Highly selective separation of dyes using compressed CO2 and spherical polyelectrolyte brushes†
Abstract
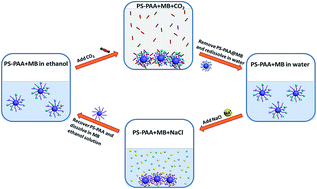
Spherical polyelectrolyte brushes (SPBs), consisting of a poly(styrene) core and poly(acrylic acid) shell densely grafted from the core surface, were synthesized by photoemulsion polymerization. A novel method for highly selective separation of methylene blue (MB) and other dyes is proposed herein, which employs spherical polyelectrolyte brushes as the adsorbent and compressed CO2 as the antisolvent; neither polymer brush nor CO2 on their own can separate the dyes. The SPBs and adsorbed dyes can be precipitated simultaneously from organic solutions by the easy control of CO2 pressure. The effects of several parameters such as CO2 pressure, initial dye concentration and temperature on the removal of MB by PS-PAA have been determined. MB can be selectively adsorbed by PS-PAA from the mixed dye solution with high efficiency, indicating that the binding of MB onto PS-PAA is probably dominated by electrostatic interactions. Due to the Donnan effect of the polymer brush, the adsorbed dyes can be easily eluted by NaCl aqueous solution through ion exchange to obtain the regeneration of the polymer brush, and the recovered PS-PAA retains high adsorption capacity even being regenerated five times. This provides a simple and effective way for the separation of ionic materials, which could be applied in environmental engineering.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...