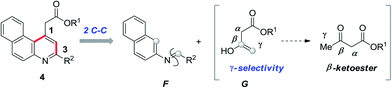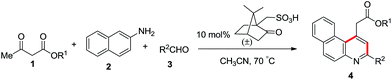DOI:
10.1039/C5RA23413A
(Paper)
RSC Adv., 2016,
6, 11675-11682
One-pot three-component regioselective synthesis of C1-functionalised 3-arylbenzo[f]quinoline†
Received
6th November 2015
, Accepted 11th January 2016
First published on 14th January 2016
Abstract
An efficient method for regioselective synthesis of C1-functionalised 3-arylbenzo[f]quinoline has been demonstrated via γ-selective aromatization using β-ketoester, 2-naphthylamine and aromatic aldehyde by employing 10 mol% camphorsulfonic acid as the catalyst in acetonitrile at 70 °C. In this approach, two C–C bond formations will result in functionalised benzo[f]quinoline in a one-pot three-component reaction. In addition, the present protocol has a diverse substrate scope with good yields. Furthermore, the protocol was directly utilised for the synthesis of alkyl 2-(3-(naphthalen-2-yl)benzo[f]quinolin-1-yl)acetate, allyl 2-(3-(heteroaromatic)benzo[f]quinolin-1-yl)acetate and functionalised 1,2,3-trisubstituted benzo[f]quinoline.
Introduction
C4-functionalized quinolines are recognized to be at the forefront of heterocycles1a and are found in many alkaloid natural products, bioactive scaffolds and potent marketed drugs (Fig. 1).1b–e Around the active quinoline skeleton,2,1e the integral core unit of benzoquinoline features as an eminent biological probe in pharmaceuticals, including selective 5-HT3 receptor ligands,3 CFTR activators,4 D3 dopamine agonists,5 vesicular glutamate transporter inhibitors,6 α1-receptor agonists7 and in vitro human type 1 & 2 steroid 5α-reductase inhibitors,8 and shows dopaminergic activity in nerve assays.9 Certainly, few of them are found to possess antibacterial,10 antimicrobial,11 antipsychotic,12 and antimalarial13 activities. This emerging wide array of applications demands the development of a facile synthetic method for the future bioactive scaffold of functionalised benzoquinoline. The design and synthesis of functionalised benzoquinoline using β-ketoester 1, 2-naphthylamine 2 and an aldehyde 3 favours the possible reaction pathways shown in Scheme 1.
 |
| | Fig. 1 Biologically active molecules containing the C4-functionalized quinoline skeleton. | |
 |
| | Scheme 1 Possible reaction pathways. | |
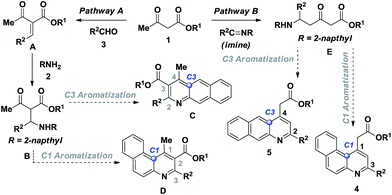
In pathway A, the reaction of β-ketoester with aldehyde results in species A which reacts with amine via Michael addition to give B and it may aromatize either at the C3 or C1 position of the naphthylamine to form alkyl 4-methyl-2-arylbenzo[g]quinoline-3-carboxylate C and alkyl 1-methyl-3-arylbenzo[f]quinoline-2-carboxylate D. On the other hand, in pathway B, alkyl-5-(naphthalen-2-ylamino)-3-oxo-5-arylpentanoate E prefers to form alkyl 2-(3-arylbenzo[f] quinolin-1-yl)acetate 4 and alkyl 2-(2-arylbenzo[g]quinolin-4-yl)acetate 5. Among the possible reaction pathways, the regioselective synthesis of alkyl 2-(3-arylbenzo[f]quinolin-1-yl)acetate 4 is highly desirable, as it may act as a scaffold in drug discovery. Since the reported methods in the literature14 are limited, we were interested in finding an elegant method for the synthesis of functionalised benzo[f]quinoline 4. The schematic route leading to the synthesis of alkyl 2-(3-arylbenzo[f]quinolin-1-yl)acetate 4 is shown in Scheme 2.
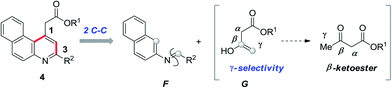 |
| | Scheme 2 Synthetic route of alkyl 2-(3-arylbenzo[f]quinolin-1-yl)acetate. | |
The γ-selectivity in a synthetic precursor plays a vital key role in the transformation to obtain complex heterocycles15 in pharmaceuticals.16 In particular, the γ-selectivity of β-ketoester17a,b through multicomponent reactions17c–f remains a challenging puzzle to synthetic chemists. Multicomponent reactions are often considered as providing growth in molecular diversity18 to assemble complex molecules having a diverse range of biomedical applications.19 The existing demand in these reactions is to achieve significant biomolecular scaffolds which are widely accessed through intermolecular C–C bond formation.20 We envisaged that functionalised benzo[f]quinoline may be accessible through progressive MCR intermolecular C–C bond formations.
The convenient, cheap and readily available camphorsulfonic acid has well-defined versatile applications in organic tranformations21 and it is used extensively in cyclisation reactions,22 alkylation of anilines,23 asymmetric reactions24 and natural product synthesis.22,25 We believed that catalytic camphorsulfonic acid might be suitable for the required γ-selectivity in the regioselective synthesis of functionalised benzo[f]quinoline.
Overall, herein we wish to report the efficient synthesis of C1-functionalised 3-arylbenzo[f]quinoline from β-ketoester, 2-naphthylamine and aromatic aldehyde using 10 mol% camphorsulfonic acid as the catalyst in acetonitrile at 70 °C, as shown in Scheme 3.
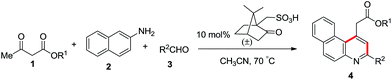 |
| | Scheme 3 Synthesis of alkyl 2-(3-arylbenzo[f]quinolin-1-yl)acetate. | |
Results and discussion
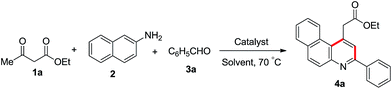
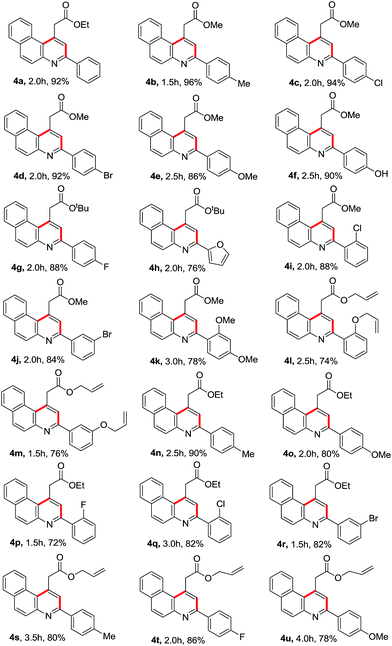
In an attempt to optimise the reaction conditions, we tested a series of reactions with ethyl acetoacetate 1a, 2-napthylamine 2 and benzaldehyde 3a as depicted in Table 1. It is to be noted that the 10 mol% camphorsulfonic acid catalyst in acetonitrile at 70 °C gave best yield (Table 1, entry 5). However, different solvents such as DCE, THF and n-BuOH afford lower yield (Table 1, entries 8–10). It is also noteworthy that in our present protocol we have not observed any other byproducts such as C, D and 5 in the reaction medium. After optimisation, we conducted reactions with 2-naphthylamine (2), methyl acetoacetate (1b) and a diverse range of para-substituted benzaldehydes such as those containing 4-methyl (3b), 4-chloro (3c), 4-bromo (3d), 4-methoxy (3e) and 4-hydroxy (3f) moieties, which afforded the desired products 4b–f in 86–96% yield. Subsequent reaction with tert-butyl acetoacetate (1c) and 4-fluorobenzaldehyde (3g)/furfural (3h) delivered the required products 4g and 4h in 88% and 76% yield.
Table 1 Optimization of the reaction conditionsa
|
| Entry |
Catalyst (mol%) |
Solvent |
Time (h) |
Yieldb (%) |
| All the reactions were carried out using ethyl acetoacetate (1a, 0.5 equiv.), 2-naphthylamine (2, 0.5 equiv.) and benzaldehyde (3a, 0.5 equiv.). Isolated yield. Reaction temperature at 55 °C. NR = no reaction. |
| 1 |
AcOH (10) |
CH3CN |
8.0 |
55 |
| 2 |
p-TSA (10) |
CH3CN |
12 |
NR |
| 3 |
Iodine (10) |
CH3CN |
2.5 |
60 |
| 4 |
L-Proline (10) |
CH3CN |
12 |
NR |
| 5 |
(±)-CSA (10) |
CH3CN |
2.0 |
92 |
| 6 |
(±)-CSA (05) |
CH3CN |
3.0 |
80 |
| 7 |
(±)-CSA (15) |
CH3CN |
2.5 |
89 |
| 8 |
(±)-CSA (10) |
DCE |
12 |
35 |
| 9 |
(±)-CSA (10) |
THFc |
6.0 |
65 |
| 10 |
(±)-CSA (10) |
n-BuOH |
12 |
25 |
Further, the reaction was examined with 2/3-halobenzaldehyde (3i/3j)/2,4-dimethoxy benzaldehyde (3k), 2-naphthylamine and methyl acetoacetate (1b) and the resultant products 4i–k were obtained in 78–88% yield. In addition, 2/3-(allyloxy)benzaldehyde (3l/3m) underwent reaction with allyl acetoacetate (1d) and 2-naphthylamine, which gave the corresponding products 4l and 4m in 74% and 76% yield, respectively. Reactions with different substituted benzaldehydes, ethyl acetoacetate (1a) and 2-naphthylamine resulted in 4n–r in 72–90% yield.
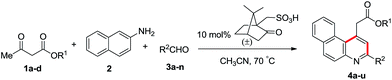
Inspired by these results, we performed reactions of allyl acetoacetate (1d), 2-naphthylamine and a variety of para-substituted benzaldehydes such as 4-methyl (3b), 4-fluoro (3g) and 4-methoxy (3e) under the optimized reaction conditions, which afforded the required benzo[f]quinolines 4s–u in 78–86% yield as shown in Table 2. The crystal structure of 4g was determined through single crystal XRD analysis, which is shown in Fig. 2.
Table 2 Synthesis of alkyl 2-(3-arylbenzo[f]quinolin-1-yl)acetate using (±)-camphorsulfonic acid as the catalystab
|
| All the reactions were carried out using β-ketoester (0.5 equiv.), 2-naphthylamine (0.5 equiv.) and aromatic aldehyde (0.5 equiv.). Isolated yield. |
 |
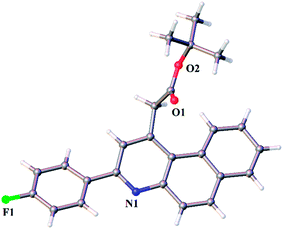 |
| | Fig. 2 X-ray crystal structure of 4g. | |
We have also performed the reaction of a fused aromatic aldehyde, 2-napthaldehyde (6), with 2-napthylamine (2) and different β-ketoesters in the presence of 10 mol% camphorsulfonic acid as the catalyst in acetonitrile at 70 °C. The desired product alkyl 2-(3-(naphthalen-2-yl)benzo[f]quinolin-1-yl)acetate 7 was obtained in good yield as shown in Scheme 4.
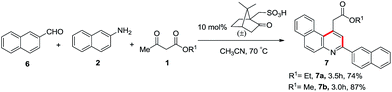 |
| | Scheme 4 Synthesis of alkyl 2-(3-(naphthalen-2-yl)benzo[f] quinolin-1-yl)acetate. | |
The protocol in hand was further investigated with heteroaromatic aldehydes, such as 1-benzyl-1,2,3-triazole-4-carbaldehyde (8)/2-thiophenecarboxaldehyde (9), 2-napthylamine (2) and allyl acetoacetate (1d) using a catalytic amount of camphorsulfonic acid and the expected product allyl 2-(3-(heteroaromatic)benzo[f]quinolin-1-yl)acetate 10 and 11 were obtained in 60% and 76% yield as shown in Scheme 5.
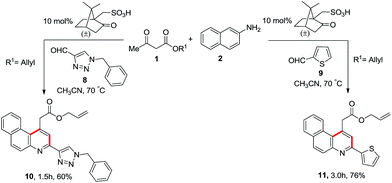 |
| | Scheme 5 Synthesis of allyl 2-(3-(heteroaromatic)benzo[f]quinolin-1-yl)acetate. | |
Furthermore, we have synthesized a functionalised 1,2,3-trisubstituted benzo[f]quinoline from ethyl 3-oxopentanoate (1e), 2-napthylamine (2) and 4-methoxybenzaldehyde (3e) using 10 mol% camphorsulfonic acid in acetonitrile at 70 °C, which afforded the resultant product 12 in 72% yield as shown in Scheme 6.
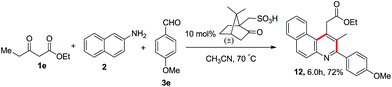 |
| | Scheme 6 Synthesis of 1,2,3-trisubstituted benzo[f]quinoline. | |
A plausible mechanism is described as follows: the β-ketoester 1 is most likely to react with camphorsulfonic acid to form an intermediate I, which subsequently undergoes rearrangement and reacts with the generated imine to form a Michael-type addition product from γ-selective reaction of β-ketoester with imine via II17a to attain III. Further, III favors aromatization to form the desired product 4 as shown in Scheme 7. It is to be highlighted here that we have observed the HRMS of the intermediate III of 4p after 10 min under reflux conditions, which indirectly supports the proposed mechanism (see ESI†).
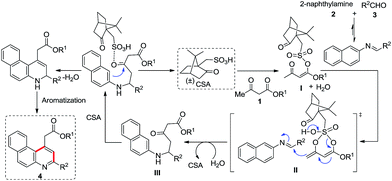 |
| | Scheme 7 Proposed mechanism for the formation of alkyl 2-(3-arylbenzo[f]quinolin-1-yl)acetate. | |
Conclusions
In summary, the regioselective synthesis of alkyl 2-(3-arylbenzo[f]quinolin-1-yl)acetate has been achieved using camphorsulfonic acid through the γ-selective reaction of β-ketoester. It is a straight forward methodology which provides flexible access to a diverse range of substrates. The prominent aspect of this present method was that two new C–C bonds were formed in a one-pot fashion under mild reaction conditions. In addition, the protocol enables the synthesis of naphthalen-2-yl, heteroaromatic and trisubstituted benzo[f]quinoline analogues in good yields.
General procedure
Synthesis of alkyl 2-(3-arylbenzo[f]quinolin-1-yl)acetate (4)
A mixture of β-ketoester (1, 0.5 mmol), 2-naphthylamine (2, 0.5 mmol) and aromatic aldehyde (3, 0.5 mmol) was taken in 5 ml acetonitrile. Camphorsulfonic acid (0.011 g, 0.05 mmol) was added and the mixture allowed to stir at 70 °C. After completion of the reaction, the solvent was removed under reduced pressure and the mixture was extracted with DCM, washed with water, dried over sodium sulphate and concentrated under reduced pressure. Then, the residue was purified through column chromatography to obtain the pure product 4. Similarly, compounds 7 and 10–12 were synthesized by following the above reaction procedure.
Ethyl 2-(3-phenylbenzo[f]quinolin-1-yl)acetate (4a). Yield 92%, white solid, mp 131–132 °C, 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.54 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 8.22 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 8.09 (d, J = 9.2 Hz, 1H), 7.99–7.97 (m, 2H), 7.87 (s, 1H), 7.67–7.64 (m, 2H), 7.56 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 7.49 (t, J = 6.8 Hz, 1H), 4.49 (s, 2H), 4.25 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 1.23 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 170.8, 155.9, 150.3, 141.1, 139.2, 133.2, 131.5, 130.0, 129.8, 129.5, 129.4, 129.1, 127.6, 127.0, 126.9, 126.8, 124.6, 123.2, 61.7, 44.0, 14.4; IR (KBr) νmax 3056, 2980, 2902, 1735, 1584, 1552, 1484, 1455, 1391, 1367, 1322, 1255, 1194, 1156, 1029 cm−1; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C23H20NO2 342.1489 (M + H+); found 342.1489.
Methyl 2-(3-(p-tolyl)benzo[f]quinolin-1-yl)acetate (4b)14a. Yield 96%, light yellow solid, mp 168–169 °C, 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.49 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 8.12 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 8.08 (s, 1H), 7.97–7.93 (m, 2H), 7.83 (s, 1H), 7.68–7.61 (m, 2H), 7.35 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 4.47 (s, 2H), 3.77 (s, 3H), 2.45 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 171.3, 155.8, 150.2, 140.8, 139.6, 136.2, 133.1, 131.4, 129.9, 129.7, 129.6, 129.4, 128.2, 127.5, 126.8, 126.7, 124.3, 122.9, 52.7, 43.7, 21.5; IR (KBr) νmax 3029, 2952, 2922, 2853, 1737, 1579, 1548, 1481, 1452, 1437, 1392, 1353, 1259, 1184, 1132, 1057 cm−1; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C23H20NO2 342.1489 (M + H+); found 342.1505.
Methyl 2-(3-(4-chlorophenyl)benzo[f]quinolin-1-yl)acetate (4c)14a. Yield 94%, white solid, mp 138–139 °C, 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.49 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 8.17 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 8.12 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 8.00–7.96 (m, 2H), 7.83 (s, 1H), 7.69–7.66 (m, 2H), 7.51 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 4.51 (s, 2H), 3.78 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 171.1, 154.3, 149.9, 141.4, 137.0, 135.9, 133.2, 131.9, 129.7, 129.5, 129.2, 128.9, 127.2, 127.0, 126.8, 124.7, 122.9, 52.8, 43.7; IR (KBr) νmax 3056, 2942, 2924, 2852, 1741, 1585, 1550, 1481, 1435, 1390, 1328, 1257, 1198, 1157, 1091, 1012 cm−1; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C22H17ClNO2 362.0943 (M + H+); found 362.0942.
Methyl 2-(3-(4-bromophenyl)benzo[f]quinolin-1-yl)acetate (4d)14a. Yield 92%, light yellow solid, mp 143–144 °C, 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.51 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 1H), 8.11 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 8.06 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 1H), 7.99–7.96 (m, 2H), 7.83 (s, 1H), 7.68–7.66 (m, 4H), 4.51 (s, 2H), 3.78 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 171.2, 154.5, 150.3, 141.1, 137.9, 133.2, 132.2, 131.7, 129.8, 129.6, 129.5, 129.1, 127.1, 126.9, 126.8, 124.7, 124.1, 122.7, 52.8, 43.6; IR (KBr)νmax 3051, 2951, 2915, 2854, 1736, 1584, 1549, 1481, 1455, 1434, 1387, 1356, 1328, 1257, 1199, 1159, 1087, 1008 cm−1; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C22H17BrNO2 406.0437 (M + H+); found 406.0437.
Methyl 2-(3-(4-methoxyphenyl)benzo[f]quinolin-1-yl)acetate (4e). Yield 86%, light yellow solid, mp 149–150 °C, 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.47 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 8.18 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 8.09 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 1H), 7.93 (t, J = 9.0 Hz, 2H), 7.78 (s, 1H), 7.65–7.56 (m, 2H), 7.04 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 4.46 (s, 2H), 3.87 (s, 3H), 3.76 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3): δ 171.2, 161.1, 155.3, 149.9, 140.9, 132.9, 131.8, 131.5, 131.2, 129.9, 129.4, 128.9, 126.8, 126.7, 126.6, 124.1, 122.7, 114.4, 55.5, 52.7, 43.6; IR (KBr) νmax 3068, 2995, 2948, 2937, 2830, 1737, 1604, 1544, 1503, 1434, 1354, 1337, 1252, 1202, 1183, 1161, 1028 cm−1; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C23H20NO3 358.1438 (M + H+); found 358.1430.
Methyl 2-(3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)benzo[f]quinolin-1-yl)acetate (4f). Yield 90%, white solid, mp 141–142 °C, 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3): δ 9.30 (s, 1H), 8.40 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 1H), 8.02 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, 2H), 7.93 (d, J = 2.4, 1H), 7.92 (d, J = 1.8 Hz, 2H), 7.75 (s, 1H), 7.56–7.53 (m, 2H), 6.91 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H), 4.44 (s, 2H), 3.69 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3): δ 170.4, 158.5, 154.8, 149.2, 140.1, 132.0, 129.1, 129.0, 128.6, 128.5, 128.1, 128.0, 126.1, 125.9, 125.7, 122.9, 121.8, 121.7, 115.4, 115.3, 51.8, 42.8; IR (KBr) νmax 3058, 2995, 2953, 2838, 1738, 1608, 1588, 1549, 1514, 1484, 1451, 1353, 1258, 1171, 1130, 1058 cm−1; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C22H18NO3 344.1281 (M + H+); found 344.1286.
tert-Butyl 2-(3-(4-fluorophenyl)benzo[f]quinolin-1-yl)acetate (4g). Yield 88%, white solid, mp 140–141 °C, 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.58 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 8.23–8.21 (m, 2H), 8.06 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.98–7.95 (m, 2H), 7.81 (s, 1H), 7.67–7.64 (m, 2H), 7.23–7.20 (m, 2H), 4.41 (s, 2H), 1.44 (s, 9H); 13C NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3): δ 169.5, 165.2, 163.5, 154.1, 133.5, 133.1, 131.2, 131.1, 130.3, 130.1, 129.7, 129.6, 129.3, 128.3, 127.3, 127.2, 127.1, 127.0, 126.6, 124.8, 123.6, 116.3, 116.1, 115.6, 115.5, 82.6, 45.6, 28.2; IR (KBr)νmax 3057, 2976, 2927, 2850, 1727, 1602, 1585, 1553, 1532, 1510, 1483, 1455, 1392, 1368, 1329, 1226, 1149, 1073, 1014 cm−1; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C25H23FNO2 388.1708 (M + H+); found 388.1707.
tert-Butyl 2-(3-(furan-2-yl)benzo[f]quinolin-1-yl)acetate (4h). Yield 76%, brown solid, mp 94–95 °C, 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.56 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 8.04 (d, J = 9.2 Hz, 1H), 7.96–7.95 (m, 3H), 7.84 (s, 1H), 7.66–7.64 (m, 2H), 7.27 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 6.62–6.61 (m, 1H), 4.41 (s, 2H), 1.43 (s, 9H); 13C NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3): δ 169.8, 153.6, 150.2, 147.8, 144.1, 141.7, 133.1, 131.6, 129.4, 129.4, 126.9, 126.8, 126.7, 124.6, 121.6, 112.4, 110.0, 82.2, 45.3, 28.2; IR (KBr) νmax 3029, 2974, 2926, 1728, 1601, 1551, 1491, 1454, 1393, 1368, 1325, 1254, 1224, 1072 cm−1; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C23H22NO3 360.1594 (M + H+); found 360.1609.
Methyl 2-(3-(2-chlorophenyl)benzo[f]quinolin-1-yl)acetate (4i). Yield 88%, brown solid, mp 79–80 °C, 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.56 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 8.19 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 8.00 (t, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.84 (s, 2H), 7.69 (s, 2H), 7.53 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 7.42 (t, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 4.52 (s, 2H), 3.77 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 170.9, 155.0, 149.4, 133.3, 132.7, 132.3, 132.2, 130.4, 129.6, 128.6, 127.5, 127.4, 127.2, 127.1, 126.9, 124.8, 52.8, 43.6; IR (KBr) νmax 3059, 2987, 2953, 2850, 1738, 1596, 1580, 1550, 1476, 1435, 1395, 1351, 1330, 1258, 1201, 1160, 1094, 1057 cm−1; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C22H17ClNO2 362.0943 (M + H+); found 362.0943.
Methyl 2-(3-(3-bromophenyl)benzo[f]quinolin-1-yl)acetate (4j). Yield 84%, white solid, mp 130–131 °C, 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.50 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H), 8.40 (s, 1H), 8.12 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H), 8.06 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H), 7.97 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 2H), 7.81 (s, 1H), 7.69–7.65 (m, 2H), 7.59 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H), 7.39 (t, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H), 4.49 (s, 2H), 3.78 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 171.4, 154.1, 150.3, 141.1, 141.0, 133.3, 132.4, 131.8, 130.6, 130.5, 129.8, 129.6, 129.5, 127.1, 126.9, 126.8, 126.1, 124.9, 123.3, 122.9, 52.8, 43.7; IR (KBr) νmax 3031, 2950, 2916, 2848, 1724, 1605, 1582, 1549, 1488, 1454, 1424, 1383, 1357, 1323, 1306, 1247, 1161, 1053 cm−1; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C22H17BrNO2 406.0437 (M + H+); found 406.0435.
Methyl 2-(3-(2,4-dimethoxyphenyl)benzo[f]quinolin-1-yl)acetate (4k). Yield 78%, brown solid, mp 111–112 °C, 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.52 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 8.12 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 8.02–7.94 (m, 4H), 7.64 (s, 2H), 6.69 (d, J = 6.8 Hz, 1H), 6.60 (s, 1H), 4.49 (s, 2H), 3.87 (s, 6H), 3.75 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 171.3, 162.1, 158.8, 154.6, 149.7, 139.8, 133.0, 132.7, 131.2, 129.9, 129.4, 129.2, 127.3, 126.7, 123.9, 105.7, 99.2, 55.9, 55.7, 52.6, 43.7; IR (KBr) νmax 3059, 3003, 2950, 2837, 1736, 1608, 1579, 1547, 1505, 1455, 1437, 1300, 1283, 1209, 1160, 1030 cm−1; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C24H22NO4 388.1544 (M + H+); found 388.1542.
Allyl 2-(3-(2-(allyloxy)phenyl)benzo[f]quinolin-1-yl)acetate (4l). Yield 74%, light yellow solid, mp 169–170 °C, 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.55 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 8.17 (s, 1H), 8.07 (s, 1H), 8.04 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 7.98 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.66–7.64 (m, 2H), 7.42 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 7.17 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 7.04 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 6.09–6.00 (m, 1H), 5.91–5.81 (m, 1H), 5.38 (d, J = 17.2 Hz, 1H), 5.26 (d, J = 13.6 Hz, 2H), 5.22–5.18 (m 1H), 4.67–4.63 (m, 4H), 4.51 (s, 2H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 170.5, 156.5, 155.1, 150.1, 139.3, 133.3, 133.1, 131.8, 131.7, 131.0, 130.5, 129.9, 129.7, 129.3, 129.2, 127.8, 126.8, 126.7, 126.6, 124.2, 121.7, 118.9, 117.2, 113.3, 69.5, 66.1, 43.8; IR (KBr) νmax 3055, 2969, 2948, 2930, 2835, 1741, 1687, 1624, 1577, 1544, 1480, 1451, 1352, 1316, 1257, 1224, 1182, 1148, 1059 cm−1; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C27H24NO3 410.1751 (M + H+); found 410.1755.
Allyl 2-(3-(3-(allyloxy)phenyl)benzo[f]quinolin-1-yl)acetate (4m). Yield 76%, white solid, mp 81–82 °C, 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.53 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 1H), 8.08 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 1H), 7.98–7.95 (m, 2H), 7.86–7.84 (m, 2H), 7.76 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 1H), 7.66–7.63 (m, 2H), 7.44 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 1H), 7.04 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 1H), 6.17–6.10 (m, 1H), 5.92–5.85 (m, 1H), 5.49 (d, J = 18.0 Hz, 1H), 5.33 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 1H), 5.28 (d, J = 18.0 Hz, 1H), 5.22 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H), 4.68 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 4H), 4.52 (s, 2H); 13C NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3): δ 170.4, 159.4, 155.6, 150.2, 140.8, 140.5, 133.5, 133.2, 131.8, 131.5, 130.0, 129.9, 129.7, 129.4, 126.9, 126.8, 126.8, 124.7, 123.3, 120.2, 119.1, 117.9, 116.3, 113.7, 69.2, 66.3, 43.8; IR (KBr) νmax 3056, 2924, 2896, 1733, 1647, 1583, 1552, 1488, 1455, 1423, 1358, 1319, 1281, 1231, 1195, 1154, 1024, 991 cm−1; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C27H24NO3 410.1756 (M + H+); found 410.1754.
Ethyl 2-(3-(p-tolyl)benzo[f]quinolin-1-yl)acetate (4n). Yield 90%, brown solid, mp 102–103 °C, 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.53 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 8.13 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 8.08 (s, 1H), 7.96 (d, J = 9.6 Hz, 2H), 7.85 (s, 1H), 7.67–7.63 (m, 2H), 7.34 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 4.48 (s, 2H), 4.24 (q, J = 6.8 Hz, 2H), 2.45 (s, 3H), 1.23 (t, J = 6.8 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 170.8, 155.8, 150.2, 141.1, 139.7, 136.2, 133.1, 131.4, 130.0, 129.8, 129.7, 129.4, 127.5, 126.9, 126.8, 126.7, 124.4, 123.0, 61.7, 43.9, 21.6, 14.4; IR (KBr) νmax 3053, 3025, 2980, 2923, 2855, 1734, 1606, 1585, 1550, 1512, 1482, 1455, 1391, 1366, 1322, 1248, 1217, 1184, 1156, 1094, 1054 cm−1; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C24H22NO2 356.1645 (M + H+); found 356.1646.
Ethyl 2-(3-(4-methoxyphenyl)benzo[f]quinolin-1-yl)acetate (4o). Yield 80%, white solid, mp 120–121 °C, 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.53 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 1H), 8.19 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H), 8.06 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H), 7.96 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 1H), 7.95–7.94 (m, 1H), 7.81 (s, 1H), 7.66–7.63 (m, 2H), 7.07 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H), 4.48 (s, 2H), 4.24 (q, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H), 3.90, (s, 3H), 1.23 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3): δ 170.8, 161.0, 155.5, 150.2, 140.9, 133.0, 131.7, 131.3, 130.1, 129.7, 129.4, 128.9, 126.8, 126.7, 126.7, 124.1, 122.6, 114.4, 61.7, 55.6, 44.0, 14.4; IR (KBr) νmax 3027, 2957, 2924, 2852, 1732, 1631, 1606, 1583, 1550, 1531, 1512, 1482, 1455, 1392, 1364, 1324, 1248, 1224, 1175, 1145, 1030 cm−1; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C24H22NO3 372.1594 (M + H+); found 372.1594.
Ethyl 2-(3-(2-fluorophenyl)benzo[f]quinolin-1-yl)acetate (4p). Yield 72%, semi-solid, 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.57 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 1H), 8.24–8.21 (m, 1H), 8.08 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 1H), 7.98 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H), 7.97–7.95 (m, 1H), 7.68–7.66 (m, 2H), 7.43 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 1H), 7.34 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 1H), 7.23–7.20, (m, 1H), 4.50 (s, 2H), 4.24 (q, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H), 1.23 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3): δ 170.7, 161.9, 160.2, 152.2, 150.2, 140.7, 133.3, 131.6, 131.6, 131.5, 131.1, 131.0, 129.9, 129.6, 129.4, 127.1, 127.0, 126.8, 124.9, 124.9, 124.7, 116.6, 116.4, 61.7, 44.0, 14.3; IR (KBr) νmax 3028, 2956, 2923, 2852, 1733, 1586, 1582, 1550, 1484, 1452, 1371, 1364, 1320, 1249, 1215, 1155, 1080, 1030 cm−1; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C23H19FNO2 360.1395 (M + H+); found 360.1396.
Ethyl 2-(3-(2-chlorophenyl)benzo[f]quinolin-1-yl)acetate (4q). Yield 82%, white solid, mp 151–152 °C, 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.60 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 8.12 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 8.01–7.97 (m, 2H), 7.83–7.81 (m, 2H), 7.70–7.67 (m, 2H), 7.53 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.45–7.31 (m, 1H), 7.43–7.38 (m, 1H), 4.49 (s, 2H), 4.24 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 1.23 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 170.4, 155.9, 149.3, 133.2, 132.7, 132.3, 132.1, 130.5, 130.4, 129.7, 129.6, 129.5, 128.6, 127.5, 127.4, 127.3, 127.1, 124.9, 61.8, 43.9, 14.3; IR (KBr) νmax 3060, 2982, 2933, 2849, 1734, 1627, 1596, 1578, 1550, 1475, 1442, 1394, 1369, 1350, 1330, 1244, 1210, 1160, 1133, 1094, 1055, 1038 cm−1; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C23H19ClNO2 376.1099 (M + H+); found 376.1099.
Ethyl 2-(3-(3-bromophenyl)benzo[f]quinolin-1-yl)acetate (4r). Yield 82%, white solid, mp 125–126 °C, 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.54 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H), 8.40 (s, 1H), 8.13 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 1H), 8.07 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 1H), 8.00–7.97, (m, 2H), 7.84 (s, 1H), 7.68–7.66 (m, 2H), 7.60 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 1H), 7.41 (t, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H), 4.50 (s, 2H), 4.25 (q, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H), 1.25 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3): δ 170.7, 154.2, 150.2, 141.4, 141.1, 133.3, 132.5, 131.7, 130.7, 130.6, 129.9, 129.6, 129.4, 126.9, 126.2, 126.1, 124.9, 123.4, 123.1, 123.0, 61.5, 43.9, 13.9; IR (KBr) νmax 3025, 2922, 2852, 1733, 1586, 1572, 1550, 1480, 1452, 1442, 1428, 1371, 1322, 1213, 1197, 1158, 1019 cm−1; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C23H19BrNO2 420.0594 (M + H+); found 420.0623.
Allyl 2-(3-(p-tolyl)benzo[f]quinolin-1-yl)acetate (4s). Yield 80%, brown solid, mp 83–84 °C, 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.52 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 8.12 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 8.08 (d, J = 9.2 Hz, 1H), 7.99–7.95 (m, 2H), 7.86 (s, 1H), 7.69–7.63 (m, 2H), 7.35 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 5.92–5.83 (m, 1H), 5.30–5.17 (m, 2H), 4.68 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 2H), 4.52 (s, 2H), 2.45 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 170.4, 155.8, 150.2, 140.7, 139.6, 136.2, 133.1, 131.8, 131.4, 130.0, 129.8, 129.4, 128.7, 127.5, 126.8, 124.4, 122.9, 119.0, 66.2, 43.8, 21.5; IR (KBr) νmax 3062, 3035, 2923, 2853, 1735, 1653, 1605, 1582, 1548, 1479, 1451, 1352, 1330, 1274, 1216, 1185, 1154, 1130, 1054 cm−1; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C25H22NO2 368.1645 (M + H+); found 368.1649.
Allyl 2-(3-(4-fluorophenyl)benzo[f]quinolin-1-yl)acetate (4t). Yield 86%, white solid, mp 154–155 °C, 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.52–8.51 (m, 1H), 8.22–8.20 (m, 2H), 8.09 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.98–7.95 (m, 2H), 7.83 (s, 1H), 7.67–7.63 (m, 2H), 7.22 (t, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 5.92–5.85 (m, 1H), 5.29 (t, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 5.23 (d, J = 11.4 Hz, 1H), 4.69 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H), 4.52 (s, 2H); 13C NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3): δ 170.3, 164.9, 163.3, 154.6, 150.0, 141.2, 133.2, 131.8, 131.7, 129.8, 129.6, 129.5, 129.5, 129.3, 127.0, 126.9, 126.8, 124.5, 122.9, 119.2, 116.1, 115.9, 66.3, 43.8; IR (KBr) νmax 3059, 2954, 2924, 2848, 1735, 1653, 1601, 1585, 1552, 1508, 1483, 1454, 1390, 1358, 1322, 1228, 1191, 1156, 1014 cm−1; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C24H19FNO2 372.1395 (M + H+); found 372.1384.
Allyl 2-(3-(4-methoxyphenyl)benzo[f]quinolin-1-yl)acetate (4u). Yield 78%, pale yellow solid, mp 92–95 °C, 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.50 (d, J = 6.4 Hz, 1H) 8.18 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 8.05 (d, J = 9.2 Hz, 1H), 7.95 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 7.81 (s, 1H), 7.62 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 2H), 7.05 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 5.89–5.85 (m, 1H), 5.31–5.21 (m, 2H), 4.68 (s, 2H), 4.49 (s, 2H), 3.89 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3): δ 170.5, 161.0, 155.4, 150.2, 140.6, 133.0, 131.8, 131.6, 131.3, 129.9, 129.6, 129.3, 128.9, 126.7, 126.6, 124.1, 122.6, 119.0, 114.4, 66.1, 55.5, 43.8; IR (KBr) νmax 3051, 2959, 2933, 2836, 1735, 1675, 1653, 1606, 1583, 1550, 1530, 1511, 1482, 1455, 4140, 1358, 1323, 1306, 1176, 1155, 1111, 1030 cm−1; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C25H22NO3 384.1594 (M + H+); found 384.1612.
Ethyl 2-(3-(naphthalen-2-yl)benzo[f]quinolin-1-yl)acetate (7a). Yield 74%, pale yellow solid, mp 76–77 °C, 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.69 (s, 1H), 8.56 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 8.41 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 8.18 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 8.03–8.02 (m, 3H), 8.00–7.96 (m, 2H), 7.92–7.89 (m, 1H), 7.69–7.64 (m, 2H), 7.55–7.53 (m, 2H), 4.54 (s, 2H), 4.27 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 1.25 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 170.8, 155.6, 150.2, 141.4, 136.2, 134.1, 133.7, 133.2, 131.7, 130.0, 129.5, 129.4, 129.1, 128.8, 127.9, 127.3, 127.0, 126.9, 126.9, 126.8, 126.5, 125.1, 124.7, 123.5, 61.7, 44.1, 14.4; IR (KBr) νmax 3056, 2978, 2923, 2851, 1734, 1583, 1552, 1509, 1482, 1452, 1389, 1367, 1321, 1256, 1215, 1195, 1156, 1029; cm−1; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C27H22NO2 392.1645 (M + H+); found 392.1648.
Methyl 2-(3-(naphthalen-2-yl)benzo[f]quinolin-1-yl)acetate (7b). Yield 87%, white solid, mp 80–81 °C, 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.68 (s, 1H), 8.52 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 1H), 8.41–8.39 (m, 1H), 8.14 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 1H), 8.02–8.01 (m, 4H), 7.99–7.96 (m, 1H), 7.90 (t, J = 6 Hz, 1H), 7.68–7.65 (m, 2H), 7.55–7.53 (m, 2H), 4.54 (s, 2H), 3.79 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3): δ 171.3, 155.6, 150.3, 141.0, 136.3, 134.1, 133.7, 133.2, 131.6, 129.9, 129.6, 129.4, 129.0, 128.8, 127.9, 127.2, 127.0, 126.9, 126.8, 126.8, 126.6, 125.1, 124.6, 123.4, 52.8, 43.7; IR (KBr) νmax 3057, 2986, 2952, 2848, 1736, 1595, 1549, 1472, 1432, 1391, 1347, 1198, 1158, 1088, 1055 cm−1; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C26H20NO2 378.1489 (M + H+); found 378.1486.
Allyl 2-(3-(1-benzyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)benzo[f]quinolin-1-yl)acetate (10). Yield 60%, brown solid, mp 124–125 °C, 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.53 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 8.45 (s, 1H), 8.02–7.97 (m, 2H), 7.69 (s, 2H), 7.40–7.39 (m, 6H), 7.28 (s, 1H), 5.86–5.83 (m, 1H), 5.65 (s, 2H), 5.26 (d, J = 17.4 Hz, 1H), 5.20 (d, J = 10.8 Hz, 1H), 4.66 (d, J = 5.6 Hz, 2H), 4.57 (s, 2H); 13C NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3): δ 170.3, 150.2, 148.9, 148.7, 141.3, 134.7, 133.2, 131.8, 131.7, 130.1, 129.4, 129.1, 129.0, 128.5, 128.1, 127.0, 126.8, 125.3, 123.4, 123.1, 122.9, 119.1, 66.3, 54.7, 43.9; IR (KBr) νmax 3148, 3062, 2924, 2853, 1736, 1647, 1597, 1557, 1497, 1454, 1430, 1362, 1338, 1296, 1232, 1187, 1156, 1092, 1043, 1017 cm−1; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C27H23N4O2 435.1821 (M + H+); found 435.1813.
Allyl 2-(3-(thiophen-2-yl)benzo[f]quinolin-1-yl)acetate (11). Yield 76%, brown solid, mp 114–115 °C, 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.48 (d, J = 9.6 Hz, 1H), 8.01 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 1H), 7.95–7.93 (m, 2H), 7.78 (s, 1H), 7.76 (d, J = 3.4 Hz, 1H), 7.65–7.61 (m, 2H), 7.47 (d, J = 5.4 Hz, 1H), 7.18–7.16 (m, 1H), 5.91–5.84 (m, 1H), 5.29–5.26 (m, 1H), 5.22 (d, J = 9.6 Hz, 1H), 4.68 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H), 4.48 (s, 2H); 13C NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3): δ 170.3, 151.1, 150.2, 144.7, 140.8, 133.1, 131.8, 131.7, 129.9, 129.5, 129.3, 128.6, 128.3, 126.9, 126.8, 126.7, 125.9, 124.9, 121.7, 119.1, 66.2, 43.7; IR (KBr) νmax 3071, 2958, 2930, 2857, 1739, 1584, 1552, 1523, 1482, 1455, 1423, 1365, 1326, 1259, 1155, 1071, 1015 cm−1; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C22H18NO2S 360.1053 (M + H+); found 360.1052.
Ethyl 2-(3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-methylbenzo[f]quinolin-1-yl)acetate (12). Yield 72%, white solid, mp 76–77 °C, 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.37 (d, J = 6.8 Hz, 1H), 7.94 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.88 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 7.63–7.62 (m, 3H), 7.58 (s, 1H), 7.03 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 4.42 (s, 2H), 4.38 (q, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 3.89 (s, 3H), 2.47 (s, 3H), 1.38 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 171.2, 159.9, 158.9, 147.1, 139.4, 133.9, 133.4, 130.9, 130.4, 129.8, 129.6, 129.2, 129.1, 128.9, 127.2, 126.9, 126.3, 125.0, 122.1, 114.0, 61.7, 55.6, 40.1, 17.7, 14.6; IR (KBr)νmax 3055, 2957, 2932, 2836, 1738, 1607, 1577, 1516, 1549, 1510, 1477, 1451, 1427, 1368, 1301, 1178, 1109, 1019 cm−1; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C25H24NO3 386.1751 (M + H+); found 386.1753.
Acknowledgements
RK is grateful to IIT Guwahati for providing a research fellowship. RSB acknowledges CSIR, New Delhi for a Research Associate Fellowship. PRB thanks UGC, New Delhi for his SRF Fellowship. We thank the director of IIT Guwahati for creating general laboratory facilities. We gratefully acknowledge financial support (grant no. 02(0181)/14/EMR-II) from the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi. We are grateful to the Department of Science and Technology, New Delhi for supplying single crystal XRD under the FIST program.
Notes and references
-
(a) T. Iwai and M. Sawamura, ACS Catal., 2015, 5, 5031 CrossRef CAS;
(b) J. P. Michael, Nat. Prod. Rep., 2008, 25, 166 RSC;
(c) A. Lilienkampf, J. Mao, B. Wan, Y. Wang, S. G. Franzblau and A. P. Kozikowski, J. Med. Chem., 2009, 52, 2109 CrossRef CAS PubMed;
(d) V. K. Zishiri, M. C. Joshi, R. Hunter, K. Chibale, P. J. Smith, R. L. Summers, R. E. Martin and T. J. Egan, J. Med. Chem., 2011, 54, 6956 CrossRef CAS PubMed;
(e) J. B. Bharate, R. A. Vishwakarma and S. B. Bharate, RSC Adv., 2015, 5, 42020 RSC.
- R. V. Patel and S. W. Park, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2014, 71, 24 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Cappelli, M. Anzini, S. Vomero, L. Mennuni, F. Makovec, E. Doucet, M. Hamon, G. Bruni, M. R. Romeo, M. C. Menziani, P. G. De Benedetti and T. Langer, J. Med. Chem., 1998, 41, 728 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Murthy, N. Pedemonte, L. MacVinish, L. Galietta and A. Cuthbert, Eur. J. Pharmacol., 2005, 516, 118 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. H. Clark, J. D. McCorvy, J. M. Conley, W. K. Williams, M. Bekkam, V. J. Watts and D. E. Nichols, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2012, 20, 6366 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. N. Carrigan, S. A. Patel, H. D. Cox, E. S. Bolstad, J. M. Gerdes, W. E. Smith, R. J. Bridges and C. M. Thompson, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2014, 24, 850 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Nozulak, J. M. Vigouret, A. L. Jaton, A. Hofmann, A. R. Dravid, H. P. Weber, H. O. Kalkman and M. D. Walkinshaw, J. Med. Chem., 1992, 35, 480 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. D. Abell, K. F. Erhard, H. K. Yen, D. S. Yamashita, M. Brandt, H. Mohammed, M. A. Levy and D. A. Holt, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 1994, 4, 1365 CrossRef CAS.
- J. G. Cannon, K. A. Walker, A. Montanari, J. P. Long and J. R. Flynn, J. Med. Chem., 1990, 33, 2000 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
-
(a) G. Selvi and S. P. Rajendran, Chem.–Asian J., 2004, 16, 1017 CAS;
(b) R. P. Bahuguna and B. C. Joshi, Indian J. Heterocycl. Chem., 1994, 3, 265 CAS.
- R. P. Bahuguna, B. C. Joshi and H. N. Mangal, J. Indian Chem. Soc., 1992, 69, 401 CAS.
- J. Szmuszkovicz, W. H. Darlington and P. F. Von Voigtlander, WO 8804292 A1, 1988Chem. Abstr., 1988, 110, 75335.
- F. S. Mikhailitsyn, N. P. Kozyreva, S. A. Rabinovich, Y. V. Maksakovskaya, I. M. Kulikovskaya, N. R. Dadasheva, M. N. Lebedeva, A. F. Bekhli, N. D. Lychko and N. A. Uvarova, Med. Parazitol. Parazit. Bolezni, 1992, 1, 50 Search PubMed.
-
(a) X.-S. Wang, Q. Li, J.-R. Wu, Y.-L. Li, C.-S. Yao and S.-J. Tu, Synthesis, 2008, 1902 CrossRef CAS;
(b) N. G. Kozlov, R. D. Sauts and K. N. Gusak, Russ. J. Org. Chem., 2000, 36, 531 CAS;
(c) N. G. Kozlov, K. N. Gusak and A. P. Kadutskii, Chem. Heterocycl. Compd., 2010, 46, 505 CrossRef CAS;
(d) K. N. Gusak and N. G. Kozlov, Russ. J. Org. Chem., 2007, 43, 706 CrossRef CAS.
-
(a) P. Langer, Chem.–Eur. J., 2001, 7, 3858 CrossRef CAS;
(b) P. Langer and E. Bellur, J. Org. Chem., 2003, 68, 9742 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. B. Jannet, A. Al Mourabit, A. Gateau-Olesker, C. Marazano and Z. Mighri, Tetrahedron: Asymmetry, 1999, 10, 2381 CrossRef CAS.
-
(a) M. Chen and J. F. Hartwig, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2014, 53, 12172 CrossRef CAS PubMed;
(b) P. B. Thakur, K. Sirisha, A. V. S. Sarma, J. B. Nanubolu and H. M. Meshram, Tetrahedron, 2013, 69, 6415 CrossRef CAS;
(c) M. Lal, R. S. Basha, S. Sarkar and A. T. Khan, Tetrahedron Lett., 2013, 54, 4264 CrossRef CAS;
(d) E. Sotoca, C. Allais, T. Constantieux and J. Rodriguez, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2009, 7, 1911 RSC;
(e) K. Murai, R. Nakatani, Y. Kita and H. Fujioka, Tetrahedron, 2008, 64, 11034 CrossRef CAS;
(f) H. Fujioka, K. Murai, O. Kubo, Y. Ohba and Y. Kita, Org. Lett., 2007, 9, 1687 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Kalinski, M. Umkehrer, L. Weber, J. Kolb, C. Burdack and G. Ross, Mol. Diversity, 2010, 14, 513 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
-
(a) A. Dӧmling, W. Wang and K. Wang, Chem. Rev., 2012, 112, 3083 CrossRef PubMed;
(b) A. Dӧmling, Chem. Rev., 2006, 106, 17 CrossRef PubMed.
- C. M. R. Volla, I. Atodiresei and M. Rueping, Chem. Rev., 2014, 114, 2390 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
-
(a) G. Shen, H. Zhou, P. Du, S. Liu, K. Zou and Y. Uozumi, RSC Adv., 2015, 5, 85646 RSC;
(b) S.-J. Chen, G.-P. Lu and C. Cai, Chem. Commun., 2015, 51, 11512 RSC;
(c) S. N. R. Mule, S. K. Battula, G. Velupula, D. R. Guda and H. B. Bollikolla, RSC Adv., 2014, 4, 58397 RSC;
(d) N. Paul, M. Murugavel, S. Muthusubramanian and D. Sriram, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2012, 22, 1643 CrossRef CAS PubMed;
(e) B. K. Gorityala, S. Cai, J. Ma and X.-W. Liu, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2009, 19, 3093 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. A. Powell and R. A. Batey, Org. Lett., 2002, 4, 2913 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. R. Wallach, P. C. Stege, J. P. Shah and J. D. Chisholm, J. Org. Chem., 2015, 80, 1993 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
-
(a) S. Mekala and R. C. Hahn, J. Org. Chem., 2015, 80, 1610 CrossRef CAS PubMed;
(b) C. Liu, Q. Zhu, K.-W. Huang and Y. Lu, Org. Lett., 2011, 13, 2638 CrossRef CAS PubMed;
(c) C. Liu and Y. Lu, Org. Lett., 2010, 12, 2278 CrossRef CAS PubMed;
(d) W. Zhou, L.-W. Xu, L. Li, L. Yang and C.-G. Xia, Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2006, 23, 5225 CrossRef;
(e) M. Kubryk and K. B. Hansen, Tetrahedron: Asymmetry, 2006, 17, 205 CrossRef CAS.
-
(a) G. R. Pettit, B. R. Moser, D. L. Herald, J. C. Knight, J.-C. Chapuis and X. Zheng, J. Nat. Prod., 2015, 78, 1067 CrossRef CAS PubMed;
(b) Y. Shi and J. G. Pierce, Org. Lett., 2015, 17, 968 CrossRef CAS PubMed;
(c) S. Mondal and K. M. Sureshan, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2014, 12, 7279 RSC;
(d) G. Pattenden, N. J. Ashweek, C. A. G. Baker-Glenn, J. Kempson, G. M. Walker and J. G. K. Yee, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2008, 6, 1478 RSC;
(e) M. Cases, F. G.-L. de Turiso, M. S. Hadjisoteriou and G. Pattenden, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2005, 3, 2786 RSC;
(f) G. Pattenden, M. A. González, P. B. Little, D. S. Millan, A. T. Plowright, J. A. Tornos and T. Ye, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2003, 1, 4173 RSC;
(g) T. B. Lowinger, J. Chu and P. L. Spence, Tetrahedron Lett., 1995, 36, 8383 CrossRef CAS.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: XRD of 4g and copies of 1H & 13C NMR. CCDC 1434638. For ESI and crystallographic data in CIF or other electronic format see DOI: 10.1039/c5ra23413a |
|
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 |