Highly sensitive visual detection of catalase based on the accelerating decomposition of H2O2 using Au nanorods as a sensor
Abstract
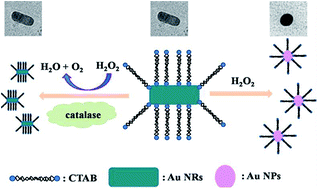
The detection of catalase associated with various diseases is very important due to the fact that it is frequently downregulated in human cancer tissues. Noble metal nanomaterial-assisted sensors have achieved rapid development for wide applications but few for detecting catalase. Thus, a novel colourimetric strategy has been developed for the selective and rapid visual detection of catalase by using the decelerating etching of gold nanorods (NRs). In the presence of hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide and SCN−, which can reduce the redox potential of Au(I)/Au (0), Au NRs would be etched by H2O2 along the longitudinal direction. As a consequence, the colour of solutions changed from bluish green to pink accompanied by the localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) extinction peak being shifted to short wavelength. In contrast, the etching process would be prohibited in the presence of catalase, and the colour and LSPR extinction peak of Au NRs would remain unchanged. Furthermore, this Au NR based sensor is applied to test paper that could be used in the detection of catalase in real samples. The discussion of the mechanism indicates that such a sensing method has an ideal performance in terms of sensitivity, selectivity, and linearity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...