Systematic study on the impact of water on the performance and stability of perovskite solar cells†
Abstract
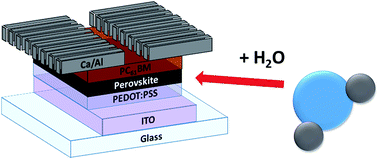
The effects of water on the photovoltaic performance of methylammonium lead iodide perovskite devices has recently become a topic of interest within the perovskite community. However, existing studies report contrasting and sometimes contradictory observations. In this work, small concentrations of water, consistent with those present in air-exposed DMF, were systematically incorporated directly into the PbI2 precursor solution in order to investigate its effect on the performance of sequentially spin-coated, inverted perovskite solar cells. Increasing concentrations of water in the PbI2 solution were found to have a negative impact on photovoltaic performance. The addition of water was observed to exaggerate the scan-rate and directional-dependent hysteresis and introduce new transient behaviours in comparison to the “dry” devices. Interestingly, the addition of water was also found to improve the long-term device stability in comparison with devices fabricated from “dry” precursors.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...