N-Ester-substituted polyacrylamides with a tunable lower critical solution temperature (LCST): the N-ester-substitute dependent thermoresponse†
Abstract
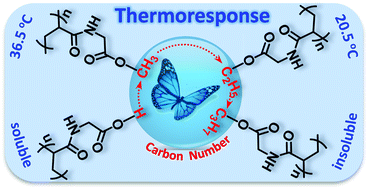
A series of N-ester-substituted polyacrylamides containing different N-ester-substitutes including poly(N-acryloylglycine) (PNAG), poly(N-acryloylglycine methyl ester) (PNAGME), poly(N-acryloylglycine ethyl ester) (PNAGEE) and poly(N-acryloylglycine propyl ester) (PNAGPE) are prepared by RAFT polymerization. The controlled RAFT synthesis of the N-ester-substituted polyacrylamides is achieved at moderate monomer conversion using trithiocarbonate or dithiobenzoate as a RAFT agent. The solution property of the N-ester-substituted polyacrylamides is investigated, and the N-ester-substitute dependent solution property of polyacrylamides is found. That is, with the carbon number in the N-ester-substitutes gradually increasing from 0 to 3, the solution property of the N-ester-substituted polyacrylamides changes greatly. The parameters affecting the lower critical solution temperature (LCST) of PNAGME are investigated, and it is found that the CONHCH2 moiety contributes mainly to the dehydration of PNAGME at temperatures above the LCST. The present study clarifies how the structure of the N-ester-substitutes affects the solution property of N-ester-substituted polyacrylamides.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...