Recent advances in organic–inorganic well-defined hybrid polymers using controlled living radical polymerization techniques
Abstract
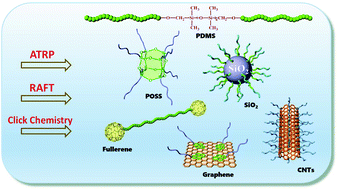
Hybrid organic–inorganic materials comprised of well-defined polymers have been widely recognized for a variety of applications due to their extraordinary properties based on the combination of the different building compositions. During the past decades, many kinds of well-defined hybrid polymers with a variety of architectures have been constructed by polymerization in the presence of inorganic compositions, or by the coupling reaction of functional polymers with inorganic nanoparticles. Thus, techniques could be utilized for the preparation of well-defined organic–inorganic hybrid polymers, including controlled living radical polymerizations (CLRP), such as atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) and reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization. Organic–inorganic hybrid polymers based on polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (POSS), poly(dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS), silica nanoparticles, graphene, carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and fullerene will be discussed in this paper.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...