Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel 2-phenyl-1-benzopyran-4-one derivatives as potential poly-functional anti-Alzheimer's agents†
Abstract
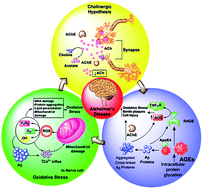
The development of Multi-Target Directed Ligands (MTDLs) has emerged as a promising approach for targeting the complex etiology of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Following this approach, a new series of 2-phenyl-1-benzopyran-4-one derivatives was designed, synthesized and biologically evaluated as inhibitors of acetylcholinesterases (AChEs), advanced glycation end product (AGEs) formation and also for their radical scavenging activity. The in vitro studies showed that the majority of the synthesized derivatives inhibited acetylcholinesterase (AChE) with IC50 values in the low-micromolar range. Among them, inhibitors 7a, 7h and 7k, strongly inhibited AChE, with IC50 values of 6.33, 7.56 and 11.0 nM, respectively, and were more potent than the reference compound donepezil. Moreover, the molecular docking study showed that most potent compounds simultaneously bind to the catalytic active site and the peripheral anionic site of AChE. Additionally, these compounds exhibited a greater ability to inhibit advanced glycation end product formation with additional radical scavenging properties. Thus, 2-phenyl-1-benzopyran-4-one derivatives might be promising lead compounds for potential poly-functional anti-Alzheimer's agents.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...