Formulation of pea protein for increased satiety and improved foaming properties†
Abstract
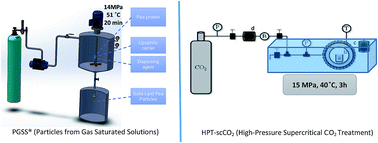
Pea protein has been associated with promoting the satiety effect. One of the issues associated with the incorporation of pea protein in food products is the product homogeneity due to its solubility and dispersibility issues. Within this context, one goal of this study was to exploit the use of supercritical fluid technology to develop Solid Lipid Pea Particle (SLPP) aiming at improving dispersibility in fat-based products. PP was encapsulated by the PGSS® (Particles from Gas Saturated Solutions) technique into glyceryl dipalmitostearate (E471) and olive oil. Different process conditions, namely pressure (7.3–20.7 MPa), temperature (51–75 °C) and equilibrium time (3–37 min) were tested in order to optimize the encapsulation of pea protein via Response Surface Methodology (RSM), following a Central Composite Rotatable Design (CCRD). Results showed that pressure and the interaction between pressure and temperature had a significant impact (p < 0.05) on the protein load and thus on the encapsulation efficiency. The highest encapsulation efficiency (96%) was achieved at 14 MPa, 51 °C and 20 min. Under these conditions, SLPP presented 0.15 mg of protein per mg of particles and 84% of lipase inhibitory activity. When compared with the PP (non-encapsulated), liposoluble pea protein particles contributed to a better product homogenization. The food industry can also take advantage of the ability of pea protein for foam stabilization in aqueous food products. Therefore, PP was treated with high-pressure supercritical CO2 treatment (HPT-scCO2) that has led to improved foaming properties when compared with the non-treated PP.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...