Nanoparticles highly loaded with gentamicin sulfate by a combination of polyhydroxylated macromonomers and ROMP for the synthesis of bioactive biomaterials†
Abstract
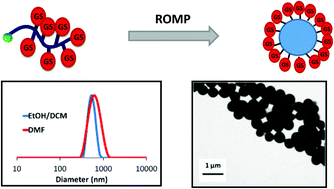
Antibiotic functionalized polymeric nanoparticles (NPs) are obtained by the copolymerization of macromonomers, which is a powerful way to synthesize bioactive biomaterial surfaces able to fight a bacterial strain in the case of infection. The active molecule loading can be modulated/increased by the use of highly charged macromonomers (typically polyhydroxylated macromonomers). This paper presents the synthesis of α-norbornenyl hydroxylated macromonomers (polyglycidol and poly(ethylene oxide)-block-polyglycidol) functionalized with an antibiotic: gentamicin sulfate. Then, these macromonomers are copolymerized with norbornene (Nb) by ring-opening metathesis polymerization in a dispersion to form core–shell NPs which have application as antibiotic platforms for the synthesis of bioactive biomaterial surfaces.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...