Enhanced photocurrent response on a CdTe incorporated coordination polymer based on 3-(3-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl)-5-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl)-1-methyl-1H-1,2,4-triazole†
Abstract
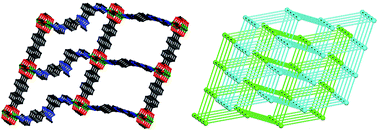
By using a rigid N donor, 3-(3-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl)-5-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl)-1-methyl-1H-1,2,4-triazole(L), two coordination polymers (CPs) formulated as Zn4L2(bpca)4·4DMF·9H2O (H2bpca = biphenyl-4,4′-dicarboxylic acid) (1) and Cd2L2(4,4′-cdba)2·2DMF (4,4′-H2cdba = 4,4′-carbonyldibenzoic acid) (2) were solvothermally synthesized and structurally characterized by single-crystal X-ray diffraction. CP 1 is a 2-fold interpenetrated uninodal 6-connected three-dimensional (3D) framework with a {412·63}-pcu topology. CP 2 displays a uninodal 4-connected two-dimensional (2D) layer with a 44-sql topology. The two CPs exhibit different electrochemical properties and photoelectrochemical behaviors. Their UV-vis spectra and band structures have been investigated. Meanwhile, CdTe and the CP 1@CdTe composite were synthesized by electrodeposition, and the CP 1@CdTe composite exhibits a much higher photocurrent density than CP 1 and CdTe.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...