philips, Netherlands) using monochromatized Cu Kα radiation under 40 kV and 100 mA and the scanning range was from 20° to 80°. UV/Vis absorbance was recorded on an UV/Vis visible spectrophotometer (U2100, Shimadzu, Japan). X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) data were obtained with a XSAM800 electron spectrometer from England Krators Scientific using 300 W Al Kα radiations. The base pressure was about 3 × 10−9 mbar. The binding energies were referenced to the C 1s line at 284.8 eV from the adventitious carbon. Their magnetic properties (M–H curve) were measured on a VSM 9600 magnetometer at room temperature.
2.4 Photocatalytic experiments
The photocatalytic activities of the catalysts were evaluated on the degradation of E2 under visible light irradiation. A 400 W metal halide lamp with a cutoff filter (λ > 415 nm) was used as a visible light source. 0.1 g of prepared BTMCs was added to 200 mL E2 solution (5 mg L−1), and the suspension pH was adjusted to 3.0 by 1.0 M HCl and 1.0 M NaOH. The mixture was vigorously stirred in the dark for 60 min to ensure the adsorption equilibrium of E2. The dispersion was then exposed to visible light irradiation to initiate the reaction and was maintained at 25 °C by using water in the cooling jacket of the reactor. 2 mL samples were periodically withdrawn at fixed times and were collected and centrifuged at 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 rpm for 5 min. The supernatant was analyzed in 12 hours. In the recycling section, the BTMCs were separated from the suspension with a hand-held permanent magnet and were washed with ethanol and deionized three times sequentially. Triplicate experiments were performed, and the average values with the standard deviations were presented.
000 rpm for 5 min. The supernatant was analyzed in 12 hours. In the recycling section, the BTMCs were separated from the suspension with a hand-held permanent magnet and were washed with ethanol and deionized three times sequentially. Triplicate experiments were performed, and the average values with the standard deviations were presented.
2.5 Analytical methods
The concentrations of E2 was determined by using an high performance liquid chromatography (Waters, e2695) equipped with a 2489 UV-visible detector at 280 nm, and Waters C18 reversed phase column (150 × 4.6 mm, 5 μm particle) was adopted. The mobile phase consisted of methanol and water (70/30) was maintained for 10 min with a flow rate at 0.8 mL min−1. The column temperature was maintained at 35 °C.
To identify the degradation products of E2, samples were analyzed by LC/MS (Agilent 1200 LC-MSD modular system) equipped with electrospray interface in negative ionization mode. The chromatographic device was equipped with a UV detector and triple quadrupole mass spectrometers. A reversed-phase C18 analytical column (Waters SB-C18, 150 mm × 3.5 mm, USA) with 3.5 μm particle diameter was used and the column temperature was set at 30 °C. The injected volume of sample was 5 μL and the mobile phase was the same as described for the HPLC analysis at a flow rate of 0.2 mL min−1.
3. Results and discussion
3.1 Characterization
Fig. 1(A) shows the XRD patterns of the Bi2WO6 and BMTCs composites. The diffraction peaks of the products are consistent with those of russellite Bi2WO6 [JCPDS no. 39-0256], the diffraction peaks at about 26.5°, 28.2°, 47.2°, 55.8°, 58.6 and 68.8° can be indexed to the (131), (200), (202), (133), (226) and (40) planes respectively. This agrees with the result reported by Chen,28 in which they prepared Bi2WO6 at different pHs by the hydrothermal method. As shown in Fig. 1(A), with the content of Fe3O4 increases, the peak intensities at 35.8°and 62.5° ascend consistently, indicating that pure Fe3O4 was successfully loaded on pure Bi2WO6.
 |
| | Fig. 1 (A) The XRD patterns of Bi2WO6/Fe3O4 and Fe3O4; (B) diffuse reflectance UV-vis spectra of the prepared Bi2WO6, Fe3O4 and Bi2WO6/Fe3O4; (C) M–H cures of Fe3O4 (a), Bi2WO6/Fe3O4 (b); magnetic separation of Bi2WO6/Fe3O4 catalyst within 3 min (c). | |
Fig. 1(B) shows the diffuse reflectance UV-vis spectra of Bi2WO6, Fe3O4 and BMTCs. As can be noted, the pure Bi2WO6 samples both have a strong visible light region with an absorption edge at 450 nm. By comparing the UV-vis diffuse reflectance spectra of Bi2WO6 and BMTCs, the light absorption of the BMTCs photocatalyst increased and extended in a wider range of 200–800 nm. This might have resulted from the presence of Fe3O4 nanoparticles in the BMTCs photocatalyst.
The magnetic properties of pure Fe3O4 and BMTCs powers were analyzed using a vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) at room temperature. As shown in Fig. 1(C), the M–H hysteresis loop indicates that Fe3O4 and BMTCs possessed permanent magnetic properties. The saturation magnetization of Fe3O4 is about 90 emu g−1 (curve a), whereas the saturation magnetization of BMTCs is about 7.4 emu g−1 (curve b). It demonstrates the facile separability of the BMTCs nanocomposites by a magnet. The BTMCs particles could be easily separated from the reaction solution by an external magnetic field in 3 min, as shown in the lower right panel of Fig. 1(C).
The morphologies of the samples were observed by scanning (SEM), and the results are illustrated in Fig. 2. The SEM images of the BTMCs and Fe3O4 powers are shown in Fig. 2(A) and (B). The low-magnification SEM images (Fig. 2(A)) shows that the BTMCs are composed of Bi2WO6 microspheres loaded with spherical Fe3O4 particles. As shown in Fig. 2(B), the Fe3O4 nanosphere particles were aggregated together due to their magnetic properties. Fig. 2(C) and (D) show the sides of the BTMCs and the surfaces of the BTMCs, respectively. It is clear that the Fe3O4 nanoparticles are eventually distributed on the surface on the nanoflake of Bi2WO6.
 |
| | Fig. 2 The SEM images of the prepared catalysts. (A) Bi2WO6/Fe3O4 (B) Fe3O4 (C) the side of Bi2WO6/Fe3O4 (D) the surface of Bi2WO6/Fe3O4. | |
The elemental composites and chemical states of BTMCs were further elucidated with X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The binding energy of 284.6 eV for C 1s was used as a reference. The full-scan XPS spectra of BTMCs is shown in Fig. 3(a), and curve fitting for W, Bi, O and Fe of the high-resolution XPS spectra was conducted to quantify and evaluate the contribution of each chemical species. The XPS spectra of W 4f, Bi 4f, O 1s and Fe 2p are shown in Fig. 3(b–e). The W 4f orbital has two binding energies of 35.5 and 37.5 eV for W 4f (W-1) and W 4f (W-2), respectively (Fig. 3(b)). As shown in Fig. 3(c) and (d), the binding energy of Bi 4f (Bi-1), Bi 4f (Bi-2), O 1s (O-1) and O 1s (O-2) are 159.0, 164.5, 530.0 and 532.5 eV, respectively. Fe 2p spectrum is composed of a doublet structure due to multiple splitting, as shown in Fig. 3(e). According to the curve fitting analysis of Fe 2p, there shows two bands with binding energies of 711.6 eV and 724.0 eV that can be assigned to Fe 2p (Fe-1) and Fe 2p (Fe-2), respectively. Both bands consist of Fe2+ (FeO) and Fe3+ (Fe2O3) peaks that are typical characteristics of Fe3O4. The obtained results confirm that the Fe3O4 was doped on Bi2WO6.
 |
| | Fig. 3 X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) of Bi2WO6/Fe3O4 (a), W 4f (b), Bi 4f (c), O 1s (d) and Fe 2p of Bi2WO6/Fe3O4 (e). | |
3.2 Photocatalytic performance
The photocatalytic efficiency of the Bi2WO6 and BTMCs was evaluated in various systems (Fig. 4(a)). Negligible degradation of E2 was observed by using single PS (0.92 mM) under visible light. As shown in Fig. 4(b), the adsorption capacity of BTWCs is ineffective with only 17.6% of E2 adsorbed after 1 h. In order to eliminate the influence of the adsorption, all the solution was magnetically stirred in dark conditions for 60 min to ensure adsorption–desorption equilibrium. Fig. 4(a) shows that the Bi2WO6 and BTMCs did not display high removal efficiency for E2 under visible light, with the removal rate reaching 19.5% and 14.7%, respectively. However, once PS (0.92 mM) was added to the reaction system with visible light, the degradation rate for E2 was much increased and promoting removal rates of E2 were observed for Bi2WO6 (72.9%) or BTMCs (67.8%) after reacting for 60 min. It suggests that the extra Fe3O4 have little negative effect on the photocatalytic activity of Bi2WO6, but could provide the magnetic properties for BTMCs. It was reported that the Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles could active PS to produce ˙SO4− as in eqn (1) and (2).43 However, limited degradation of E2 (6.1%) was observed by PS and BTMCs without irradiation due to the low content of Fe3O4 (4.6%).| | |
Fe2+ + S2O82− → Fe3+ + SO42− + ˙SO4−
| (1) |
| | |
Fe2+ + ˙SO4− → Fe3+ + SO42−
| (2) |
 |
| | Fig. 4 (a) Photocatalytic removal of E2 with the prepared Bi2WO6/Fe3O4 in presence of PS ([E2] = 5 mg L−1, initial pH 3.0, [E2]![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) [PS] = 1 [PS] = 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10, [catalyst] = 0.5 g L−1); (b) adsorption capacity of Bi2WO6/Fe3O4 under different initial pHs. 10, [catalyst] = 0.5 g L−1); (b) adsorption capacity of Bi2WO6/Fe3O4 under different initial pHs. | |
As a key factor the solution pH could influence the morphology and structure of nanomaterials.29 Xu found that preparing Bi2WO6/Fe3O4 at pH 3 can receive in 3D flower-like microspheres structures.13 Shan demonstrated that the adsorbed dye molecules might block the pore structures or occupy the reactive sites on the surface of the BTMCs.25 In order to investigate the properties of E2 adsorption by BTMCs, the pH of the solutions was adjusted to 7.0, 9.0, 11.0. The results are presented in Fig. 4(b). Although a low adsorption capacity was observed at various pH conditions, the removal of E2 increased to 39.7% at pH 11.0, 2–3 times more than in other pH conditions. The increase in adsorption capacity was probably attributed to the number of increasing adsorption sites on the surface of the BTMCs under a strong alkaline solution.
3.3 Effects of initial concentration of S2O82− and initial pH
The effect of persulfate dosages on photo-degradation of E2 was evaluated with the molar ratios of E2 and PS 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 5, 1
5, 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10, 1
10, 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 20 and 1
20 and 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 50. A pseudo-first-order reaction model was applied, as in the following equation:11where Kapp is the apparent pseudo-first-order rate constant, C0 is the initial concentration of E2, and Ct is the concentration of E2 at the time of t. Fig. 5(a) shows that the degradation of E2 fits well with the pseudo-first-order kinetic model, with the reaction rate constants calculated and shown in Table 1. The increasing PS concentration had a positive effect on the degradation of E2. Although it was reported that excessive persulfate would react with sulfate radicals (˙SO4−) inhibiting the target compound degradation (eqn (4) and (5)), the inhibition was not observed in our study.30
50. A pseudo-first-order reaction model was applied, as in the following equation:11where Kapp is the apparent pseudo-first-order rate constant, C0 is the initial concentration of E2, and Ct is the concentration of E2 at the time of t. Fig. 5(a) shows that the degradation of E2 fits well with the pseudo-first-order kinetic model, with the reaction rate constants calculated and shown in Table 1. The increasing PS concentration had a positive effect on the degradation of E2. Although it was reported that excessive persulfate would react with sulfate radicals (˙SO4−) inhibiting the target compound degradation (eqn (4) and (5)), the inhibition was not observed in our study.30| | |
˙SO4− + S2O82− → SO42− + ˙S2O8−, k = 6.1 × 105 M−1 s−1
| (4) |
| | |
˙SO4− + ˙SO4− → S2O82−, k = 4.0 × 108 M−1 s−1
| (5) |
 |
| | Fig. 5 Effect of PS dosages and pH on degradation of E2 with PS activated by BTMCs under vis-light irradiation (a) PS dosages; (b) pH. ([E2] = 5 mg L−1, [catalyst] = 0.5 g L−1). | |
Table 1 Fitting parameters of pseudo first-order kinetic model at different PS dosages and initial pHs
| pH |
|
Kapp(×10−2)/min−1 |
T1/2/min |
R2 |
| 3.0 |
1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 5 5 |
1.44(±0.094) |
48.14(±3.16) |
0.97 |
| 3.0 |
1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10 10 |
1.80(±0.091) |
38.51(±1.95) |
0.98 |
| 3.0 |
1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 20 20 |
2.32(±0.061) |
29.88(±0.79) |
0.99 |
| 3.0 |
1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 50 50 |
3.54(±0.146) |
19.58(±0.81) |
0.99 |
| 3.0 |
1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 50 50 |
3.48(±0.230) |
19.92(±1.32) |
0.97 |
| 5.0 |
1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 50 50 |
3.09(±0.086) |
22.43(±0.62) |
0.99 |
| 7.0 |
1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 50 50 |
3.431(±0.255) |
20.20(±1.51) |
0.97 |
| 9.0 |
1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 50 50 |
2.86(±0.488) |
28.18(±2.17) |
0.96 |
To further investigate the effect of pH on the degradation of E2 using BTMCs with PS under vis-light irradiation, the solution pH was adjusted to 3.0, 5.0, 7.0, 9.0, 11.0 using 1.0 M dilute hydrochloric acid and 1.0 M sodium hydroxide solution. The result is shown in Fig. 5(b). The degradation of E2 was slightly affected in various pH solutions, indicating the stability of the BTMCs. The results are in accord with the study of Shan et al., and he has been confirmed that BTMCs can be suitable in a wide pH range (3.0–9.0) for treating the practical wastewater.25 Liang demonstrated that the alkali could active the persulfate resulting in the formation of ˙SO4−, ˙OH and ˙O2 radicals.31 In our former experiment, the degradation of E2 also dramatically increased, reaching nearly 100% within 2 min (data is not presented). However, the purpose of our study is in exploring the photocatalytic properties of BTMCs with PS under vis-light irradiation. Therefore, the pH was adjusted to 3.0 for the later experiments, unless otherwise stated.
3.4 Effects of the catalyst dosage and the materials recycling
A set of experiments on E2 degradation was carried out within 60 min for several dosages of BTMCs (the results are shown in Fig. 6). The dosages were examined in the range of 0.05–1.00 g L−1, with the molar ratios of E2 and PS set at 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 50. It is clearly observed from Fig. 6 that the degradation rate of E2 was enhanced with increase of the catalyst dosage. The Kapp of E2 for the 1.0 g L−1 catalyst dosage was six times higher than that for 0.5 g L−1 (shown in Table 2). It was found that the catalytic process taking place on the surface of the catalyst, and the increasing doses of catalyst could enhance the efficiency of photocatalysis and allow more efficient transport of the reactant molecules onto the active sites.
50. It is clearly observed from Fig. 6 that the degradation rate of E2 was enhanced with increase of the catalyst dosage. The Kapp of E2 for the 1.0 g L−1 catalyst dosage was six times higher than that for 0.5 g L−1 (shown in Table 2). It was found that the catalytic process taking place on the surface of the catalyst, and the increasing doses of catalyst could enhance the efficiency of photocatalysis and allow more efficient transport of the reactant molecules onto the active sites.
 |
| | Fig. 6 Effect of catalyst concentration on degradation of E2 with PS activated by BTMCs under visible light irradiation ([E2] = 5 mg L−1, initial pH 3.0, [E2]![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) [PS] = 1 [PS] = 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 50). 50). | |
Table 2 Fitting parameters of pseudo first-order kinetics model at different catalyst dosages
| [BTMCs]/g L−1 |
Kapp(×10−2)/min−1 |
T1/2/min |
R2 |
| 0.05 |
1.18(±0.08) |
58.75(±4.00) |
0.97 |
| 0.1 |
1.71(±0.11) |
40.53(±2.62) |
0.97 |
| 0.5 |
4.26(±0.08) |
16.27(±0.31) |
0.98 |
| 1.0 |
7.10(±0.61) |
9.76(±0.84) |
0.96 |
The stability and reusability of BTMCs used for PS activation under vis-light irradiation was evaluated. The solids were recycled by an external permanent magnet, and pretreated using the process described in Section 2.4. Five-time reusing experiments were conducted. The recycling results are indicated in Fig. 7. The BTMCs synthesized in our study could still maintain a high photocatalytic activity after five-time recycling. The removal of E2 achieved 94.5%, 95.4%, 96.4%, 95.3% and 94.8% for the first, second, third, fourth and fifth recycling, respectively, which demonstrated excellent stability for the BTMCs. Similar results were found using TiO2/Bi2WO6 hollow microspheres as a photo-catalyst according to the study of Liu.12 It is demonstrated the synthesized material can be recovered and reused with loss-free activity for the vis-light catalytic degradation of an organic compound with PS.
 |
| | Fig. 7 Recycling test on the BTMCs for the degradation of E2 with PS activated by BTMCs under visible light irradiation ([E2] = 5 mg L−1, initial pH 3.0, [E2]![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) [PS] = 1 [PS] = 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 50, [catalyst] = 0.5 g L−1). 50, [catalyst] = 0.5 g L−1). | |
3.5 Photocatalytic reaction mechanism in the presence of S2O82−
The detection of the main active species during the photocatalytic reaction is important with respect to the elucidation of the photocatalytic reaction mechanism. To detect the major oxidants in the photocatalytic reactions under vis-light irradiation in the presence of BTMCs and PS, isopropanol (IPA), 1,4-benzoquinone (BQ) and tert-butanol (TBA) were selected as probe chemicals for the considerable reaction rates with free radicals (k˙SO4−/IPA = 2.8 × 109 M−1 s−1, k˙OH/IPA = 6.0 × 107 M−1 s−1, k˙SO4−/TBA = 4.0 × 105–9.1 × 105 M−1 s−1, k˙OH/TBA = 3.8 × 108–7.6 × 108 M−1 s−1).32–35 As reported in the study by Wu, IPA is an effective scavenger for both sulfate radicals (˙SO4−) and hydroxyl radicals (˙OH), while TBA is an effective scavenger only for hydroxyl radicals (˙OH),34 and BQ was used as superoxide radical (˙O2−) quencher.36 The results are illustrated in Fig. 8(a). Once excess TBA was dosed, the degradation rate of E2 decreased from 94.2% to 59.2%. The addition of 3 mM BQ brought 56.8% reduction (from 94.2% to 37.4%) in the degradation of E2 at 60 min, which suggests the presences of ˙O2− as the active species. Nevertheless, the addition of excess IPA decreased the degradation efficiency of E2 by approximately 14.4%, compared to the control system. The results suggested that ˙SO4−, ˙OH and ˙O2− exist in the BTMCs/PS coupled system under vis-light irradiation as the main active species.
 |
| | Fig. 8 Effect of free-radical inhibitors and photoelectron or hole scavengers on degradation of E2; (a) free-radical inhibitors [IPA]![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) [PS] = 1 [PS] = 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 50, [TBA] 50, [TBA]![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) [PS] = 1 [PS] = 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10 or 1 10 or 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 50, [catalyst] = 0.5 g L−1, ([E2] 50, [catalyst] = 0.5 g L−1, ([E2]![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) [PS] = 1 [PS] = 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 50 and [E2] = 5 mg L−1); (b) photoelectron or hole scavengers [EDTA] = 5 mM, [MA] = 5 mM, [KBrO3] = 5 mM, [catalyst] = 0.5 g L−1, ([E2] 50 and [E2] = 5 mg L−1); (b) photoelectron or hole scavengers [EDTA] = 5 mM, [MA] = 5 mM, [KBrO3] = 5 mM, [catalyst] = 0.5 g L−1, ([E2]![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) [PS] = 1 [PS] = 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 50 and [E2] = 5 mg L−1). 50 and [E2] = 5 mg L−1). | |
In order to study the function of the electron–hole pairs on the surface of BTMCs, EDTA, KBrO3 and MA were added as holes (h+) scavengers, photoelectron acceptors and holes (h+) or hydroxyl radicals (˙OH) scavengers, respectively.11,37 As shown in Fig. 8(b), significant inhibition was observed for the three scavengers. Compared with 94.2% for the control experiment, the removal of E2 achieved 15.9%, 36.6%, 55.5% within 60 min for adding EDTA, KBrO3 and MA, respectively. Therefore, the results indicated that the electron–hole pairs on the surface of BTMCs might take part in the PS activation.
The mechanism on PS activation via BTMCs under vis-light irradiation can be described in eqn (6)–(12). When the light possesses of photo energy greater than or equal the band gap energy of BTMCs, the Bi2WO6 can be excited to produce electron–hole pairs on the catalyst surface under simulated visible light irradiation. The excited photoelectron will activate PS to produce ˙SO4− in this system, because it was found that sulfate radicals could be produced via electrolytic activation of persulfate anions in a previous study by Chen in a previous study by Chen and the molecular oxygen (O2) could also accept excited photoelectron to produce ˙O2−.36,38 Furthermore, in Section 3.2, it was mentioned that the Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles could active PS to produce ˙SO4− in a previous study (shown as eqn (1) and (2)).39 Surassa et al. have confirmed that the presence of Fe3+ can also act as a photo-generated electron trap inhibiting the hole–electron recombination in the semiconductor photocatalytic reaction.40 In other words, Fe3+ can be reduced to Fe2+ by photoelectrons, which could active PS to produce more ˙SO4−. Therefore, the recycling of Fe2+ in the solution promoted the degradation of E2 because of ˙SO4− continues to function in the vis-light/BTMCs/PS system. According to the previous study by K. Dalrymple, h+ exists in the photocatalytic reaction can be oxidized to produce ˙OH.5 Based on the above results, the mechanism of the degradation of E2 concerning the interaction between BTMCs and PS under vis-light irradiation is proposed in Fig. 9.
| |
 | (6) |
| | |
S2O82− + eCB− → SO42− + ˙SO4−
| (8) |
| | |
4h+ + 2H2O(OH−) → 4H+ + ˙OH
| (11) |
| | |
˙SO4− + H2O → ˙OH + SO42−
| (12) |
 |
| | Fig. 9 Schematic diagrams of the degradation of E2 by vis-light/BTMCs/PS system. | |
3.6 Identification of products during E2 photo-degradation
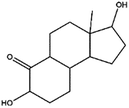
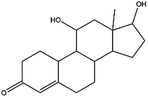
The main intermediates and products of E2 were analyzed and identified by LC/MS and the sample was withdrawed at the end of E2 degradation (60 min). The identification results are presented in Table 3. It has been demonstrated that the main oxidative pathway for E2 was breaking the phenol ring E2 under visible light irradiation.41 In our study, E2 was found to be stable in the absence of BTMCs under visible light irradiation, but degradation easily occurs in the presence of photo-generating active species (˙OH, ˙O2− and ˙SO4−). Superoxide radical, sulfate radicals and hydroxyl radicals might attack E2, through hydrogen abstraction at the aliphatic ring (allylic position), and addition of hydroxyl radical or other active species at different positions of the phenol ring.42 Nine main degradation products were detected, and are identified as the deprotonated molecule of intermediates ([M–H]−). The chemical structure and m/z of intermediates shown in Table 3 is consistent with those reported by other researchers.
Table 3 The proposed intermediates on degradation of E2
4. Conclusion
Bi2WO6 loaded with the Fe3O4 composite was successfully synthesized by a solvothermal method. The catalyst can enhance the decomposition efficiency of E2 with PS, assisted with vis-light irradiation, caused by free radicals (˙SO4− and ˙OH). The degradation is influenced by the persulfate concentration and catalyst dosage, while independent of the solution pH, except for strong basic conditions. Recycling experiments demonstrated that BTMCs are stable for activating PS after five cycles. In addition, a degradation mechanism of E2 was proposed with 9 products identified. Based on the promotion of the photocatalytic efficiency and good recycling characteristic, BTMCs can provide a feasible way to degrade organic pollutants in water under solar light combined with activated PS.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51508354). The authors are thankful to all the anonymous reviewers for their insightful comments and suggestions.
References
- H. M. Yuan, J. L. Liu, J. Li, Y. P. Li, X. P. Wang, Y. Q. Zhang, J. B. Jiang, S. Y. Chen, C. Zhao and D. Qian, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2015, 444, 58–66 CrossRef CAS PubMed
 .
. - M. N. Chong, B. Jin, C. W. K. Chow and C. Saint, Water Res., 2010, 44, 2997–3027 CrossRef CAS PubMed
 .
. - H. Tong, S. X. Ouyang, Y. P. Bi, N. Umezawa, M. Oshikiri and J. H. Ye, Adv. Mater., 2012, 24, 229–251 CrossRef CAS PubMed
 .
. - M. J. Chen and W. Chu, Appl. Catal., B, 2015, 168, 175–182 CrossRef
 .
. - O. K. Dalrymple, E. Stefanakos, M. A. Trotz and D. Y. Goswami, Appl. Catal., B, 2010, 98, 27–38 CrossRef CAS
 .
. - G. Carre, E. Hamon, S. Ennahar, M. Estner, M. C. Lett, P. Horvatovich, J. P. Gies, V. Keller, N. Keller and P. Andre, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2014, 80, 2573–2581 CrossRef PubMed
 .
. - H. Huang, X. Han, X. Li, S. Wang, P. K. Chu and Y. Zhang, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2015, 7, 482–492 CAS
 .
. - H. W. Huang, S. B. Wang, N. Tian and Y. H. Zhang, RSC Adv., 2014, 4, 5561–5567 RSC
 .
. - C. Y. Wang, H. Zhang, F. Li and L. Y. Zhu, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2010, 44, 6843–6848 CrossRef CAS PubMed
 .
. - M. Ge, Y. Li, L. Liu, Z. Zhou and W. Chen, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2011, 115, 5220–5225 CAS
 .
. - H. W. Huang, K. Liu, K. Chen, Y. L. Zhang, Y. H. Zhang and S. C. Wang, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2014, 118, 14379–14387 CAS
 .
. - Y. Liu, H. Tang, H. Lv, P. Zhang, Z. Ding, S. Li and J. Guang, Powder Technol., 2015, 283, 246–253 CrossRef CAS
 .
. - X. Xu, X. P. Shen, G. X. Zhu, L. Q. Jing, X. S. Liu and K. M. Chen, Chem. Eng. J., 2012, 200, 521–531 CrossRef
 .
. - G. Q. Zhu, M. Hojamberdiev, W. X. Que and P. Liu, Ceram. Int., 2013, 39, 9163–9172 CrossRef CAS
 .
. - J. Zou, J. Ma, L. W. Chen, X. C. Li, Y. H. Guan, P. C. Xie and C. Pan, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2013, 47, 11685–11691 CrossRef CAS PubMed
 .
. - M. G. Antoniou, A. A. de la Cruz and D. D. Dionysiou, Appl. Catal., B, 2010, 96, 290–298 CrossRef CAS
 .
. - G. D. Fang, D. D. Dionysiou, S. R. Al-Abed and D. M. Zhou, Appl. Catal., B, 2013, 129, 325–332 CrossRef CAS
 .
. - X. M. Xiong, B. Sun, J. Zhang, N. Y. Gao, J. M. Shen, J. L. Li and X. H. Guan, Water Res., 2014, 62, 53–62 CrossRef CAS PubMed
 .
. - H. Hori, Y. Nagano, M. Murayama, K. Koike and S. Kutsuna, J. Fluorine Chem., 2012, 141, 5–10 CrossRef CAS
 .
. - O. S. Furman, A. L. Teel and R. J. Watts, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2010, 44, 6423–6428 CrossRef CAS PubMed
 .
. - K. L. Ivanov, E. M. Glebov, V. F. Plyusnin, Y. V. Ivanov, V. P. Grivin and N. M. Bazhin, J. Photochem. Photobiol., A, 2000, 133, 99–104 CrossRef CAS
 .
. - X. X. He, A. A. de la Cruz and D. D. Dionysiou, J. Photochem. Photobiol., A, 2013, 251, 160–166 CrossRef CAS
 .
. - G. D. Fang, J. Gao, D. D. Dionysiou, C. Liu and D. M. Zhou, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2013, 47, 4605–4611 CrossRef CAS PubMed
 .
. - M. Ahmad, A. L. Teel and R. J. Watts, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2013, 47, 5864–5871 CrossRef CAS PubMed
 .
. - G. Q. Shan, Y. Fu, X. L. Chu, C. Chang and L. Y. Zhu, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2015, 444, 123–131 CrossRef CAS PubMed
 .
. - J. H. Writer, J. N. Ryan, S. H. Keefe and L. B. Barber, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2012, 46, 860–868 CrossRef CAS PubMed
 .
. - T. Susa, R. Ikaga, T. Kajitani, M. Iizuka, H. Okinaga, M. Tamamori-Adachi and T. Okazaki, J. Cell. Physiol., 2015, 230, 1594–1606 CrossRef CAS PubMed
 .
. - P. Chen, L. Zhu, S. Fang, C. Wang and G. Shan, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2012, 46, 2345–2351 CrossRef CAS PubMed
 .
. - J. Ren, W. Z. Wang, M. Shang, S. M. Sun and E. P. Gao, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2011, 3, 2529–2533 CAS
 .
. - C.-W. Wang and C. Liang, Chem. Eng. J., 2014, 254, 472–478 CrossRef CAS
 .
. - C. J. Liang and J. H. Lei, Water Environ. Res., 2015, 87, 656–659 CrossRef CAS PubMed
 .
. - G. V. Buxton, C. L. Greenstock, W. P. Helman and A. B. Ross, J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data, 1988, 17, 513–886 CrossRef CAS
 .
. - P. Neta, R. E. Huie and A. B. Ross, J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data, 1988, 17, 1027–1284 CrossRef CAS
 .
. - X. L. Wu, X. G. Gu, S. G. Lu, Z. F. Qiu, Q. Sui, X. K. Zang, Z. W. Miao and M. H. Xu, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2015, 147, 186–193 CrossRef CAS
 .
. - C. J. Liang and H. W. Su, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2009, 48, 5558–5562 CrossRef CAS
 .
. - Y. F. Tao, Q. Ni, M. Y. Wei, D. S. Xia, X. X. Li and A. H. Xu, RSC Adv., 2015, 5, 44128–44136 RSC
 .
. - S. J. Armakovic, S. Armakovic, N. L. Fincur, F. Sibul, D. Vione, J. P. Setrajcic and B. F. Abramovic, RSC Adv., 2015, 5, 54589–54604 RSC
 .
. - W. S. Chen and C. P. Huang, Chemosphere, 2015, 125, 175–181 CrossRef CAS PubMed
 .
. - Y. S. Zhao, C. Sun, J. Q. Sun and R. Zhou, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2015, 142, 182–188 CrossRef CAS
 .
. - S. Sriwichai, H. Ranwongsa, K. Wetchakun, S. Phanichphant and N. Wetchakun, Superlattices Microstruct., 2014, 76, 362–375 CrossRef CAS
 .
. - Y. Ohko, K. Iuchi, C. Niwa, T. Tatsuma, T. Nakashima, T. Iguchi, Y. Kubota and A. Fujishima, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2002, 36, 4175–4181 CrossRef CAS PubMed
 .
. - M. Brienza, M. Mahdi Ahmed, A. Escande, G. Plantard, L. Scrano, S. Chiron, S. A. Bufo and V. Goetz, Chem. Eng. J., 2014, 257, 191–199 CrossRef CAS
 .
. - Y. P. Zhao, J. Y. Hu and W. Jin, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2008, 42, 5277–5284 CrossRef CAS PubMed
 .
. - M. M. Huber, T. A. Ternes and U. von Gunten, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2004, 38, 5177–5186 CrossRef CAS PubMed
 .
. - P. Mazellier, L. Meite and J. De Laat, Chemosphere, 2008, 73, 1216–1223 CrossRef CAS PubMed
 .
. - P. Mazellier, L. Meite and J. De Laat, Chemosphere, 2008, 73, 1216–1223 CrossRef CAS PubMed
 .
. - J. Y. Hu, S. J. Cheng, T. Aizawa, Y. Terao and S. Kunikane, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2003, 37, 5665–5670 CrossRef CAS PubMed
 .
. - S. Irmak, O. Erbatur and A. Akgerman, J. Hazard. Mater., 2005, 126, 54–62 CrossRef CAS PubMed
 .
. - O. Pereira Rde, M. L. de Alda, J. Joglar, L. A. Daniel and D. Barcelo, Chemosphere, 2011, 84, 1535–1541 CrossRef PubMed
 .
. - J. X. Mai, W. L. Sun, L. Xiong, Y. Liu and J. R. Ni, Chemosphere, 2008, 73, 600–606 CrossRef CAS PubMed
 .
. - L. Gao, L. Sun, S. Wan, Z. Yu and M. Li, Chem. Eng. J., 2013, 228, 790–798 CrossRef CAS
 .
.
|
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 |
Click here to see how this site uses Cookies. View our privacy policy here. ![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 in the as-prepared Bi2WO6/Fe3O4 compound. The bare Bi2WO6 was prepared by the same method without Fe3O4.
1 in the as-prepared Bi2WO6/Fe3O4 compound. The bare Bi2WO6 was prepared by the same method without Fe3O4.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 rpm for 5 min. The supernatant was analyzed in 12 hours. In the recycling section, the BTMCs were separated from the suspension with a hand-held permanent magnet and were washed with ethanol and deionized three times sequentially. Triplicate experiments were performed, and the average values with the standard deviations were presented.
000 rpm for 5 min. The supernatant was analyzed in 12 hours. In the recycling section, the BTMCs were separated from the suspension with a hand-held permanent magnet and were washed with ethanol and deionized three times sequentially. Triplicate experiments were performed, and the average values with the standard deviations were presented.


![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 5, 1
5, 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10, 1
10, 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 20 and 1
20 and 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 50. A pseudo-first-order reaction model was applied, as in the following equation:11
50. A pseudo-first-order reaction model was applied, as in the following equation:11
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 5
5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10
10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 20
20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 50
50![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 50
50![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 50
50![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 50
50![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 50
50![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 50. It is clearly observed from Fig. 6 that the degradation rate of E2 was enhanced with increase of the catalyst dosage. The Kapp of E2 for the 1.0 g L−1 catalyst dosage was six times higher than that for 0.5 g L−1 (shown in Table 2). It was found that the catalytic process taking place on the surface of the catalyst, and the increasing doses of catalyst could enhance the efficiency of photocatalysis and allow more efficient transport of the reactant molecules onto the active sites.
50. It is clearly observed from Fig. 6 that the degradation rate of E2 was enhanced with increase of the catalyst dosage. The Kapp of E2 for the 1.0 g L−1 catalyst dosage was six times higher than that for 0.5 g L−1 (shown in Table 2). It was found that the catalytic process taking place on the surface of the catalyst, and the increasing doses of catalyst could enhance the efficiency of photocatalysis and allow more efficient transport of the reactant molecules onto the active sites.

![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) [PS] = 1
[PS] = 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 50).
50).
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) [PS] = 1
[PS] = 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 50, [catalyst] = 0.5 g L−1).
50, [catalyst] = 0.5 g L−1).
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.