A paper-based lanthanide smart device for acid–base vapour detection, anti-counterfeiting and logic operations†
Abstract
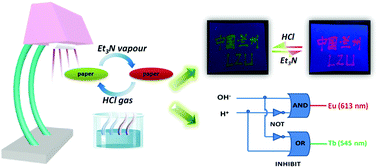
Paper-based devices have attracted extensive attention due to their portability, low-cost, ubiquity, low environmental footprint and ease of operation. In the present study, two lanthanide complexes, namely [Eu(PBA)3(H2O)2] (Eu-PBA) and [Tb(HPBA)2(NO3)3] (Tb-HPBA) were synthesized using an amide-type β-diketone building block, N-(2-pyridinyl)benzoylacetamide (HPBA), which is capable of changing its energy-level to match that of Tb3+ and Eu3+ ions in an acid–base environment. This feature was used for the design and assembly of a simple and cost-effective paper-based lanthanide smart device (abbreviated as Paper-Eu/Tb), which was obtained by impregnating the filter paper with both the Eu-PBA and Tb-HPBA complexes; related homometallic Paper-Eu and Paper-Tb materials were also generated and characterized for comparative purposes. The obtained Paper-Eu/Tb device shows excellent luminescence properties, thus allowing its efficient use as a smart sensor for the naked-eye detection of various acid–base vapours with quick response, good reversibility and selectivity. A similar concept and the resulting paper-based device was also successfully expanded for other applications that include anti-counterfeiting and logic gate systems. Full characterization of the paper-based materials and examples of their use are described.
The present article is a part of an ongoing collaboration between the College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering of Lanzhou University (P.R. China) and Instituto Superior Técnico of University of Lisbon (Portugal). Starting from 2013, this collaboration has been successful in merging the expertise of the Chinese group on novel rare-earth complexes and their smart devices for luminescent probes, tumor marker/treatment, optical anti-counterfeiting, and catalysis with that of the Portuguese group on coordination chemistry, crystal engineering, and catalysis. This Sino-European collaboration has already resulted in the publication of 10 research papers devoted to the design and assembly of various smart nanocomposite materials for applications ranging from cancer therapy and detection of biomarkers to oxidation catalysis and sensing or separation of metal ions.
- This article is part of the themed collections: HOT articles in Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers for 2016 and Sino-European Collaborators

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...