Boron difluoride formazanate copolymers with 9,9-di-n-hexylfluorene prepared by copper-catalyzed alkyne–azide cycloaddition chemistry†
Abstract
The synthesis and characterization of copolymers based on boron difluoride formazanate (BF2L) and 9,9-di-n-hexylfluorene (hex2Fl) units are described. A series of model compounds [(BF2L)-(hex2Fl), (hex2Fl)-(BF2L)-(hex2Fl), and (BF2L)-(hex2Fl)-(BF2L)] were also studied in order to fully understand the spectroscopic properties of the title copolymers [(BF2L)-(hex2Fl)]n. The model compounds and copolymers, which were synthesized by copper catalyzed alkyne–azide cycloaddition chemistry, exhibited high molar absorptivities (25 700–54 900 M−1 cm−1), large Stokes shifts (123–143 nm, 3590–3880 cm−1), and tunable electrochemical behaviour (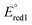 ca. −0.75 V and
ca. −0.75 V and 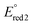 ca. −1.86 V vs. ferrocene/ferrocenium). The low-energy wavelength of maximum absorption and emission of the model compounds red-shifted relative to the BF2L repeating unit by ca. 30 nm per triazole ring formed, to maximum values of 557 nm and 700 nm in DMF, respectively. The low-energy absorption and emission properties of the copolymer were consistent with the model compound bearing two triazole rings [(hex2Fl)-(BF2L)-(hex2Fl)] and were not dependent on copolymer molecular weight. However, the title copolymers may show promise as light-harvesting materials based on their thin-film optical band gap of 1.67 eV.
ca. −1.86 V vs. ferrocene/ferrocenium). The low-energy wavelength of maximum absorption and emission of the model compounds red-shifted relative to the BF2L repeating unit by ca. 30 nm per triazole ring formed, to maximum values of 557 nm and 700 nm in DMF, respectively. The low-energy absorption and emission properties of the copolymer were consistent with the model compound bearing two triazole rings [(hex2Fl)-(BF2L)-(hex2Fl)] and were not dependent on copolymer molecular weight. However, the title copolymers may show promise as light-harvesting materials based on their thin-film optical band gap of 1.67 eV.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...