Substituted Co–Cu–Zn nanoferrites: synthesis, fundamental and redox catalytic properties for the degradation of methyl orange†
Abstract
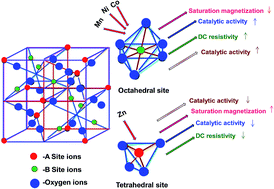
Co0.6Zn0.4Cu0.2MxFe1.8−xO4 (M = Zn2+, Co2+, Ni2+ and Mn3+. x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6 and 0.8) magnetically recyclable catalysts have been synthesized via a sol–gel auto combustion method. The structural and magnetic properties of the prepared samples were investigated using X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy and vibrating sample magnetometry (VSM). The XRD analysis of the synthesized samples confirmed the formation of a single-phase cubic spinel structure and the average crystallite sizes of the nanoparticles estimated using the Debye–Scherrer's equation were found to be 40–60 nm after annealing at 1000 °C (within an error of ±2 nm). The lattice constant increases with an increase in all metal ion substitution. The hysteresis curves of the samples exhibited reduction of the saturation magnetization and coercivity with substitution of all the metal ions in Co–Cu–Zn nano ferrites. The DC electrical resistivity decreased with an increase in temperature, indicating the semiconducting nature of the ferrite samples. Manganese substituted Co–Cu–Zn nanoferrites showed the best catalytic activity among all the magnetic nanoferrites. All the magnetic nanoferrites can be easily recovered by using a magnet and no decrease in the efficiency was observed after several consecutive rounds of reaction.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...