Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Synthesis of 28a-homoselenolupanes and 28a-homoselenolupane saponins†
Katarzyna
Sidoryk
ab,
Lucie
Rárová
c,
Jana
Oklešťková
d,
Zbigniew
Pakulski
*a,
Miroslav
Strnad
*d,
Piotr
Cmoch
a and
Roman
Luboradzki
e
aInstitute of Organic Chemistry, Polish Academy of Sciences, Kasprzaka 44/52, 01-224 Warsaw, Poland. E-mail: zbigniew.pakulski@icho.edu.pl
bPharmaceutical Research Institute, Rydygiera 8, 01-793 Warsaw, Poland
cDepartment of Chemical Biology and Genetics, Centre of the Region Haná for Biotechnological and Agricultural Research, Palacký University, Šlechtitelů 27, 783 71 Olomouc, Czech Republic
dLaboratory of Growth Regulators, Centre of the Region Haná for Biotechnological and Agricultural Research, Institute of Experimental Botany ASCR & Palacký University, Šlechtitelů 27, 783 71 Olomouc, Czech Republic. E-mail: miroslav.strnad@upol.cz
eInstitute of Physical Chemistry, Polish Academy of Sciences, Kasprzaka 44/52, 01-224 Warsaw, Poland
First published on 7th October 2016
Abstract
A practical synthesis of 28a-homo-28a-selenolupane triterpenes and the corresponding selenosaponins containing D-mannose, L-arabinose, L-rhamnose, and D-idose moieties is described. Selenium containing triterpenes were obtained from the readily available 3-O-allyl-homobetulin mesylate by nucleophilic substitution with the selenocyanate ion which upon reduction of the –SeCN group afforded the free selenol. Glycosylation using classical Schmidt donors gave 1,2-trans selenosaponins as the main product as well as minute amounts of 1,2-cis isomers. This is one of the very few examples of the synthesis of selenoglycosides by direct glycosylation of free selenols. The studied selenol showed high resistance to air oxidation resulting in good stability during the synthesis of selenolupane derivatives. Cytotoxic activities of new homoselenolupane derivatives were also evaluated in vitro and revealed that some triterpenes exhibited an interesting profile against human cancer cell lines.
Introduction
In the last few decades, the application of organoselenium compounds,1 including steroid derivatives,2 in cancer prevention and treatment became an objective of investigations of many scientific groups. These studies show that organoselenium compounds display a high cytotoxic activity against different cancer cell lines. Moreover, in some cases a positive effect on the cytotoxic properties was achieved by replacing the sulphur atom with selenium without modifying the basic structure of the compound.3 Additionally, some heterocycles containing selenium possess an interesting anti-inflammatory activity profile with a significant analgesic effect.4 Furthermore, many organoselenium derivatives demonstrate antimicrobial, antiviral and antifungal activities.5Previously, we reported the structure–activity relationships of the cytotoxic activity of ichopanol (28a-homobetulin) and ichopanothiol (28a-homothiobetulin) derivatives and saponins based on a homobetulin scaffold. We found, that the heteroatom (oxygen or sulphur) located on the C-17 side-chain is necessary for the anticancer activity of the studied compounds.6–8 Based on the high biological activity of selenium derivatives, we reasoned that replacing these heteroatoms on the C-17 side-chain of the lupane core with selenium could enhance their anticancer effect. These results will broaden our knowledge regarding the synthesis, reactivity and stability of selenium-containing triterpenes and steroids as they are virtually unknown in the literature.2,9 Herein, we report the first synthesis of homobetulin and homobetulin based saponins bearing a selenium atom. Furthermore, cytotoxic activities of all new derivatives were investigated.
Results and discussion
Mesylate 1, readily prepared via the reaction of 3-O-allyl-ichopanol and mesyl chloride,8 was used for the synthesis of selenolupane triterpenes. Standard synthesis of selenocyanate 3 involves the nucleophilic replacement of sulfonyl ester with potassium selenocyanate. Our first attempt using acetone as a solvent failed giving only selenide 2. However, changing the solvent from acetone to DMF resulted in the formation of the desired product 3 in 87% yield; a small amount of by-product selenol 4 (7%) was also isolated. Reduction of 3 with LiAlH4 gave the corresponding selenol 4 in 93% yield. Compound 5, needed for SAR studies, was prepared in 69% yield from allyl ether 3 by treatment with palladium(II) chloride (Scheme 1).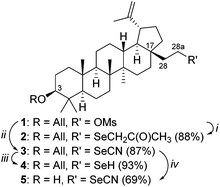 | ||
| Scheme 1 Reagents and conditions: (i) KSeCN (5 equiv.), acetone, 60 °C; (ii) KSeCN (5 equiv.), DMF, 60 °C; (iii) LiAlH4 (2 equiv.), THF; (iv) PdCl2, CH3OH, CH2Cl2. | ||
Synthesis of selenoglycosides by direct glycosylation of selenols is rarely found in the literature. Due to high susceptibility of selenols to oxidation the introduction of selenium at the anomeric position of a monosaccharide is achieved by the treatment of the sugar component with alkyl or aryl selenolates usually generated in situ from the corresponding diselenides in the presence of a reducing agent.10 Free selenols were used occasionally to react with anomeric halogenides,11 acetates,11b,12 orthoesters,13 or Schmidt donors.11a,14
For the synthesis of lupane-type selenoglycosides we chose the Schmidt methodology. TMSOTf promoted glycosylation was carried out by the treatment of selenol 4 with perbenzoylated glycosyl trichloroacetimidates 6,157,168,16 and 9,17 which gave the desired selenoglycosides in 29–51% yield. A significant amount of unreacted starting selenol 4 was also recovered (13–40%). Although yields were rather moderate, further manipulation of the reaction conditions did not improve the yields of the selenoglycosides. As expected, the presence of the benzoyl protecting groups in the donor molecules directed the anomeric selectivity of glycosylation.18 Regioselectivity was, however, slightly lower than that in the case of the corresponding sulfur analogues.8 With the exception of α-D-mannopyranoside 10, mixtures of α and β anomers 11–16 of L-arabino, L-rhamno, and D-ido derivatives were obtained as specified in Scheme 2.
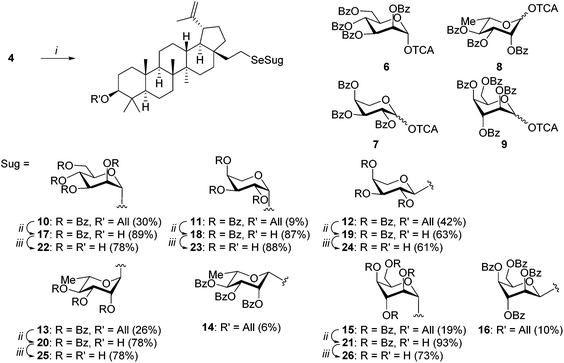 | ||
| Scheme 2 Reagents and conditions: (i) 6–9, CH2Cl2, TMSOTf, −40 °C; (ii) (a) [Ir(COD)(PMePh2)]PF6, H2, THF; (b) p-TsOH, CHCl3, CH3OH; (iii) K2CO3, CH3OH. | ||
Selenols are considered highly susceptible to air oxidation leading to diselenides, however, selenol 4 was relatively resistant to oxidation. Recovered selenol 4 was reused for glycosylation without any significant decrease in the reaction yields. It must be noted, however, that prolonged storage slowly decreased its reactivity, although the physicochemical properties of 4 did not change. Considering the above observations which are crucial criteria in the synthesis of selenolupane derivatives, a study examining the stability of selenol 4 was undertaken. First, the independent synthesis of diselenide 27, the expected product of the air oxidation of 4, was conducted. The homogeneous product was prepared by the reaction of mesylate 1 with dilithium diselenide (Li2Se2)19 affording compound 27 in 88% yield (Scheme 3). The same compound containing inseparable unknown byproducts, may also be obtained by the oxidation of selenol 4 with hydrogen peroxide in the presence of NaOH (79%) and from the equimolar mixture of selenocyanide 3 and selenol 4 in the presence of a base (94%) according to Krief's method.20 Surprisingly, in all cases, the physichochemical properties of 27, including 77Se NMR, were identical as found for selenol 4 but differences in reactivity were observed. In contrast to compound 4, compound 27 did not react with Schmidt donors. On the other hand, both derivatives were alkylated by treatment with methyl iodide to afford selenide 28. However, in the case of the reaction of compound 27 with methyl iodide a longer reaction time was required (5 days, 70%), whereas the alkylation of freshly prepared selenol 4 in the presence of sodium hydride was complete within a few hours giving compound 28 in 74% yield (Scheme 3).
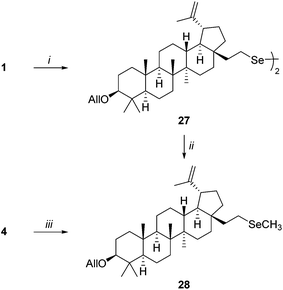 | ||
| Scheme 3 Reagents and conditions: (i) Se, Super Hydride, THF, 88%; (ii) NaH, CH3I, THF, rt, 5 days, 70%; (iii) NaH, CH3I, THF, rt, 12 h, 74%. | ||
There are two possible explanations for such unusual behaviour. The first is that both compounds (4 and 27) have identical spectroscopic properties but they are different compounds. This speculation may be supported by the result of alkylation described above. In the first case (considering diselenide 27) sodium hydride acting first as a reducing agent (breaking Se–Se bond) and then as a base was required for alkylation.21 It significantly prolonged the reaction time. On the other hand, when the formation of the Se–Se bond was not possible due to high steric hindrance, selenol was formed in both cases. However, reaction conditions and/or long storage time promoted the aggregation of selenol and the formation of relatively unreactive polymeric forms which caused a decrease in reactivity. Similar aggregation of betulin derivatives was described in the literature.22
Attempts to remove the allyl block from 3-O-allylselenosaponins with palladium(II) chloride were unsuccessful and caused decomposition of the starting materials. Therefore, deallylation was performed under neutral conditions by isomerisation of the allyl double bond in the presence of the hydrogen activated iridium complex [Ir(COD)(PMePh2)]PF6 followed by hydrolysis of 1-propenyl ether in the presence of p-TsOH.17 Deallylated saponins 17–21 were obtained in high yields (78–93%) with the exception of 19 which was isolated in slightly lower yield (63%). Debenzoylation with potassium carbonate in methanol gave free saponins 22–26 in good yields (61–88%, Scheme 2).
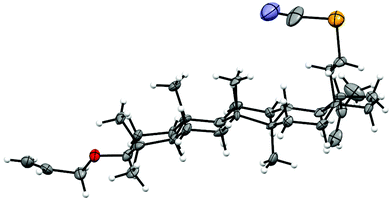
Structures of all new compounds were confirmed by extended 1D and 2D NMR experiments, as well as elemental analysis and mass spectroscopy. Stereochemistry at the anomeric center was proven by measuring 1JC1,H1 coupling constants. Observed 1JC1,H1 coupling constants for 11 (170.4 Hz), 13 (171.0 Hz), and 15 (168.0 Hz) proved the equatorial position of the anomeric proton, whereas 1JC1,H1 measured for 12 (158.0 Hz), 14 (153.0 Hz), and 16 (154.0 Hz) indicated the presence of axially oriented anomeric protons.23 In the case of rhamnosides 13 and 14 (6-deoxy-hexopyranosides) the configuration at the anomeric carbon atom was additionally confirmed by the almost forgotten Sinclair–Sleeter rule.24 The signal for the H-6 protons of 13 in which aglycon is in the axial position was observed upfield (1.39 ppm) in comparison with its epimer in which the signal for the H-6 protons appeared downfield (1.46 ppm). In addition, the structure of 3β-O-allyl-28a-selenocyanato-28a-homolup-20(29)-ene (3) was unequivocally confirmed by X-ray analysis (Fig. 1).
Antiproliferative activities of the studied derivatives of homobetulin were tested in vitro. Activity against normal human BJ fibroblasts was compared with cytotoxicity on cancer cell lines of various histopathological origins, including T-lymphoblastic leukaemia (CEM), breast adenocarcinoma (MCF7), malignant melanoma (G-361) and cervical carcinoma (HeLa) lines. The cells of all these lines were exposed to six serial 3-fold dilutions of each drug for 72 h, the proportions of surviving cells were then estimated and IC50 values (50% inhibitory concentrations) were calculated. A detailed procedure for the cytotoxicity assay was described previously.7 The results obtained from Calcein AM assays are presented in Table 1.
| Comp. no. | IC50 [μM] | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | R′ | CEM | MCF7 | HeLa | G-361 | BJ | |
| 2 | All | SeCH2COCH3 | >50 | >50 | >50 | >50 | >50 |
| 5 | H | SeCN | 2.0 ± 0.6 | 5.2 ± 1.4 | 3.4 ± 0.6 | 3.8 ± 0.8 | 3.7 ± 0.8 |
29![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 8 8 |
H | SCN | 4.4 ± 1.8 | 13.6 ± 4.8 | 6.7 ± 0.0 | 3.0 ± 0.1 | 4.6 ± 0.5 |
30![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 7 7 |
H | OH | 15.3 ± 1.4 | >50 | >50 | 10.2 ± 0.9 | >50 |
| 22 | H | Se-α-D-Manp | >50 | 46.4 ± 5.2 | >50 | >50 | >50 |
| 23 | H | Se-β-L-Arap | >50 | >50 | >50 | >50 | >50 |
| 24 | H | Se-α-L-Arap | >50 | >50 | >50 | >50 | >50 |
| 25 | H | Se-α-L-Rhap | 32.5 ± 4.4 | 45.4 ± 3.0 | 42.3 ± 0.0 | 41.0 ± 2.5 | 46.9 ± 0.1 |
| 26 | H | Se-α-D-Idop | >50 | >50 | >50 | >50 | >50 |
| Betulinic acid | — | — | 40.0 ± 2.8 | >50 | 47.6 ± 1.9 | >50 | >50 |
Selenosaponins were practically inactive, except L-rhamnoside 25 which showed low activity (IC50 32.5–45.4 μM). Similar results were obtained for oxygen7 and sulphur analogs8 which suggest that homobetulin saponins do not affect the growth of the cancer lines. Compound 30 was selective against malignant melanoma and leukemia cell lines (IC50 10.2 or 15.3 μM) without affecting the growth of normal human fibroblasts and other cancer cells which suggested a high therapeutic index. By comparison, selenocyanate 5 showed the highest cytotoxic activity of all compounds tested (IC50 2.0–5.2 μM). Its cytotoxicity was also higher than that measured for the appropriate sulphur analogue 29, and much higher than those observed for ichopanol (30). Sulphur analogue 29 showed an interesting profile as much more higher activity was determined for G-361 melanoma cells than for other cancer cell lines and fibroblasts. Both compounds, however, exhibit a relatively low therapeutic index.
Conclusions
In conclusion, a series of 28a-homo-28a-selenolupane triterpenes and the corresponding homoselenosaponins bearing D-mannose, L-arabinose, L-rhamnose, and D-idose moieties were synthesised. Required selenol was obtained by a nucleophilic substitution of the corresponding mesylate with potassium selenocyanate followed by the reduction of the –SeCN group. Its unusual stability to air oxidation was discussed. Further glycosylation of selenol with Schmidt donors under the standard conditions followed by deprotection afforded homoselenosaponins. All new compounds were evaluated for their cytotoxic activities towards normal and cancer cell lines. Homobetulin selenocyanate was the most cytotoxic compound, whereas the corresponding saponins were mostly inactive. To our best knowledge this is the first synthesis of lupane-type triterpenes containing selenium as the core component.Experimental section
General procedures
Silica gel HF254 and silica gel 230–400 mesh (E. Merck) were used for TLC and column chromatography, respectively. 1H, 13C and 77Se NMR spectra were recorded at 298 K with a Varian NMR-vnmrs600 or vnmrs500 spectrometer, using standard experimental conditions and Varian software (ChemPack 4.1). Configurational assignments were based on the NMR measurements, generated using two-dimensional techniques like COSY and 1H–13C gradient selected HSQC (g-HSQC), as well as 1H–13C gradient selected HMBC (g-HMBC). TMS was used as the internal standard for determining 1H and 13C NMR chemical shifts. J values are given in hertz. High-resolution mass spectra (HRMS-ESI) were acquired with Mariner and MaldiSYNAPT G2-S HDMS (Waters) mass spectrometers. Optical rotations were measured with a Jasco P-2000 automatic polarimeter. IR spectra were recorded on a Jasco 6200 FT-IR spectrophotometer.Single crystal X-ray diffraction measurements were carried out on an Agilent Supernova diffractometer, at 100 K with monochromated Cu Kα radiation (1.54184 Å). The data reduction was made by using CrysAlisPRO software.25 The structures were solved by direct methods and refined on F2 by full-matrix least-squares by using SHELXS97 and SHELXL97.26 All non-hydrogen atoms were refined anisotropically while hydrogen atoms were placed in calculated positions, and refined in riding mode. Crystals of 3 suitable for X-ray analysis were obtained by cooling of a hot methanol solution: monoclinic, P21, a = 13.729(2), b = 8.3619(9), c = 14.594(3) Å, β = 114.96(2), V = 1518.9(5) Å3, Z = 2, Dcalc = 1.279 g cm−1, μ = 1.864 mm−1, R1 = 0.0894 for 2177 [Fo > 4σ(Fo)] and 0.1157 for all data, wR2 = 0.2644, S = 1.046. Crystallographic data for the structure have been deposited with the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre as supplementary material (deposition numbers: CCDC 1422676).
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 → 10
1 → 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) gave 2 as a white solid (45 mg, 88%). M.p. 166–167 °C; [α]20D 14.2 (c 0.3, chloroform); νmax (film): 2942, 2868, 1700, 1641, 1455, 1230, 1072, 757 cm−1. 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ: 5.90–5.96 (m, CH
1) gave 2 as a white solid (45 mg, 88%). M.p. 166–167 °C; [α]20D 14.2 (c 0.3, chloroform); νmax (film): 2942, 2868, 1700, 1641, 1455, 1230, 1072, 757 cm−1. 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ: 5.90–5.96 (m, CH![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) ), 5.24–5.27 (m,
), 5.24–5.27 (m, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 5.11–5.13 (m,
CH2), 5.11–5.13 (m, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 4.68 (H-29), 4.57 (H-29), 4.10–4.13 (m, OCH2), 3.87–3.90 (m, OCH2), 3.23 (m, SeCH2COCH3), 2.80 (dd, J 4.1, 11.7 Hz, H-3), 2.52 (H-28a), 2.42 (H-28a), 2.40 (H-19), 2.35 (s, SeCH2COCH3), 1.92 (H-21), 1.85 (H-28), 1.76 (H-13), 1.71 (H-2), 1.71 (H-16), 1.68 (H-1), 1.68 (s, H-30), 1.64 (H-12), 1.64 (H-22), 1.59 (H-15), 1.50 (H-6), 1.48 (H-18), 1.47 (H-2), 1.42 (H-11), 1.38 (H-6), 1.38 (H-7), 1.35 (H-21), 1.30 (H-28), 1.26 (H-9), 1.24 (H-11), 1.17 (H-16), 1.06 (H-12), 1.05 (s, H-26), 1.01 (H-15), 1.00 (H-22), 0.95 (s, H-23), 0.95 (s, H-27), 0.83 (s, H-25), 0.82 (H-1), 0.78 (s, H-24), 0.67 (H-5). 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 203.5 (SeCH2COCH3), 150.6 (C-20), 135.9 (CH
CH2), 4.68 (H-29), 4.57 (H-29), 4.10–4.13 (m, OCH2), 3.87–3.90 (m, OCH2), 3.23 (m, SeCH2COCH3), 2.80 (dd, J 4.1, 11.7 Hz, H-3), 2.52 (H-28a), 2.42 (H-28a), 2.40 (H-19), 2.35 (s, SeCH2COCH3), 1.92 (H-21), 1.85 (H-28), 1.76 (H-13), 1.71 (H-2), 1.71 (H-16), 1.68 (H-1), 1.68 (s, H-30), 1.64 (H-12), 1.64 (H-22), 1.59 (H-15), 1.50 (H-6), 1.48 (H-18), 1.47 (H-2), 1.42 (H-11), 1.38 (H-6), 1.38 (H-7), 1.35 (H-21), 1.30 (H-28), 1.26 (H-9), 1.24 (H-11), 1.17 (H-16), 1.06 (H-12), 1.05 (s, H-26), 1.01 (H-15), 1.00 (H-22), 0.95 (s, H-23), 0.95 (s, H-27), 0.83 (s, H-25), 0.82 (H-1), 0.78 (s, H-24), 0.67 (H-5). 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 203.5 (SeCH2COCH3), 150.6 (C-20), 135.9 (CH![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) ), 115.9 (
), 115.9 (![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 109.5 (C-29), 86.3 (C-3), 70.6 (OCH2), 55.8 (C-5), 50.4 (C-9), 49.9 (C-18), 47.2 (C-19), 46.8 (C-17), 42.5 (C-14), 40.4 (C-8), 38.8 (C-4), 38.6 (C-1), 37.1 (C-10), 37.1 (C-13), 35.4 (C-22), 34.2 (C-7), 31.6 (SeCH2COCH3), 30.7 (C-16), 29.9 (C-21), 28.4 (C-28), 28.1 (C-23), 27.4 (SeCH2COCH3), 27.1 (C-15), 24.9 (C-12), 23.1 (C-2), 20.8 (C-11), 20.1 (C-28a), 19.3 (C-30), 18.2 (C-6), 16.3 (C-24), 16.1 (C-25), 16.0 (C-26), 14.8 (C-27). 77Se NMR (CDCl3, 114.4 MHz) δ: 209.8. HR-MS (ESI) calc. for C37H61O2Se [M + H]+: 616.3759. Found: 616.3758. Anal. Calcd for C37H60O2Se (615.85): C, 72.16; H, 9.82. Found: C 71.90; H 10.25.
CH2), 109.5 (C-29), 86.3 (C-3), 70.6 (OCH2), 55.8 (C-5), 50.4 (C-9), 49.9 (C-18), 47.2 (C-19), 46.8 (C-17), 42.5 (C-14), 40.4 (C-8), 38.8 (C-4), 38.6 (C-1), 37.1 (C-10), 37.1 (C-13), 35.4 (C-22), 34.2 (C-7), 31.6 (SeCH2COCH3), 30.7 (C-16), 29.9 (C-21), 28.4 (C-28), 28.1 (C-23), 27.4 (SeCH2COCH3), 27.1 (C-15), 24.9 (C-12), 23.1 (C-2), 20.8 (C-11), 20.1 (C-28a), 19.3 (C-30), 18.2 (C-6), 16.3 (C-24), 16.1 (C-25), 16.0 (C-26), 14.8 (C-27). 77Se NMR (CDCl3, 114.4 MHz) δ: 209.8. HR-MS (ESI) calc. for C37H61O2Se [M + H]+: 616.3759. Found: 616.3758. Anal. Calcd for C37H60O2Se (615.85): C, 72.16; H, 9.82. Found: C 71.90; H 10.25.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 → 20
1 → 20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) gave selenol 4 (63 mg, 7%) as a side product and selenocyanate 3 as a cream-white solid (872 mg, 87%). M.p. 178–179 °C; [α]20D 7.9 (c 0.2, chloroform); νmax (film): 2943, 2869, 2150 (SeCN), 1641, 1456, 1376, 1070, 883, 756, 548 cm−1. 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ: 5.90–5.96 (m, CH
1) gave selenol 4 (63 mg, 7%) as a side product and selenocyanate 3 as a cream-white solid (872 mg, 87%). M.p. 178–179 °C; [α]20D 7.9 (c 0.2, chloroform); νmax (film): 2943, 2869, 2150 (SeCN), 1641, 1456, 1376, 1070, 883, 756, 548 cm−1. 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ: 5.90–5.96 (m, CH![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) ), 5.24–5.27 (m,
), 5.24–5.27 (m, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 5.11–5.13 (m,
CH2), 5.11–5.13 (m, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 4.70 (H-29), 4.60 (H-29), 4.10–4.13 (m, OCH2), 3.87–3.90 (m, OCH2), 3.03 (H-28a), 2.88 (H-28a), 2.79 (dd, J 4.2, 11.7 Hz, H-3), 2.43 (H-19), 2.12 (H-28), 1.92 (H-21), 1.78 (H-13), 1.72 (H-2), 1.68 (H-1), 1.68 (H-16), 1.68 (s, H-30), 1.65 (H-12), 1.60 (H-22), 1.59 (H-15), 1.59 (H-28), 1.52 (H-18), 1.50 (H-6), 1.48 (H-2), 1.42 (H-11), 1.40 (H-6), 1.40 (H-21), 1.38 (H-7), 1.26 (H-9), 1.26 (H-16), 1.24 (H-11), 1.08 (H-22), 1.07 (s, H-26), 1.06 (H-12), 1.05 (H-15), 0.96 (s, H-27), 0.95 (s, H-23), 0.84 (s, H-25), 0.82 (H-1), 0.78 (s, H-24), 0.67 (H-5). 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 150.0 (C-20), 135.9 (CH
CH2), 4.70 (H-29), 4.60 (H-29), 4.10–4.13 (m, OCH2), 3.87–3.90 (m, OCH2), 3.03 (H-28a), 2.88 (H-28a), 2.79 (dd, J 4.2, 11.7 Hz, H-3), 2.43 (H-19), 2.12 (H-28), 1.92 (H-21), 1.78 (H-13), 1.72 (H-2), 1.68 (H-1), 1.68 (H-16), 1.68 (s, H-30), 1.65 (H-12), 1.60 (H-22), 1.59 (H-15), 1.59 (H-28), 1.52 (H-18), 1.50 (H-6), 1.48 (H-2), 1.42 (H-11), 1.40 (H-6), 1.40 (H-21), 1.38 (H-7), 1.26 (H-9), 1.26 (H-16), 1.24 (H-11), 1.08 (H-22), 1.07 (s, H-26), 1.06 (H-12), 1.05 (H-15), 0.96 (s, H-27), 0.95 (s, H-23), 0.84 (s, H-25), 0.82 (H-1), 0.78 (s, H-24), 0.67 (H-5). 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 150.0 (C-20), 135.9 (CH![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) ), 115.9 (
), 115.9 (![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 109.9 (C-29), 101.5 (SeCN), 86.3 (C-3), 70.6 (OCH2), 55.8 (C-5), 50.4 (C-9), 50.0 (C-18), 47.1 (C-17), 47.0 (C-19), 42.5 (C-14), 40.9 (C-8), 38.8 (C-4), 38.6 (C-1), 37.1 (C-10), 37.1 (C-13), 35.2 (C-22), 34.2 (C-7), 30.6 (C-16), 29.7 (C-21), 30.1 (C-28), 28.1 (C-23), 27.1 (C-15), 25.5 (C-28a), 25.1 (C-12), 23.1 (C-2), 20.8 (C-11), 19.3 (C-30), 18.2 (C-6), 16.3 (C-24), 16.1 (C-25), 16.0 (C-26), 14.8 (C-27). 77Se NMR (CDCl3, 114.4 MHz) δ: 232.1. HR-MS (ESI) calc. for C35H56NOSe [M + H]+: 585.3449. Found: 585.3450. Anal. Calcd for C35H55NOSe (584.79): C, 71.89; H, 9.48; N, 2.40. Found: C, 71.80; H, 9.45; N, 2.39.
CH2), 109.9 (C-29), 101.5 (SeCN), 86.3 (C-3), 70.6 (OCH2), 55.8 (C-5), 50.4 (C-9), 50.0 (C-18), 47.1 (C-17), 47.0 (C-19), 42.5 (C-14), 40.9 (C-8), 38.8 (C-4), 38.6 (C-1), 37.1 (C-10), 37.1 (C-13), 35.2 (C-22), 34.2 (C-7), 30.6 (C-16), 29.7 (C-21), 30.1 (C-28), 28.1 (C-23), 27.1 (C-15), 25.5 (C-28a), 25.1 (C-12), 23.1 (C-2), 20.8 (C-11), 19.3 (C-30), 18.2 (C-6), 16.3 (C-24), 16.1 (C-25), 16.0 (C-26), 14.8 (C-27). 77Se NMR (CDCl3, 114.4 MHz) δ: 232.1. HR-MS (ESI) calc. for C35H56NOSe [M + H]+: 585.3449. Found: 585.3450. Anal. Calcd for C35H55NOSe (584.79): C, 71.89; H, 9.48; N, 2.40. Found: C, 71.80; H, 9.45; N, 2.39.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) afforded 302 mg (93%) of the title compound as a light yellow powder. M.p. 210–213 °C; [α]20D 41.6 (c 0.2, chloroform); νmax (film): 3072, 2943, 2868, 1642, 1456, 1376, 1216, 1135, 1106, 1086, 1071, 920, 883, 758 (s) cm−1. 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ: 5.90–5.96 (m, CH
1) afforded 302 mg (93%) of the title compound as a light yellow powder. M.p. 210–213 °C; [α]20D 41.6 (c 0.2, chloroform); νmax (film): 3072, 2943, 2868, 1642, 1456, 1376, 1216, 1135, 1106, 1086, 1071, 920, 883, 758 (s) cm−1. 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ: 5.90–5.96 (m, CH![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) ), 5.24–5.27 (m,
), 5.24–5.27 (m, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 5.11–5.13 (m,
CH2), 5.11–5.13 (m, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 4.68 (H-29), 4.58 (H-29), 4.10–4.13 (m, OCH2), 3.87–3.90 (m, OCH2), 2.88 (H-28a), 2.79 (dd, J 4.1, 11.7 Hz, H-3), 2.72 (H-28a), 2.42 (H-19), 2.00 (H-28), 1.92 (H-21), 1.81 (H-13), 1.71 (H-2), 1.70 (H-16), 1.69 (s, H-30), 1.68 (H-1), 1.64 (H-15), 1.64 (H-22), 1.60 (H-28), 1.51 (H-6), 1.49 (H-18), 1.47 (H-2), 1.39 (H-6), 1.36 (H-21), 1.35 (H-7), 1.26 (H-9), 1.21 (H-16), 1.08 (s, H-26), 1.03 (H-22), 1.01 (H-15), 0.97 (s, H-27), 0.96 (s, H-23), 0.85 (s, H-25), 0.83 (H-1), 0.79 (s, H-24), 0.68 (H-5). 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 150.6 (C-20), 109.6 (C-29), 86.3 (C-3), 55.8 (C-5), 50.5 (C-9), 49.9 (C-18), 47.3 (C-19), 46.8 (C-17), 42.5 (C-14), 41.0 (C-8), 38.8 (C-4), 38.6 (C-1), 37.2 (C-13), 37.1 (C-10), 35.6 (C-22), 34.3 (C-7), 30.7 (C-16), 30.2 (C-28), 30.0 (C-21), 28.1 (C-23), 27.2 (C-15), 25.2 (C-11 or 12), 24.9 (C-28a), 23.1 (C-2), 21.0 (C-11 or 12), 19.3 (C-30), 18.3 (C-6), 16.3 (C-24), 16.2 (C-25), 16.2 (C-26), 14.9 (C-27). 77Se NMR (CDCl3, 114.4 MHz) δ: 325.6. HR-MS (ESI) calc. for C34H56OSe [M]+: 560.3496. Found: 560.3511. Anal. Calcd for C34H56OSe (559.78): C, 72.95; H, 10.08. Found: C, 73.50; H, 10.48.
CH2), 4.68 (H-29), 4.58 (H-29), 4.10–4.13 (m, OCH2), 3.87–3.90 (m, OCH2), 2.88 (H-28a), 2.79 (dd, J 4.1, 11.7 Hz, H-3), 2.72 (H-28a), 2.42 (H-19), 2.00 (H-28), 1.92 (H-21), 1.81 (H-13), 1.71 (H-2), 1.70 (H-16), 1.69 (s, H-30), 1.68 (H-1), 1.64 (H-15), 1.64 (H-22), 1.60 (H-28), 1.51 (H-6), 1.49 (H-18), 1.47 (H-2), 1.39 (H-6), 1.36 (H-21), 1.35 (H-7), 1.26 (H-9), 1.21 (H-16), 1.08 (s, H-26), 1.03 (H-22), 1.01 (H-15), 0.97 (s, H-27), 0.96 (s, H-23), 0.85 (s, H-25), 0.83 (H-1), 0.79 (s, H-24), 0.68 (H-5). 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 150.6 (C-20), 109.6 (C-29), 86.3 (C-3), 55.8 (C-5), 50.5 (C-9), 49.9 (C-18), 47.3 (C-19), 46.8 (C-17), 42.5 (C-14), 41.0 (C-8), 38.8 (C-4), 38.6 (C-1), 37.2 (C-13), 37.1 (C-10), 35.6 (C-22), 34.3 (C-7), 30.7 (C-16), 30.2 (C-28), 30.0 (C-21), 28.1 (C-23), 27.2 (C-15), 25.2 (C-11 or 12), 24.9 (C-28a), 23.1 (C-2), 21.0 (C-11 or 12), 19.3 (C-30), 18.3 (C-6), 16.3 (C-24), 16.2 (C-25), 16.2 (C-26), 14.9 (C-27). 77Se NMR (CDCl3, 114.4 MHz) δ: 325.6. HR-MS (ESI) calc. for C34H56OSe [M]+: 560.3496. Found: 560.3511. Anal. Calcd for C34H56OSe (559.78): C, 72.95; H, 10.08. Found: C, 73.50; H, 10.48.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 → 7
1 → 7![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3) gave the title compound as a white solid (49 mg, 69%). M.p. 232–236 °C; [α]20D –3.2 (c 0.1, chloroform). νmax (film): 2943, 2870, 2148 (SeCN), 1455, 1377, 1043, 1033, 882, 757, 547, 521 cm−1. 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ: 4.71 (H-29), 4.60 (H-29), 3.18 (dd, J 4.8, 11.5 Hz, H-3), 3.04 (H-28a), 2.88 (H-28a), 2.43 (H-19), 2.14 (H-28), 1.92 (H-21), 1.79 (H-13), 1.68 (H-16), 1.68 (s, H-30), 1.67 (H-1), 1.66 (H-12), 1.60 (H-2), 1.60 (H-15), 1.60 (H-22), 1.60 (H-28), 1.56 (H-2), 1.52 (H-6), 1.52 (H-18), 1.43 (H-11), 1.41 (H-6), 1.40 (H-21), 1.39 (H-7), 1.27 (H-9), 1.26 (H-16), 1.24 (H-11), 1.08 (H-22), 1.07 (H-12), 1.07 (s, H-26), 1.06 (H-15), 0.97 (s, H-27), 0.96 (s, H-23), 0.90 (H-1), 0.83 (s, H-25), 0.76 (s, H-24), 0.68 (H-5). 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 150.0 (C-20), 109.9 (C-29), 101.5 (SeCN), 79.0 (C-3), 55.3 (C-5), 50.4 (C-9), 50.0 (C-18), 47.2 (C-17), 47.1 (C-19), 42.5 (C-14), 40.9 (C-8), 38.8 (C-4), 38.7 (C-1), 37.2 (C-10), 37.1 (C-13), 35.3 (C-22), 34.2 (C-7), 30.6 (C-16), 30.1 (C-28), 29.7 (C-21), 27.9 (C-23), 27.2 (C-15), 25.5 (C-28a), 25.1 (C-12), 27.4 (C-2), 20.8 (C-11), 19.3 (C-30), 18.3 (C-6), 16.1 (C-25), 16.0 (C-26), 15.3 (C-24), 14.9 (C-27). 77Se NMR (CDCl3, 114.4 MHz) δ: 232.4. HR-MS (ESI) calc. for C32H51NNaOSe [M + Na]+: 568.3034. Found: 568.3029.
3) gave the title compound as a white solid (49 mg, 69%). M.p. 232–236 °C; [α]20D –3.2 (c 0.1, chloroform). νmax (film): 2943, 2870, 2148 (SeCN), 1455, 1377, 1043, 1033, 882, 757, 547, 521 cm−1. 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ: 4.71 (H-29), 4.60 (H-29), 3.18 (dd, J 4.8, 11.5 Hz, H-3), 3.04 (H-28a), 2.88 (H-28a), 2.43 (H-19), 2.14 (H-28), 1.92 (H-21), 1.79 (H-13), 1.68 (H-16), 1.68 (s, H-30), 1.67 (H-1), 1.66 (H-12), 1.60 (H-2), 1.60 (H-15), 1.60 (H-22), 1.60 (H-28), 1.56 (H-2), 1.52 (H-6), 1.52 (H-18), 1.43 (H-11), 1.41 (H-6), 1.40 (H-21), 1.39 (H-7), 1.27 (H-9), 1.26 (H-16), 1.24 (H-11), 1.08 (H-22), 1.07 (H-12), 1.07 (s, H-26), 1.06 (H-15), 0.97 (s, H-27), 0.96 (s, H-23), 0.90 (H-1), 0.83 (s, H-25), 0.76 (s, H-24), 0.68 (H-5). 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 150.0 (C-20), 109.9 (C-29), 101.5 (SeCN), 79.0 (C-3), 55.3 (C-5), 50.4 (C-9), 50.0 (C-18), 47.2 (C-17), 47.1 (C-19), 42.5 (C-14), 40.9 (C-8), 38.8 (C-4), 38.7 (C-1), 37.2 (C-10), 37.1 (C-13), 35.3 (C-22), 34.2 (C-7), 30.6 (C-16), 30.1 (C-28), 29.7 (C-21), 27.9 (C-23), 27.2 (C-15), 25.5 (C-28a), 25.1 (C-12), 27.4 (C-2), 20.8 (C-11), 19.3 (C-30), 18.3 (C-6), 16.1 (C-25), 16.0 (C-26), 15.3 (C-24), 14.9 (C-27). 77Se NMR (CDCl3, 114.4 MHz) δ: 232.4. HR-MS (ESI) calc. for C32H51NNaOSe [M + Na]+: 568.3034. Found: 568.3029.
General procedure for glycosylation
A solution of glycosyl donor (6–9, 1.00 mmol) and selenol 4 (280 mg, 0.5 mmol) in DCM (10 mL) was stirred for 20 min at room temperature over molecular sieves (4 Å, 400 mg, finely ground), then cooled to −40 °C and TMSOTf (76 μL, 0.42 mmol) was added. After 60 min the reaction was quenched with Et3N (1 mL), and the solvents were removed under diminished pressure. Column chromatography (hexane–ethyl acetate, 40![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 → 5
1 → 5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) of the residue gave the protected saponins as white foams.
1) of the residue gave the protected saponins as white foams.
![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) ), 5.95 (br s, H-1′), 5.89 (H-3′), 5.87 (d, J 3.3 Hz, H-2′), 5.24–5.27 (m,
), 5.95 (br s, H-1′), 5.89 (H-3′), 5.87 (d, J 3.3 Hz, H-2′), 5.24–5.27 (m, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 5.11–5.13 (m,
CH2), 5.11–5.13 (m, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 4.76 (H-5′), 4.68 (H-29), 4.64 (dd, J 2.5, 12.3 Hz, H-6′), 4.56 (H-29), 4.48 (dd, J 3.8, 12.3 Hz, H-6′), 4.10–4.13 (m, OCH2), 3.87–3.90 (m, OCH2), 2.73 (H-3), 2.72 (H-28a), 2.53 (H-28a), 2.41 (H-19), 1.99 (H-28), 1.90 (H-21), 1.74 (H-13), 1.66 (H-2), 1.66 (H-16), 1.65 (s, H-30), 1.61 (H-22), 1.59 (H-1), 1.59 (H-12), 1.54 (H-15), 1.43 (H-18), 1.41 (H-28), 1.40 (H-2), 1.34 (H-21), 1.33 (H-11), 1.20 (H-7), 1.18 (H-6), 1.14 (H-7), 1.14 (H-9), 1.11 (H-11), 1.11 (H-16), 1.00 (H-12), 0.99 (H-22), 0.90 (H-6), 0.90 (H-15), 0.88 (s, H-27), 0.87 (s, H-23), 0.82 (s, H-26), 0.73 (H-1), 0.67 (s, H-24), 0.55 (s, H-25), 0.53 (H-5). 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 150.4 (C-20), 135.9 (CH
CH2), 4.76 (H-5′), 4.68 (H-29), 4.64 (dd, J 2.5, 12.3 Hz, H-6′), 4.56 (H-29), 4.48 (dd, J 3.8, 12.3 Hz, H-6′), 4.10–4.13 (m, OCH2), 3.87–3.90 (m, OCH2), 2.73 (H-3), 2.72 (H-28a), 2.53 (H-28a), 2.41 (H-19), 1.99 (H-28), 1.90 (H-21), 1.74 (H-13), 1.66 (H-2), 1.66 (H-16), 1.65 (s, H-30), 1.61 (H-22), 1.59 (H-1), 1.59 (H-12), 1.54 (H-15), 1.43 (H-18), 1.41 (H-28), 1.40 (H-2), 1.34 (H-21), 1.33 (H-11), 1.20 (H-7), 1.18 (H-6), 1.14 (H-7), 1.14 (H-9), 1.11 (H-11), 1.11 (H-16), 1.00 (H-12), 0.99 (H-22), 0.90 (H-6), 0.90 (H-15), 0.88 (s, H-27), 0.87 (s, H-23), 0.82 (s, H-26), 0.73 (H-1), 0.67 (s, H-24), 0.55 (s, H-25), 0.53 (H-5). 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 150.4 (C-20), 135.9 (CH![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) ), 115.9 (
), 115.9 (![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 109.6 (C-29), 86.2 (C-3), 76.3 (C-1′), 72.6 (C-3′), 71.1 (C-2′), 70.6 (C-5′), 70.6 (OCH2), 66.8 (C-4′), 62.3 (C-6′), 55.7 (C-5), 50.3 (C-9), 50.0 (C-18), 47.2 (C-19), 46.7 (C-17), 42.3 (C-14), 40.9 (C-8), 38.8 (C-4), 38.5 (C-1), 37.1 (C-13), 37.0 (C-10), 35.3 (C-22), 34.0 (C-7), 30.7 (C-16), 29.9 (C-21), 28.3 (C-28), 28.0 (C-23), 27.0 (C-15), 25.0 (C-12), 23.1 (C-2), 20.8 (C-11), 19.5 (C-28a), 19.3 (C-30), 18.0 (C-6), 16.2 (C-24), 15.9 (C-25), 15.6 (C-26), 14.8 (C-27). 77Se NMR (CDCl3, 114.4 MHz) δ: 227.8. HR-MS (ESI) calc. for C68H82NaO10Se [M + Na]+: 1161.4971. Found: 1161.4980. Anal. Calcd for C68H82O10Se × H2O (1156.38): C, 70.63; H, 7.32. Found: C, 70.58; H, 7.17.
CH2), 109.6 (C-29), 86.2 (C-3), 76.3 (C-1′), 72.6 (C-3′), 71.1 (C-2′), 70.6 (C-5′), 70.6 (OCH2), 66.8 (C-4′), 62.3 (C-6′), 55.7 (C-5), 50.3 (C-9), 50.0 (C-18), 47.2 (C-19), 46.7 (C-17), 42.3 (C-14), 40.9 (C-8), 38.8 (C-4), 38.5 (C-1), 37.1 (C-13), 37.0 (C-10), 35.3 (C-22), 34.0 (C-7), 30.7 (C-16), 29.9 (C-21), 28.3 (C-28), 28.0 (C-23), 27.0 (C-15), 25.0 (C-12), 23.1 (C-2), 20.8 (C-11), 19.5 (C-28a), 19.3 (C-30), 18.0 (C-6), 16.2 (C-24), 15.9 (C-25), 15.6 (C-26), 14.8 (C-27). 77Se NMR (CDCl3, 114.4 MHz) δ: 227.8. HR-MS (ESI) calc. for C68H82NaO10Se [M + Na]+: 1161.4971. Found: 1161.4980. Anal. Calcd for C68H82O10Se × H2O (1156.38): C, 70.63; H, 7.32. Found: C, 70.58; H, 7.17.
Data for 11. [α]20D 125.8 (c 0.3, chloroform); νmax (film): 2943, 2868, 1729, 1603, 1451, 1281, 1262, 1108, 1086, 1069, 757, 710 cm−1. 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ: 6.23 (d, J 5.3 Hz, H-1′), 5.90–5.96 (m, CH
![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) ), 5.86 (dd, J 5.3, 10.0 Hz, H-2′), 5.77 (dd, J 3.5, 10.0 Hz, H-3′), 5.75 (H-4′), 5.24–5.27 (m,
), 5.86 (dd, J 5.3, 10.0 Hz, H-2′), 5.77 (dd, J 3.5, 10.0 Hz, H-3′), 5.75 (H-4′), 5.24–5.27 (m, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 5.11–5.13 (m,
CH2), 5.11–5.13 (m, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 4.66 (H-29), 4.56 (H-29), 4.52 (dd, J 1.0, 13.1 Hz, H-5′), 4.04 (dd, J 2.3, 13.1 Hz, H-5′), 4.10–4.13 (m, OCH2), 3.87–3.90 (m, OCH2), 2.78 (dd, J 4.1, 11.7 Hz, H-3), 2.58 (H-28a), 2.45, (H-28a), 2.35 (H-19), 1.92 (H-13), 1.88 (H-28), 1.71 (H-2), 1.68 (H-1), 1.68 (H-16), 1.66 (s, H-30), 1.63 (H-22), 1.60 (H-11), 1.60 (H-12), 1.52 (H-15), 1.48 (H-2), 1.48 (H-6), 1.44 (H-18), 1.36 (H-6), 1.35 (H-7), 1.34 (H-28), 1.32 (H-21), 1.26 (H-21), 1.29 (H-11), 1.24 (H-9), 1.15 (H-16), 1.02 (H-12), 0.99 (s, H-26), 0.98 (H-22), 0.96 (H-15), 0.95 (s, H-23), 0.93 (s, H-27), 0.83 (s, H-25), 0.81 (H-1), 0.78 (s, H-24), 0.66 (H-5). 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 150.5 (C-20), 109.5 (C-29), 86.3 (C-3), 79.8 (C-1′, 1JC1,H1 170.4 Hz), 69.6 (C-4′), 69.5 (C-2′), 69.3 (C-3′), 62.5 (C-5′), 55.8 (C-5), 50.4 (C-9), 49.9 (C-18), 47.2 (C-19), 46.8 (C-17), 42.4 (C-14), 40.8 (C-8), 38.8 (C-4), 38.6 (C-1), 37.0 (C-10), 37.0 (C-13), 35.3 (C-22), 34.2 (C-7), 30.6 (C-16), 29.9 (C-21), 28.9 (C-28), 28.0 (C-23), 27.1 (C-15), 25.1 (C-12), 23.1 (C-2), 20.8 (C-11), 19.3 (C-30), 18.5 (C-28a), 18.2 (C-6), 16.2 (C-24), 16.1 (C-25), 15.9 (C-26), 14.8 (C-27). 77Se NMR (CDCl3, 114.4 MHz) δ: 191.5. HR-MS (ESI) calc. for C60H76NaO8Se [M + Na]+: 1027.4603. Found: 1027.4601.
CH2), 4.66 (H-29), 4.56 (H-29), 4.52 (dd, J 1.0, 13.1 Hz, H-5′), 4.04 (dd, J 2.3, 13.1 Hz, H-5′), 4.10–4.13 (m, OCH2), 3.87–3.90 (m, OCH2), 2.78 (dd, J 4.1, 11.7 Hz, H-3), 2.58 (H-28a), 2.45, (H-28a), 2.35 (H-19), 1.92 (H-13), 1.88 (H-28), 1.71 (H-2), 1.68 (H-1), 1.68 (H-16), 1.66 (s, H-30), 1.63 (H-22), 1.60 (H-11), 1.60 (H-12), 1.52 (H-15), 1.48 (H-2), 1.48 (H-6), 1.44 (H-18), 1.36 (H-6), 1.35 (H-7), 1.34 (H-28), 1.32 (H-21), 1.26 (H-21), 1.29 (H-11), 1.24 (H-9), 1.15 (H-16), 1.02 (H-12), 0.99 (s, H-26), 0.98 (H-22), 0.96 (H-15), 0.95 (s, H-23), 0.93 (s, H-27), 0.83 (s, H-25), 0.81 (H-1), 0.78 (s, H-24), 0.66 (H-5). 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 150.5 (C-20), 109.5 (C-29), 86.3 (C-3), 79.8 (C-1′, 1JC1,H1 170.4 Hz), 69.6 (C-4′), 69.5 (C-2′), 69.3 (C-3′), 62.5 (C-5′), 55.8 (C-5), 50.4 (C-9), 49.9 (C-18), 47.2 (C-19), 46.8 (C-17), 42.4 (C-14), 40.8 (C-8), 38.8 (C-4), 38.6 (C-1), 37.0 (C-10), 37.0 (C-13), 35.3 (C-22), 34.2 (C-7), 30.6 (C-16), 29.9 (C-21), 28.9 (C-28), 28.0 (C-23), 27.1 (C-15), 25.1 (C-12), 23.1 (C-2), 20.8 (C-11), 19.3 (C-30), 18.5 (C-28a), 18.2 (C-6), 16.2 (C-24), 16.1 (C-25), 15.9 (C-26), 14.8 (C-27). 77Se NMR (CDCl3, 114.4 MHz) δ: 191.5. HR-MS (ESI) calc. for C60H76NaO8Se [M + Na]+: 1027.4603. Found: 1027.4601.
Data for 12. [α]20D 45.6 (c 0.2, chloroform); νmax (film): 2943, 2868, 1729, 1602, 1452, 1261, 1108, 1092, 1069, 757, 710 cm−1. 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ: 5.90–5.96 (m, CH
![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) ), 5.81 (t, J 6.4 Hz, H-2′), 5.75 (H-4′), 5.71 (dd, J 6.9, 3.3 Hz, H-3′), 5.29 (H-1′), 5.24–5.27 (m,
), 5.81 (t, J 6.4 Hz, H-2′), 5.75 (H-4′), 5.71 (dd, J 6.9, 3.3 Hz, H-3′), 5.29 (H-1′), 5.24–5.27 (m, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 5.11–5.13 (m,
CH2), 5.11–5.13 (m, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 4.69 (H-29), 4.57 (H-29), 4.46 (dd, J 6.1, 12.2 Hz, H-5′), 4.10–4.13 (m, OCH2), 3.95 (dd, J 2.9, 12.2 Hz, H-5′), 3.87–3.90 (m, OCH2), 2.79 (dd, J 4.2, 11.7 Hz, H-3), 2.71 (H-28a), 2.42 (H-19), 1.92 (H-28), 1.86 (H-21), 1.76 (H-16), 1.74 (H-13), 1.70 (H-2), 1.67 (H-1), 1.67 (s, H-30), 1.64 (H-22), 1.62 (H-12), 1.57 (H-15), 1.48 (H-6), 1.46 (H-2), 1.46 (H-18), 1.40 (H-11), 1.39 (H-28), 1.35 (H-7), 1.33 (H-6), 1.30 (H-21), 1.24 (H-9), 1.19 (H-11), 1.18 (H-16), 1.04 (H-12), 1.00 (H-15), 0.98 (H-22), 0.96 (s, H-26), 0.95 (s, H-23), 0.94 (s, H-27), 0.81 (H-1), 0.80 (s, H-25), 0.77 (s, H-24), 0.66 (H-5). 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 150.6 (C-20), 109.5 (C-29), 86.3 (C-3), 78.9 (C-1′, 1JC1,H1 158.0 Hz), 70.9 (C-2′), 69.9 (C-3′), 68.1 (C-4′), 64.3 (C-5′), 55.8 (C-5), 50.4 (C-9), 49.9 (C-18), 47.2 (C-19), 46.9 (C-17), 42.5 (C-14), 40.9 (C-8), 38.8 (C-4), 38.6 (C-1), 37.1 (C-10), 37.0 (C-13), 35.3 (C-22), 34.2 (C-7), 30.7 (C-16), 29.9 (C-21), 29.2 (C-28), 28.1 (C-23), 27.2 (C-15), 25.1 (C-12), 23.1 (C-2), 20.9 (C-11), 20.5 (C-28a), 19.3 (C-30), 18.2 (C-6), 16.3 (C-24), 16.1 (C-25), 16.0 (C-26), 14.8 (C-27). 77Se NMR (CDCl3, 114.4 MHz) δ: approx. 292. HR-MS (ESI) calc. for C60H76NaO8Se [M + Na]+: 1027.4603. Found: 1027.4592.
CH2), 4.69 (H-29), 4.57 (H-29), 4.46 (dd, J 6.1, 12.2 Hz, H-5′), 4.10–4.13 (m, OCH2), 3.95 (dd, J 2.9, 12.2 Hz, H-5′), 3.87–3.90 (m, OCH2), 2.79 (dd, J 4.2, 11.7 Hz, H-3), 2.71 (H-28a), 2.42 (H-19), 1.92 (H-28), 1.86 (H-21), 1.76 (H-16), 1.74 (H-13), 1.70 (H-2), 1.67 (H-1), 1.67 (s, H-30), 1.64 (H-22), 1.62 (H-12), 1.57 (H-15), 1.48 (H-6), 1.46 (H-2), 1.46 (H-18), 1.40 (H-11), 1.39 (H-28), 1.35 (H-7), 1.33 (H-6), 1.30 (H-21), 1.24 (H-9), 1.19 (H-11), 1.18 (H-16), 1.04 (H-12), 1.00 (H-15), 0.98 (H-22), 0.96 (s, H-26), 0.95 (s, H-23), 0.94 (s, H-27), 0.81 (H-1), 0.80 (s, H-25), 0.77 (s, H-24), 0.66 (H-5). 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 150.6 (C-20), 109.5 (C-29), 86.3 (C-3), 78.9 (C-1′, 1JC1,H1 158.0 Hz), 70.9 (C-2′), 69.9 (C-3′), 68.1 (C-4′), 64.3 (C-5′), 55.8 (C-5), 50.4 (C-9), 49.9 (C-18), 47.2 (C-19), 46.9 (C-17), 42.5 (C-14), 40.9 (C-8), 38.8 (C-4), 38.6 (C-1), 37.1 (C-10), 37.0 (C-13), 35.3 (C-22), 34.2 (C-7), 30.7 (C-16), 29.9 (C-21), 29.2 (C-28), 28.1 (C-23), 27.2 (C-15), 25.1 (C-12), 23.1 (C-2), 20.9 (C-11), 20.5 (C-28a), 19.3 (C-30), 18.2 (C-6), 16.3 (C-24), 16.1 (C-25), 16.0 (C-26), 14.8 (C-27). 77Se NMR (CDCl3, 114.4 MHz) δ: approx. 292. HR-MS (ESI) calc. for C60H76NaO8Se [M + Na]+: 1027.4603. Found: 1027.4592.
Data for 13. [α]20D 12.4 (c 0.2, chloroform); νmax (film): 2943, 2869, 1731, 1602, 1452, 1280, 1262, 1104, 1094, 1069, 757, 710 cm−1. 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ: 5.90–5.96 (m, CH
![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) ), 5.85 (H-2′), 5.83 (H-3′), 5.76 (br s, H-1′), 5.73 (t, J 9.7 Hz, H-4′), 5.24–5.27 (m,
), 5.85 (H-2′), 5.83 (H-3′), 5.76 (br s, H-1′), 5.73 (t, J 9.7 Hz, H-4′), 5.24–5.27 (m, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 5.11–5.13 (m,
CH2), 5.11–5.13 (m, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 4.71 (H-29), 4.58 (H-29), 4.42 (dq, J 6.2, 9.7 Hz, H-5′), 4.10–4.13 (m, OCH2), 3.87–3.90 (m, OCH2), 2.79 (dd, J 4.0, 11.7 Hz, H-3), 2.69 (H-28a), 2.46 (H-19), 2.00 (H-28), 1.92 (H-21), 1.79 (H-13), 1.76 (H-16), 1.72 (H-2), 1.68 (H-1), 1.68 (s, H-30), 1.66 (H-22), 1.65 (H-12), 1.59 (H-15), 1.48 (H-18), 1.47 (H-2), 1.47 (H-28), 1.46 (H-6), 1.43 (H-11), 1.39 (d, J 6.2 Hz, H-6′), 1.36 (H-21), 1.35 (H-7), 1.32 (H-6), 1.26 (H-9), 1.24 (H-11), 1.20 (H-16), 1.05 (H-12), 1.02 (H-15), 1.02 (H-22), 1.02 (s, H-26), 0.96 (s, H-27), 0.95 (s, H-23), 0.82 (H-1), 0.81 (s, H-25), 0.77 (s, H-24), 0.66 (H-5). 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 150.6 (C-20), 109.6 (C-29), 86.3 (C-3), 77.8 (C-1′, 1JC1,H1 171.0 Hz), 73.4 (C-2′), 70.6 (C-3′), 71.8 (C-4′), 69.5 (C-5′), 55.8 (C-5), 50.4 (C-9), 49.9 (C-18), 47.1 (C-19), 46.9 (C-17), 42.5 (C-14), 40.9 (C-8), 38.8 (C-4), 38.6 (C-1), 37.1 (C-10), 37.1 (C-13), 35.3 (C-22), 34.2 (C-7), 30.7 (C-16), 29.9 (C-21), 29.2 (C-28), 28.0 (C-23), 27.2 (C-15), 25.1 (C-12), 23.1 (C-2), 20.9 (C-11), 20.6 (C-28a), 19.3 (C-30), 18.2 (C-6), 17.6 (C-6′), 16.3 (C-24), 16.1 (C-25), 16.2 (C-26), 14.8 (C-27). 77Se NMR (CDCl3, 114.4 MHz) δ: 243.6. HR-MS (ESI) calc. for C61H78NaO8Se [M + Na]+: 1041.4760. Found: 1041.4764.
CH2), 4.71 (H-29), 4.58 (H-29), 4.42 (dq, J 6.2, 9.7 Hz, H-5′), 4.10–4.13 (m, OCH2), 3.87–3.90 (m, OCH2), 2.79 (dd, J 4.0, 11.7 Hz, H-3), 2.69 (H-28a), 2.46 (H-19), 2.00 (H-28), 1.92 (H-21), 1.79 (H-13), 1.76 (H-16), 1.72 (H-2), 1.68 (H-1), 1.68 (s, H-30), 1.66 (H-22), 1.65 (H-12), 1.59 (H-15), 1.48 (H-18), 1.47 (H-2), 1.47 (H-28), 1.46 (H-6), 1.43 (H-11), 1.39 (d, J 6.2 Hz, H-6′), 1.36 (H-21), 1.35 (H-7), 1.32 (H-6), 1.26 (H-9), 1.24 (H-11), 1.20 (H-16), 1.05 (H-12), 1.02 (H-15), 1.02 (H-22), 1.02 (s, H-26), 0.96 (s, H-27), 0.95 (s, H-23), 0.82 (H-1), 0.81 (s, H-25), 0.77 (s, H-24), 0.66 (H-5). 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 150.6 (C-20), 109.6 (C-29), 86.3 (C-3), 77.8 (C-1′, 1JC1,H1 171.0 Hz), 73.4 (C-2′), 70.6 (C-3′), 71.8 (C-4′), 69.5 (C-5′), 55.8 (C-5), 50.4 (C-9), 49.9 (C-18), 47.1 (C-19), 46.9 (C-17), 42.5 (C-14), 40.9 (C-8), 38.8 (C-4), 38.6 (C-1), 37.1 (C-10), 37.1 (C-13), 35.3 (C-22), 34.2 (C-7), 30.7 (C-16), 29.9 (C-21), 29.2 (C-28), 28.0 (C-23), 27.2 (C-15), 25.1 (C-12), 23.1 (C-2), 20.9 (C-11), 20.6 (C-28a), 19.3 (C-30), 18.2 (C-6), 17.6 (C-6′), 16.3 (C-24), 16.1 (C-25), 16.2 (C-26), 14.8 (C-27). 77Se NMR (CDCl3, 114.4 MHz) δ: 243.6. HR-MS (ESI) calc. for C61H78NaO8Se [M + Na]+: 1041.4760. Found: 1041.4764.
Data for 14. [α]20D 95.8 (c 0.3, chloroform); νmax (film): 2941, 2868, 1730, 1602, 1452, 1280, 1261, 1120, 1092, 1069, 757, 711 cm−1. 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ: 6.03 (d, J 3.0 Hz, H-2′), 5.90–5.96 (m, CH
![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) ), 5.63 (dd, J 9.4, 10.1 Hz, H-4′), 5.60 (dd, J 3.4, 10.1 Hz, H-3′), 5.30 (s, H-1′), 5.24–5.27 (m,
), 5.63 (dd, J 9.4, 10.1 Hz, H-4′), 5.60 (dd, J 3.4, 10.1 Hz, H-3′), 5.30 (s, H-1′), 5.24–5.27 (m, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 5.11–5.13 (m,
CH2), 5.11–5.13 (m, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 4.68 (H-29), 4.57 (H-29), 4.10–4.13 (m, OCH2), 3.87–3.90 (m, OCH2), 3.87 (H-5′), 2.79 (H-3), 2.77 (H-28a), 2.66 (H-28a), 2.43 (H-19), 1.86 (H-21), 1.78 (H-13), 1.72 (H-2), 1.72 (H-16), 1.68 (H-1), 1.68 (s, H-30), 1.64 (H-22), 1.55 (H-15), 1.55 (H-28), 1.51 (H-6), 1.48 (H-2), 1.48 (H-18), 1.46 (d, J 6.1 Hz, H-6′), 1.45 (H-28), 1.43 (H-11), 1.39 (H-6), 1.38 (H-7), 1.36 (H-21), 1.27 (H-9), 1.24 (H-11), 1.20 (H-16), 1.05 (H-12), 1.05 (s, H-26), 1.03 (H-22), 1.02 (H-15), 0.96 (s, H-27), 0.95 (s, H-23), 0.85 (s, H-25), 0.82 (H-1), 0.79 (s, H-24), 0.68 (H-5). 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 150.4 (C-20), 109.6 (C-29), 86.3 (C-3), 77.0 (C-1′, 1JC1,H1 153.0 Hz), 76.6 (C-5′), 72.5 (C-3′), 72.4 (C-2′), 71.3 (C-4′), 55.8 (C-5), 50.5 (C-9), 49.8 (C-18), 47.2 (C-19), 46.8 (C-17), 42.5 (C-14), 40.9 (C-8), 38.8 (C-4), 38.6 (C-1), 37.1 (C-10), 37.1 (C-13), 35.4 (C-22), 34.3 (C-7), 30.5 (C-16), 29.9 (C-21), 29.0 (C-28), 28.1 (C-23), 27.2 (C-15), 25.0 (C-12), 23.1 (C-2), 20.9 (C-11), 20.3 (C-28a), 19.3 (C-30), 18.2 (C-6), 18.1 (C-6′), 16.3 (C-24), 16.3 (C-26), 16.1 (C-25), 14.8 (C-27). 77Se NMR (CDCl3, 114.4 MHz) δ: 326.6. HR-MS (ESI) calc. for C61H78NaO8Se [M + Na]+: 1041.4760. Found: 1041.4757.
CH2), 4.68 (H-29), 4.57 (H-29), 4.10–4.13 (m, OCH2), 3.87–3.90 (m, OCH2), 3.87 (H-5′), 2.79 (H-3), 2.77 (H-28a), 2.66 (H-28a), 2.43 (H-19), 1.86 (H-21), 1.78 (H-13), 1.72 (H-2), 1.72 (H-16), 1.68 (H-1), 1.68 (s, H-30), 1.64 (H-22), 1.55 (H-15), 1.55 (H-28), 1.51 (H-6), 1.48 (H-2), 1.48 (H-18), 1.46 (d, J 6.1 Hz, H-6′), 1.45 (H-28), 1.43 (H-11), 1.39 (H-6), 1.38 (H-7), 1.36 (H-21), 1.27 (H-9), 1.24 (H-11), 1.20 (H-16), 1.05 (H-12), 1.05 (s, H-26), 1.03 (H-22), 1.02 (H-15), 0.96 (s, H-27), 0.95 (s, H-23), 0.85 (s, H-25), 0.82 (H-1), 0.79 (s, H-24), 0.68 (H-5). 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 150.4 (C-20), 109.6 (C-29), 86.3 (C-3), 77.0 (C-1′, 1JC1,H1 153.0 Hz), 76.6 (C-5′), 72.5 (C-3′), 72.4 (C-2′), 71.3 (C-4′), 55.8 (C-5), 50.5 (C-9), 49.8 (C-18), 47.2 (C-19), 46.8 (C-17), 42.5 (C-14), 40.9 (C-8), 38.8 (C-4), 38.6 (C-1), 37.1 (C-10), 37.1 (C-13), 35.4 (C-22), 34.3 (C-7), 30.5 (C-16), 29.9 (C-21), 29.0 (C-28), 28.1 (C-23), 27.2 (C-15), 25.0 (C-12), 23.1 (C-2), 20.9 (C-11), 20.3 (C-28a), 19.3 (C-30), 18.2 (C-6), 18.1 (C-6′), 16.3 (C-24), 16.3 (C-26), 16.1 (C-25), 14.8 (C-27). 77Se NMR (CDCl3, 114.4 MHz) δ: 326.6. HR-MS (ESI) calc. for C61H78NaO8Se [M + Na]+: 1041.4760. Found: 1041.4757.
Data for 15. [α]20D 83.1 (c 0.2, chloroform); νmax (film): 2943, 2869, 1726, 1602, 1452, 1265, 1105, 1093, 1067, 1027, 757, 710 cm−1. 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ: 5.94 (br s, H-1′), 5.90–5.96 (m, CH
![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) ), 5.66 (br s, H-3′), 5.41 (br s, H-2′), 5.40 (m, H-4′), 5.24–5.27 (m,
), 5.66 (br s, H-3′), 5.41 (br s, H-2′), 5.40 (m, H-4′), 5.24–5.27 (m, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 5.25 (m, H-5′), 5.11–5.13 (m,
CH2), 5.25 (m, H-5′), 5.11–5.13 (m, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 4.73 (dd, J 7.7, 11.6 Hz, H-6′), 4.68 (H-29), 4.57 (H-29), 4.56 (H-6′), 4.10–4.13 (m, OCH2), 3.87–3.90 (m, OCH2), 2.78 (dd, J 4.3, 11.7 Hz, H-3), 2.73 (H-28a), 2.52 (H-28a), 2.40 (H-19), 1.86 (H-21), 1.76 (H-13), 1.72 (H-16), 1.70 (H-2), 1.66 (s, H-30), 1.65 (H-12), 1.64 (H-1), 1.64 (H-22), 1.54 (H-15), 1.54 (H-28), 1.45 (H-2), 1.43 (H-11), 1.42 (H-18), 1.41 (H-28), 1.41 (H-6), 1.31 (H-21), 1.28 (H-7), 1.24 (H-11), 1.20 (H-9), 1.20 (H-16), 1.16 (H-6), 1.05 (H-12), 1.02 (H-22), 0.94 (s, H-23), 0.91 (H-15), 0.91 (s, H-27), 0.90 (s, H-26), 0.78 (H-1), 0.75 (s, H-24), 0.66 (s, H-25), 0.62 (H-5). 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 150.5 (C-20), 109.6 (C-29), 86.3 (C-3), 77.1 (C-1′, 1JC1,H1 168.0 Hz), 69.7 (C-2′), 66.7 (C-4′), 66.3 (C-3′), 66.3 (C-5′), 63.3 (C-6′), 55.8 (C-5), 50.3 (C-9), 49.9 (C-18), 47.2 (C-19), 46.6 (C-17), 42.3 (C-14), 40.9 (C-8), 38.8 (C-4), 38.5 (C-1), 37.0 (C-10), 37.0 (C-13), 35.3 (C-22), 34.2 (C-7), 30.5 (C-16), 29.9 (C-21), 28.8 (C-28), 28.1 (C-23), 27.1 (C-15), 25.1 (C-12), 23.1 (C-2), 20.9 (C-11), 20.3 (C-28a), 19.3 (C-30), 18.2 (C-6), 16.3 (C-24), 16.0 (C-25), 15.9 (C-26), 14.8 (C-27). 77Se NMR (CDCl3, 114.4 MHz) δ: 265.9. HR-MS (ESI) calc. for C68H82NaO10Se [M + Na]+: 1161.4971. Found: 1161.4962. Anal. Calcd for C68H82NaO10Se (1138.33): C, 71.75; H, 7.26. Found: C, 71.88; H, 7.35.
CH2), 4.73 (dd, J 7.7, 11.6 Hz, H-6′), 4.68 (H-29), 4.57 (H-29), 4.56 (H-6′), 4.10–4.13 (m, OCH2), 3.87–3.90 (m, OCH2), 2.78 (dd, J 4.3, 11.7 Hz, H-3), 2.73 (H-28a), 2.52 (H-28a), 2.40 (H-19), 1.86 (H-21), 1.76 (H-13), 1.72 (H-16), 1.70 (H-2), 1.66 (s, H-30), 1.65 (H-12), 1.64 (H-1), 1.64 (H-22), 1.54 (H-15), 1.54 (H-28), 1.45 (H-2), 1.43 (H-11), 1.42 (H-18), 1.41 (H-28), 1.41 (H-6), 1.31 (H-21), 1.28 (H-7), 1.24 (H-11), 1.20 (H-9), 1.20 (H-16), 1.16 (H-6), 1.05 (H-12), 1.02 (H-22), 0.94 (s, H-23), 0.91 (H-15), 0.91 (s, H-27), 0.90 (s, H-26), 0.78 (H-1), 0.75 (s, H-24), 0.66 (s, H-25), 0.62 (H-5). 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 150.5 (C-20), 109.6 (C-29), 86.3 (C-3), 77.1 (C-1′, 1JC1,H1 168.0 Hz), 69.7 (C-2′), 66.7 (C-4′), 66.3 (C-3′), 66.3 (C-5′), 63.3 (C-6′), 55.8 (C-5), 50.3 (C-9), 49.9 (C-18), 47.2 (C-19), 46.6 (C-17), 42.3 (C-14), 40.9 (C-8), 38.8 (C-4), 38.5 (C-1), 37.0 (C-10), 37.0 (C-13), 35.3 (C-22), 34.2 (C-7), 30.5 (C-16), 29.9 (C-21), 28.8 (C-28), 28.1 (C-23), 27.1 (C-15), 25.1 (C-12), 23.1 (C-2), 20.9 (C-11), 20.3 (C-28a), 19.3 (C-30), 18.2 (C-6), 16.3 (C-24), 16.0 (C-25), 15.9 (C-26), 14.8 (C-27). 77Se NMR (CDCl3, 114.4 MHz) δ: 265.9. HR-MS (ESI) calc. for C68H82NaO10Se [M + Na]+: 1161.4971. Found: 1161.4962. Anal. Calcd for C68H82NaO10Se (1138.33): C, 71.75; H, 7.26. Found: C, 71.88; H, 7.35.
Data for 16. [α]20D −9.2 (c 0.5, chloroform); νmax (film): 2942, 2868, 1727, 1602, 1452, 1264, 1107, 1093, 1068, 1027, 756, 710 cm−1. 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ: 5.90–5.96 (m, CH
![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) ), 5.69 (t, J 2.7 Hz, H-3′), 5.54 (d, J 1.4 Hz, H-1′), 5.44 (br s, H-4′), 5.40 (br s, H-2′), 5.24–5.27 (m,
), 5.69 (t, J 2.7 Hz, H-3′), 5.54 (d, J 1.4 Hz, H-1′), 5.44 (br s, H-4′), 5.40 (br s, H-2′), 5.24–5.27 (m, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 5.11–5.13 (m,
CH2), 5.11–5.13 (m, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 4.67 (H-6′), 4.65 (H-29), 4.58 (H-29), 4.57 (H-6′), 4.54 (H-5′), 4.10–4.13 (m, OCH2), 3.87–3.90 (m, OCH2), 2.78 (H-3), 2.78 (H-28a), 2.40 (H-19), 1.95 (H-28), 1.90 (H-21), 1.74 (H-13), 1.72 (H-16), 1.70 (H-2), 1.67 (s, H-30), 1.65 (H-1), 1.65 (H-12), 1.64 (H-22), 1.54 (H-15), 1.49 (H-6), 1.47 (H-18), 1.45, (H-2), 1.43 (H-11), 1.39 (H-28), 1.38 (H-21), 1.35 (H-6), 1.34 (H-7), 1.24 (H-9), 1.24 (H-11), 1.20 (H-16), 1.05 (H-12), 1.02 (H-22), 1.00 (s, H-26), 0.96 (H-15), 0.95 (s, H-23), 0.94 (s, H-27), 0.80 (H-1), 0.77 (s, H-25), 0.75 (s, H-24), 0.66 (H-5). 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 150.3 (C-20), 109.8 (C-29), 86.3 (C-3), 76.6 (C-1′, 1JC1,H1 154.0 Hz), 75.0 (C-5′), 69.7 (C-2′), 67.1 (C-3′), 65.7 (C-4′), 63.2 (C-6′), 55.8 (C-5), 50.4 (C-9), 49.7 (C-18), 47.3 (C-19), 46.9 (C-17), 42.5 (C-14), 40.9 (C-8), 38.8 (C-4), 38.6 (C-1), 37.1 (C-10), 37.1 (C-13), 35.4 (C-22), 34.3 (C-7), 30.6 (C-16), 30.0 (C-21), 28.7 (C-28), 28.1 (C-23), 27.2 (C-15), 25.1 (C-12), 23.1 (C-2), 20.9 (C-11), 19.7 (C-28a), 19.2 (C-30), 18.2 (C-6), 16.3 (C-24), 16.2 (C-26), 16.1 (C-25), 14.8 (C-27). 77Se NMR (CDCl3, 114.4 MHz) δ: 324.1. HR-MS (ESI) calc. for C68H82NaO10Se [M + Na]+: 1161.4971. Found: 1161.5000.
CH2), 4.67 (H-6′), 4.65 (H-29), 4.58 (H-29), 4.57 (H-6′), 4.54 (H-5′), 4.10–4.13 (m, OCH2), 3.87–3.90 (m, OCH2), 2.78 (H-3), 2.78 (H-28a), 2.40 (H-19), 1.95 (H-28), 1.90 (H-21), 1.74 (H-13), 1.72 (H-16), 1.70 (H-2), 1.67 (s, H-30), 1.65 (H-1), 1.65 (H-12), 1.64 (H-22), 1.54 (H-15), 1.49 (H-6), 1.47 (H-18), 1.45, (H-2), 1.43 (H-11), 1.39 (H-28), 1.38 (H-21), 1.35 (H-6), 1.34 (H-7), 1.24 (H-9), 1.24 (H-11), 1.20 (H-16), 1.05 (H-12), 1.02 (H-22), 1.00 (s, H-26), 0.96 (H-15), 0.95 (s, H-23), 0.94 (s, H-27), 0.80 (H-1), 0.77 (s, H-25), 0.75 (s, H-24), 0.66 (H-5). 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 150.3 (C-20), 109.8 (C-29), 86.3 (C-3), 76.6 (C-1′, 1JC1,H1 154.0 Hz), 75.0 (C-5′), 69.7 (C-2′), 67.1 (C-3′), 65.7 (C-4′), 63.2 (C-6′), 55.8 (C-5), 50.4 (C-9), 49.7 (C-18), 47.3 (C-19), 46.9 (C-17), 42.5 (C-14), 40.9 (C-8), 38.8 (C-4), 38.6 (C-1), 37.1 (C-10), 37.1 (C-13), 35.4 (C-22), 34.3 (C-7), 30.6 (C-16), 30.0 (C-21), 28.7 (C-28), 28.1 (C-23), 27.2 (C-15), 25.1 (C-12), 23.1 (C-2), 20.9 (C-11), 19.7 (C-28a), 19.2 (C-30), 18.2 (C-6), 16.3 (C-24), 16.2 (C-26), 16.1 (C-25), 14.8 (C-27). 77Se NMR (CDCl3, 114.4 MHz) δ: 324.1. HR-MS (ESI) calc. for C68H82NaO10Se [M + Na]+: 1161.4971. Found: 1161.5000.
General procedure for the deallylation reaction
A solution of iridium complex was prepared from [Ir(COD)(MePPh2)2]PF6 (3–5 mg) according to the literature procedure17 and transferred to a solution of the corresponding saponin in THF (3 mL), stirred at room temperature for 12 h, and then concentrated. The crude vinyl ether was dissolved in a chloroform (2.0 mL) and methanol (2.0 mL) mixture, and then p-TsOH (70 mg) was added. The mixture was stirred for 1 h and concentrated. Column chromatography (hexane–ethyl acetate, 20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 → 7
1 → 7![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3) of the residue gave the title compound as foam.
3) of the residue gave the title compound as foam.
General procedure for the debenzoylation reaction
A suspension of the protected saponin (0.10 mmol) and K2CO3 (20 mg) in MeOH (10 mL) was stirred for 2 h, then neutralized with Amberlyst 15 resin (H+ form) and purified by column chromatography (hexane–ethyl acetate, 5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 → 1
1 → 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1, and then hexane–ethyl acetate–methanol, 5
1, and then hexane–ethyl acetate–methanol, 5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3
3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) to afford the unprotected saponin.
1) to afford the unprotected saponin.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1); νmax (film): 2941, 2868, 1640, 1454, 1377, 1104, 1066, 1032, 880, 795, 719 cm−1. 1H NMR (CDCl3/CD3OD, 1
1); νmax (film): 2941, 2868, 1640, 1454, 1377, 1104, 1066, 1032, 880, 795, 719 cm−1. 1H NMR (CDCl3/CD3OD, 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) δ: 5.63 (s, H-1′), 4.68 (H-29), 4.57 (H-29), 4.08 (d, J 2.2 Hz, H-2′), 3.91 (H-6′), 3.87 (H-5′), 3.85 (H-4′), 3.79 (H-6′), 3.78 (H-3′), 3.18 (H-3), 2.63 (H-28a), 2.52 (H-28a), 2.41 (H-19), 1.91 (H-28), 1.90 (H-21), 1.78 (H-13), 1.74 (H-16), 1.69 (s, H-30), 1.68 (H-1), 1.67 (H-22), 1.66 (H-12), 1.59 (H-2), 1.57 (H-15), 1.54 (H-6), 1.49 (H-18), 1.44 (H-11), 1.40 (H-6), 1.40 (H-7), 1.39 (H-28), 1.37 (H-21), 1.29 (H-9), 1.25 (H-11), 1.21 (H-16), 1.07 (H-12), 1.06 (s, H-26), 1.03 (H-22), 1.02 (H-15), 0.98 (s, H-27), 0.97 (s, H-23), 0.92 (H-1), 0.85 (s, H-25), 0.77 (s, H-24), 0.70 (H-5). 13C NMR (CDCl3/CD3OD, 1
1) δ: 5.63 (s, H-1′), 4.68 (H-29), 4.57 (H-29), 4.08 (d, J 2.2 Hz, H-2′), 3.91 (H-6′), 3.87 (H-5′), 3.85 (H-4′), 3.79 (H-6′), 3.78 (H-3′), 3.18 (H-3), 2.63 (H-28a), 2.52 (H-28a), 2.41 (H-19), 1.91 (H-28), 1.90 (H-21), 1.78 (H-13), 1.74 (H-16), 1.69 (s, H-30), 1.68 (H-1), 1.67 (H-22), 1.66 (H-12), 1.59 (H-2), 1.57 (H-15), 1.54 (H-6), 1.49 (H-18), 1.44 (H-11), 1.40 (H-6), 1.40 (H-7), 1.39 (H-28), 1.37 (H-21), 1.29 (H-9), 1.25 (H-11), 1.21 (H-16), 1.07 (H-12), 1.06 (s, H-26), 1.03 (H-22), 1.02 (H-15), 0.98 (s, H-27), 0.97 (s, H-23), 0.92 (H-1), 0.85 (s, H-25), 0.77 (s, H-24), 0.70 (H-5). 13C NMR (CDCl3/CD3OD, 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) δ: 150.4 (C-20), 109.3 (C-29), 81.2 (C-1′), 78.6 (C-3), 74.1 (C-5′), 72.7 (C-2′), 72.1 (C-3′), 66.8 (C-4′), 61.1 (C-6′), 55.1 (C-5), 50.3 (C-9), 49.7 (C-18), 47.1 (C-19), 46.6 (C-17), 42.3 (C-14), 40.7 (C-8), 38.6 (C-4), 38.5 (C-1), 36.9 (C-10), 36.9 (C-13), 35.1 (C-22), 34.0 (C-7), 30.4 (C-16), 29.6 (C-21), 28.7 (C-28), 27.6 (C-23), 27.0 (C-15), 26.8 (C-2), 24.8 (C-12), 20.7 (C-11), 19.8 (C-28a), 19.0 (C-30), 18.1 (C-6), 15.8 (C-25), 15.7 (C-26), 15.1 (C-24), 14.6 (C-27). 77Se NMR (CD3OD
1) δ: 150.4 (C-20), 109.3 (C-29), 81.2 (C-1′), 78.6 (C-3), 74.1 (C-5′), 72.7 (C-2′), 72.1 (C-3′), 66.8 (C-4′), 61.1 (C-6′), 55.1 (C-5), 50.3 (C-9), 49.7 (C-18), 47.1 (C-19), 46.6 (C-17), 42.3 (C-14), 40.7 (C-8), 38.6 (C-4), 38.5 (C-1), 36.9 (C-10), 36.9 (C-13), 35.1 (C-22), 34.0 (C-7), 30.4 (C-16), 29.6 (C-21), 28.7 (C-28), 27.6 (C-23), 27.0 (C-15), 26.8 (C-2), 24.8 (C-12), 20.7 (C-11), 19.8 (C-28a), 19.0 (C-30), 18.1 (C-6), 15.8 (C-25), 15.7 (C-26), 15.1 (C-24), 14.6 (C-27). 77Se NMR (CD3OD![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) CDCl3, 1
CDCl3, 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1, 114.4 MHz) δ: 226.3. HR-MS (ESI) calc. for C37H62NaO6Se [M + Na]+: 705.3609. Found: 705.3611.
1, 114.4 MHz) δ: 226.3. HR-MS (ESI) calc. for C37H62NaO6Se [M + Na]+: 705.3609. Found: 705.3611.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1); νmax (film): 2940, 2868, 1640, 1459, 1377, 1083, 1031, 971, 880, 850, 792, 619 cm−1. 1H NMR (CDCl3/CD3OD, 1
1); νmax (film): 2940, 2868, 1640, 1459, 1377, 1083, 1031, 971, 880, 850, 792, 619 cm−1. 1H NMR (CDCl3/CD3OD, 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) δ: 5.70 (d, J 4.7 Hz, H-1′), 4.68 (H-29), 4.57 (H-29), 4.12 (dd, J 1.4, 12.4 Hz, H-5′), 3.98 (dd, J 4.7, 9.0 Hz, H-2′), 3.93 (H-4′), 3.73 (dd, J 3.0, 12.4 Hz, H-5′), 3.65 (dd, J 3.2, 9.0 Hz, H-3′), 3.17 (dd, J 7.7, 8.5 Hz, H-3), 2.57 (H-28a), 2.45 (H-28a), 2.41 (H-19), 1.93 (H-16), 1.91 (H-28), 1.89 (H-21), 1.77 (H-13), 1.68 (s, H-30), 1.67 (H-1), 1.64 (H-12), 1.58 (H-2), 1.56 (H-15), 1.56 (H-22), 1.52 (H-6), 1.48 (H-18), 1.43 (H-11), 1.40 (H-6), 1.38 (H-7), 1.38 (H-28), 1.34 (H-21), 1.28 (H-9), 1.23 (H-11), 1.18 (H-16), 1.08 (H-22), 1.06 (H-12), 1.06 (s, H-26), 0.99 (H-15), 0.96 (s, H-23), 0.96 (s, H-27), 0.90 (H-1), 0.83 (s, H-25), 0.75 (s, H-24), 0.68 (H-5). 13C NMR (CDCl3/CD3OD, 1
1) δ: 5.70 (d, J 4.7 Hz, H-1′), 4.68 (H-29), 4.57 (H-29), 4.12 (dd, J 1.4, 12.4 Hz, H-5′), 3.98 (dd, J 4.7, 9.0 Hz, H-2′), 3.93 (H-4′), 3.73 (dd, J 3.0, 12.4 Hz, H-5′), 3.65 (dd, J 3.2, 9.0 Hz, H-3′), 3.17 (dd, J 7.7, 8.5 Hz, H-3), 2.57 (H-28a), 2.45 (H-28a), 2.41 (H-19), 1.93 (H-16), 1.91 (H-28), 1.89 (H-21), 1.77 (H-13), 1.68 (s, H-30), 1.67 (H-1), 1.64 (H-12), 1.58 (H-2), 1.56 (H-15), 1.56 (H-22), 1.52 (H-6), 1.48 (H-18), 1.43 (H-11), 1.40 (H-6), 1.38 (H-7), 1.38 (H-28), 1.34 (H-21), 1.28 (H-9), 1.23 (H-11), 1.18 (H-16), 1.08 (H-22), 1.06 (H-12), 1.06 (s, H-26), 0.99 (H-15), 0.96 (s, H-23), 0.96 (s, H-27), 0.90 (H-1), 0.83 (s, H-25), 0.75 (s, H-24), 0.68 (H-5). 13C NMR (CDCl3/CD3OD, 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) δ: 150.4 (C-20), 109.2 (C-29), 83.8 (C-1′, 1JC1,H1 165.3 Hz), 78.5 (C-3), 71.1 (C-3′), 69.3 (C-2′), 68.0 (C-4′), 64.7 (C-5′), 55.1 (C-5), 50.2 (C-9), 49.6 (C-18), 47.0 (C-19), 46.6 (C-17), 42.2 (C-14), 42.2 (C-8), 38.5 (C-4), 38.5 (C-1), 36.8 (C-10), 36.8 (C-13), 35.1 (C-22), 33.9 (C-7), 30.3 (C-16), 29.6 (C-21), 28.8 (C-28), 27.6 (C-23), 26.9 (C-15), 26.7 (C-2), 24.8 (C-12), 20.6 (C-11), 18.9 (C-30), 18.1 (C-28a), 18.0 (C-6), 15.7 (C-25), 15.3 (C-26), 15.0 (C-24), 14.5 (C-27). 77Se NMR (CD3OD
1) δ: 150.4 (C-20), 109.2 (C-29), 83.8 (C-1′, 1JC1,H1 165.3 Hz), 78.5 (C-3), 71.1 (C-3′), 69.3 (C-2′), 68.0 (C-4′), 64.7 (C-5′), 55.1 (C-5), 50.2 (C-9), 49.6 (C-18), 47.0 (C-19), 46.6 (C-17), 42.2 (C-14), 42.2 (C-8), 38.5 (C-4), 38.5 (C-1), 36.8 (C-10), 36.8 (C-13), 35.1 (C-22), 33.9 (C-7), 30.3 (C-16), 29.6 (C-21), 28.8 (C-28), 27.6 (C-23), 26.9 (C-15), 26.7 (C-2), 24.8 (C-12), 20.6 (C-11), 18.9 (C-30), 18.1 (C-28a), 18.0 (C-6), 15.7 (C-25), 15.3 (C-26), 15.0 (C-24), 14.5 (C-27). 77Se NMR (CD3OD![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) CDCl3, 1
CDCl3, 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1, 114.4 MHz) δ: 328.6. HR-MS (ESI) calc. for C36H60NaO5Se [M + Na]+: 675.3504. Found: 675.3500.
1, 114.4 MHz) δ: 328.6. HR-MS (ESI) calc. for C36H60NaO5Se [M + Na]+: 675.3504. Found: 675.3500.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1); νmax (film): 2942, 2868, 1453, 1376, 1081, 1043, 992, 883, 860, 798, 757 cm−1. 1H NMR (CDCl3/CD3OD, 1
1); νmax (film): 2942, 2868, 1453, 1376, 1081, 1043, 992, 883, 860, 798, 757 cm−1. 1H NMR (CDCl3/CD3OD, 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) δ: 4.76 (d, J 7.5 Hz, H-1′), 4.69 (H-29), 4.57 (H-29), 4.04 (dd, J 4.4, 12.1 Hz, H-5′), 3.95 (H-4′), 3.79 (t, J 7.5 Hz, H-2′), 3.61 (dd, J 3.3, 7.7 Hz, H-3′), 3.56 (dd, J 2.3, 12.1 Hz, H-5′), 3.16 (dd, J 5.1, 11.2 Hz, H-3), 2.62 (H-28a), 2.44 (H-19), 1.96 (H-28), 1.90 (H-21), 1.80 (H-13), 1.76 (H-16), 1.69 (s, H-30), 1.68 (H-1), 1.68 (H-22), 1.67 (H-12), 1.63 (H-15), 1.60 (H-2), 1.54 (H-6), 1.50 (H-18), 1.44 (H-11), 1.42 (H-6), 1.41 (H-7), 1.41 (H-28), 1.36 (H-21), 1.32 (H-9), 1.24 (H-11), 1.21 (H-16), 1.08 (H-12), 1.06 (s, H-26), 1.02 (H-15), 1.02 (H-22), 0.98 (s, H-27), 0.96 (s, H-23), 0.93 (H-1), 0.85 (s, H-25), 0.76 (s, H-24), 0.70 (H-5). 13C NMR (CDCl3/CD3OD, 1
1) δ: 4.76 (d, J 7.5 Hz, H-1′), 4.69 (H-29), 4.57 (H-29), 4.04 (dd, J 4.4, 12.1 Hz, H-5′), 3.95 (H-4′), 3.79 (t, J 7.5 Hz, H-2′), 3.61 (dd, J 3.3, 7.7 Hz, H-3′), 3.56 (dd, J 2.3, 12.1 Hz, H-5′), 3.16 (dd, J 5.1, 11.2 Hz, H-3), 2.62 (H-28a), 2.44 (H-19), 1.96 (H-28), 1.90 (H-21), 1.80 (H-13), 1.76 (H-16), 1.69 (s, H-30), 1.68 (H-1), 1.68 (H-22), 1.67 (H-12), 1.63 (H-15), 1.60 (H-2), 1.54 (H-6), 1.50 (H-18), 1.44 (H-11), 1.42 (H-6), 1.41 (H-7), 1.41 (H-28), 1.36 (H-21), 1.32 (H-9), 1.24 (H-11), 1.21 (H-16), 1.08 (H-12), 1.06 (s, H-26), 1.02 (H-15), 1.02 (H-22), 0.98 (s, H-27), 0.96 (s, H-23), 0.93 (H-1), 0.85 (s, H-25), 0.76 (s, H-24), 0.70 (H-5). 13C NMR (CDCl3/CD3OD, 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) δ: 149.9 (C-20), 108.7 (C-29), 81.5 (C-1′, 1JC1,H1 156.8 Hz), 77.9 (C-3), 72.4 (C-3′), 71.1 (C-2′), 67.9 (C-5′), 67.2 (C-4′), 54.8 (C-5), 49.9 (C-9), 49.3 (C-18), 46.7 (C-19), 46.2 (C-17), 41.8 (C-14), 41.8 (C-8), 38.1 (C-4), 38.1 (C-1), 36.5 (C-10), 36.5 (C-13), 34.5 (C-22), 33.6 (C-7), 29.9 (C-16), 29.2 (C-21), 28.8 (C-28), 27.0 (C-23), 26.5 (C-15), 26.2 (C-2), 24.5 (C-12), 20.2 (C-11), 18.5 (C-28a), 18.2 (C-30), 17.6 (C-6), 15.3 (C-26), 15.2 (C-25), 14.5 (C-24), 13.9 (C-27). 77Se NMR (CD3OD
1) δ: 149.9 (C-20), 108.7 (C-29), 81.5 (C-1′, 1JC1,H1 156.8 Hz), 77.9 (C-3), 72.4 (C-3′), 71.1 (C-2′), 67.9 (C-5′), 67.2 (C-4′), 54.8 (C-5), 49.9 (C-9), 49.3 (C-18), 46.7 (C-19), 46.2 (C-17), 41.8 (C-14), 41.8 (C-8), 38.1 (C-4), 38.1 (C-1), 36.5 (C-10), 36.5 (C-13), 34.5 (C-22), 33.6 (C-7), 29.9 (C-16), 29.2 (C-21), 28.8 (C-28), 27.0 (C-23), 26.5 (C-15), 26.2 (C-2), 24.5 (C-12), 20.2 (C-11), 18.5 (C-28a), 18.2 (C-30), 17.6 (C-6), 15.3 (C-26), 15.2 (C-25), 14.5 (C-24), 13.9 (C-27). 77Se NMR (CD3OD![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) CDCl3, 1
CDCl3, 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1, 114.4 MHz) δ: 287.9. HR-MS (ESI) calc. for C36H60NaO5Se [M + Na]+: 675.3504. Found: 675.3490.
1, 114.4 MHz) δ: 287.9. HR-MS (ESI) calc. for C36H60NaO5Se [M + Na]+: 675.3504. Found: 675.3490.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1); νmax (film): 2941, 2869, 1640, 1454, 1376, 1102, 1064, 973, 882, 756, 647 cm−1. 1H NMR (CDCl3/CD3OD, 1
1); νmax (film): 2941, 2869, 1640, 1454, 1376, 1102, 1064, 973, 882, 756, 647 cm−1. 1H NMR (CDCl3/CD3OD, 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) δ: 5.55 (d, J 1.0 Hz, H-1′), 4.69 (H-29), 4.57 (H-29), 4.07 (dd, J 1.0, 3.4 Hz, H-2′), 3.92 (dq, J 6.2, 9.4 Hz, H-5′), 3.71 (dd, J 3.4, 9.4 Hz, H-3′), 3.46 (t, J 9.4 Hz, H-4′), 3.16 (dd, J 3.1, 10.2 Hz, H-3), 2.56 (H-28a), 2.42 (H-19), 1.92 (H-28), 1.91 (H-21), 1.78 (H-13), 1.76 (H-16), 1.69 (s, H-30), 1.68 (H-1), 1.68 (H-22), 1.66 (H-12), 1.60 (H-15), 1.59 (H-2), 1.54 (H-6), 1.49 (H-18), 1.44 (H-11), 1.41 (H-6), 1.40 (H-7), 1.40 (H-28), 1.36 (H-21), 1.34 (d, J 6.2 Hz, H-6′), 1.29 (H-9), 1.25 (H-11), 1.21 (H-16), 1.07 (H-12), 1.05 (s, H-26), 1.02 (H-15), 1.02 (H-22), 0.98 (s, H-27), 0.96 (s, H-23), 0.92 (H-1), 0.84 (s, H-25), 0.76 (s, H-24), 0.69 (H-5). 13C NMR (CDCl3/CD3OD, 1
1) δ: 5.55 (d, J 1.0 Hz, H-1′), 4.69 (H-29), 4.57 (H-29), 4.07 (dd, J 1.0, 3.4 Hz, H-2′), 3.92 (dq, J 6.2, 9.4 Hz, H-5′), 3.71 (dd, J 3.4, 9.4 Hz, H-3′), 3.46 (t, J 9.4 Hz, H-4′), 3.16 (dd, J 3.1, 10.2 Hz, H-3), 2.56 (H-28a), 2.42 (H-19), 1.92 (H-28), 1.91 (H-21), 1.78 (H-13), 1.76 (H-16), 1.69 (s, H-30), 1.68 (H-1), 1.68 (H-22), 1.66 (H-12), 1.60 (H-15), 1.59 (H-2), 1.54 (H-6), 1.49 (H-18), 1.44 (H-11), 1.41 (H-6), 1.40 (H-7), 1.40 (H-28), 1.36 (H-21), 1.34 (d, J 6.2 Hz, H-6′), 1.29 (H-9), 1.25 (H-11), 1.21 (H-16), 1.07 (H-12), 1.05 (s, H-26), 1.02 (H-15), 1.02 (H-22), 0.98 (s, H-27), 0.96 (s, H-23), 0.92 (H-1), 0.84 (s, H-25), 0.76 (s, H-24), 0.69 (H-5). 13C NMR (CDCl3/CD3OD, 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) δ: 150.1 (C-20), 109.0 (C-29), 80.7 (C-1′), 72.6 (C-2′), 72.6 (C-4′), 72.2 (C-3), 71.7 (C-3′), 70.1 (C-5′), 55.0 (C-5), 50.1 (C-9), 49.5 (C-18), 46.8 (C-19), 46.4 (C-17), 42.0 (C-14), 40.4 (C-8), 38.8 (C-4), 38.4 (C-1), 36.7 (C-10), 36.7 (C-13), 34.8 (C-22), 33.8 (C-7), 30.2 (C-16), 29.5 (C-21), 28.6 (C-28), 27.3 (C-23), 26.8 (C-15), 26.4 (C-2), 24.7 (C-12), 20.5 (C-11), 19.1 (C-28a), 18.7 (C-30), 17.8 (C-6), 16.8 (C-6′), 15.6 (C-26), 15.5 (C-25), 14.8 (C-24), 14.3 (C-27). 77Se NMR (CD3OD
1) δ: 150.1 (C-20), 109.0 (C-29), 80.7 (C-1′), 72.6 (C-2′), 72.6 (C-4′), 72.2 (C-3), 71.7 (C-3′), 70.1 (C-5′), 55.0 (C-5), 50.1 (C-9), 49.5 (C-18), 46.8 (C-19), 46.4 (C-17), 42.0 (C-14), 40.4 (C-8), 38.8 (C-4), 38.4 (C-1), 36.7 (C-10), 36.7 (C-13), 34.8 (C-22), 33.8 (C-7), 30.2 (C-16), 29.5 (C-21), 28.6 (C-28), 27.3 (C-23), 26.8 (C-15), 26.4 (C-2), 24.7 (C-12), 20.5 (C-11), 19.1 (C-28a), 18.7 (C-30), 17.8 (C-6), 16.8 (C-6′), 15.6 (C-26), 15.5 (C-25), 14.8 (C-24), 14.3 (C-27). 77Se NMR (CD3OD![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) CDCl3, 1
CDCl3, 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1, 114.4 MHz) δ: 229.2. HR-MS (ESI) calc. for C37H62NaO5Se [M + Na]+: 689.3660. Found: 689.3656.
1, 114.4 MHz) δ: 229.2. HR-MS (ESI) calc. for C37H62NaO5Se [M + Na]+: 689.3660. Found: 689.3656.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1); νmax (film): 2941, 2868, 1639, 1454, 1376, 1105, 1043, 982, 880, 733 cm−1. 1H NMR (CDCl3/CD3OD, 1
1); νmax (film): 2941, 2868, 1639, 1454, 1376, 1105, 1043, 982, 880, 733 cm−1. 1H NMR (CDCl3/CD3OD, 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) δ: 5.49 (br s, H-1′), 4.69 (H-29), 4.57 (H-29), 4.42 (ddd, J 1.5, 6.1, 6.1 Hz, H-5′), 3.87 (m, H-3′), 3.84 (m, H-2′), 3.81 (dd, J 5.8, 11.3 Hz, H-6′), 3.77 (dd, J 6.3, 11.3 Hz, H-6′), 3.71 (m, H-4′), 3.14 (dd, J 4.8, 11.5 Hz, H-3), 2.61 (H-28a), 2.52 (H-28a), 2.43 (H-19), 1.94 (H-21), 1.92 (H-28), 1.82 (H-13), 1.76 (H-16), 1.69 (H-1), 1.69 (s, H-30), 1.68 (H-22), 1.67 (H-12), 1.64 (H-15), 1.62 (H-2), 1.58 (H-2), 1.54 (H-6), 1.51 (H-18), 1.45 (H-28), 1.44 (H-11), 1.43 (H-6), 1.42 (H-7), 1.35 (H-21), 1.33 (H-9), 1.25 (H-11), 1.21 (H-16), 1.08 (H-12), 1.08 (s, H-26), 1.03 (H-15), 1.03 (H-22), 0.99 (s, H-27), 0.96 (s, H-23), 0.93 (H-1), 0.86 (s, H-25), 0.76 (s, H-24), 0.71 (H-5). 13C NMR (CDCl3/CD3OD, 1
1) δ: 5.49 (br s, H-1′), 4.69 (H-29), 4.57 (H-29), 4.42 (ddd, J 1.5, 6.1, 6.1 Hz, H-5′), 3.87 (m, H-3′), 3.84 (m, H-2′), 3.81 (dd, J 5.8, 11.3 Hz, H-6′), 3.77 (dd, J 6.3, 11.3 Hz, H-6′), 3.71 (m, H-4′), 3.14 (dd, J 4.8, 11.5 Hz, H-3), 2.61 (H-28a), 2.52 (H-28a), 2.43 (H-19), 1.94 (H-21), 1.92 (H-28), 1.82 (H-13), 1.76 (H-16), 1.69 (H-1), 1.69 (s, H-30), 1.68 (H-22), 1.67 (H-12), 1.64 (H-15), 1.62 (H-2), 1.58 (H-2), 1.54 (H-6), 1.51 (H-18), 1.45 (H-28), 1.44 (H-11), 1.43 (H-6), 1.42 (H-7), 1.35 (H-21), 1.33 (H-9), 1.25 (H-11), 1.21 (H-16), 1.08 (H-12), 1.08 (s, H-26), 1.03 (H-15), 1.03 (H-22), 0.99 (s, H-27), 0.96 (s, H-23), 0.93 (H-1), 0.86 (s, H-25), 0.76 (s, H-24), 0.71 (H-5). 13C NMR (CDCl3/CD3OD, 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) δ: 149.7 (C-20), 108.2 (C-29), 81.5 (C-1′), 77.6 (C-3), 71.7 (C-2′), 68.4 (C-4′), 68.3 (C-5′), 67.9 (C-3′), 60.5 (C-6′), 54.6 (C-5), 49.7 (C-9), 49.1 (C-18), 46.6 (C-19), 45.8 (C-17), 41.5 (C-8), 40.0 (C-14), 37.9 (C-1), 37.8 (C-4), 36.3 (C-13), 36.2 (C-10), 34.3 (C-22), 33.4 (C-7), 29.6 (C-16), 28.9 (C-21), 28.5 (C-28), 26.6 (C-23), 26.3 (C-15), 25.9 (C-2), 24.3 (C-12), 20.0 (C-11), 19.5 (C-28a), 17.7 (C-30), 17.4 (C-6), 14.8 (C-25), 14.7 (C-26), 14.1 (C-24), 13.5 (C-27). 77Se NMR (CD3OD
1) δ: 149.7 (C-20), 108.2 (C-29), 81.5 (C-1′), 77.6 (C-3), 71.7 (C-2′), 68.4 (C-4′), 68.3 (C-5′), 67.9 (C-3′), 60.5 (C-6′), 54.6 (C-5), 49.7 (C-9), 49.1 (C-18), 46.6 (C-19), 45.8 (C-17), 41.5 (C-8), 40.0 (C-14), 37.9 (C-1), 37.8 (C-4), 36.3 (C-13), 36.2 (C-10), 34.3 (C-22), 33.4 (C-7), 29.6 (C-16), 28.9 (C-21), 28.5 (C-28), 26.6 (C-23), 26.3 (C-15), 25.9 (C-2), 24.3 (C-12), 20.0 (C-11), 19.5 (C-28a), 17.7 (C-30), 17.4 (C-6), 14.8 (C-25), 14.7 (C-26), 14.1 (C-24), 13.5 (C-27). 77Se NMR (CD3OD![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) CDCl3, 1
CDCl3, 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1, 114.4 MHz) δ: 267.7. HR-MS (ESI) calc. for C37H62NaO6Se [M + Na]+: 705.3609. Found: 705.3605.
1, 114.4 MHz) δ: 267.7. HR-MS (ESI) calc. for C37H62NaO6Se [M + Na]+: 705.3609. Found: 705.3605.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1). The product was suspended in a hot CHCl3–MeOH (1
1). The product was suspended in a hot CHCl3–MeOH (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3) mixture, cooled to r.t. and the solid was decanted. Pure 27 (49 mg, 88%) was obtained as a yellow powder. All physicochemical properties were identical as desribed for selenol 4. HR-MS (ESI) calc. for C34H56OSe [½M]+: 560.3496. Found: 560.3489. Anal. Calcd for C68H112O2Se2 × 2 × MeOH (1183.65): C, 71.03; H, 10.22. Found: C, 71.25; H, 10.05.
3) mixture, cooled to r.t. and the solid was decanted. Pure 27 (49 mg, 88%) was obtained as a yellow powder. All physicochemical properties were identical as desribed for selenol 4. HR-MS (ESI) calc. for C34H56OSe [½M]+: 560.3496. Found: 560.3489. Anal. Calcd for C68H112O2Se2 × 2 × MeOH (1183.65): C, 71.03; H, 10.22. Found: C, 71.25; H, 10.05.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) to afford 42 mg (74%) of the title compound as light yellow foam. [α]20D 15.3 (c 0.2, chloroform); νmax (film): 2942, 2868, 1642, 1455, 1376, 1135, 1086, 1071, 919, 882, 758 cm−1. 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ: 5.90–5.96 (m, CH
1) to afford 42 mg (74%) of the title compound as light yellow foam. [α]20D 15.3 (c 0.2, chloroform); νmax (film): 2942, 2868, 1642, 1455, 1376, 1135, 1086, 1071, 919, 882, 758 cm−1. 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ: 5.90–5.96 (m, CH![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) ), 5.24–5.27 (m,
), 5.24–5.27 (m, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 5.11–5.13 (m,
CH2), 5.11–5.13 (m, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 4.57 (H-29), 4.68 (H-29), 4.10–4.13 (m, OCH2), 3.87–3.90 (m, OCH2), 2.79 (dd, J 4.2, 11.7 Hz, H-3), 2.47 (H-28a), 2.42 (H-19), 2.39 (H-28a), 2.01 (s, 2JSe,H 10.0 Hz calculated from satellite signals, SeCH3), 1.89 (H-21), 1.88 (H-28), 1.79 (H-13), 1.72 (H-2), 1.68 (H-1), 1.68 (s, H-30), 1.64 (H-22), 1.56 (H-15), 1.50 (H-6), 1.48 (H-2), 1.47 (H-18), 1.39 (H-6), 1.38 (H-7), 1.35 (H-21), 1.33 (H-28), 1.26 (H-9), 1.04 (s, H-26), 1.00 (H-15), 1.00 (H-22), 0.96 (s, H-27), 0.95 (s, H-23), 0.84 (s, H-25), 0.82 (H-1), 0.78 (s, H-24), 0.68 (H-5). 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 150.6 (C-20), 135.9 (CH
CH2), 4.57 (H-29), 4.68 (H-29), 4.10–4.13 (m, OCH2), 3.87–3.90 (m, OCH2), 2.79 (dd, J 4.2, 11.7 Hz, H-3), 2.47 (H-28a), 2.42 (H-19), 2.39 (H-28a), 2.01 (s, 2JSe,H 10.0 Hz calculated from satellite signals, SeCH3), 1.89 (H-21), 1.88 (H-28), 1.79 (H-13), 1.72 (H-2), 1.68 (H-1), 1.68 (s, H-30), 1.64 (H-22), 1.56 (H-15), 1.50 (H-6), 1.48 (H-2), 1.47 (H-18), 1.39 (H-6), 1.38 (H-7), 1.35 (H-21), 1.33 (H-28), 1.26 (H-9), 1.04 (s, H-26), 1.00 (H-15), 1.00 (H-22), 0.96 (s, H-27), 0.95 (s, H-23), 0.84 (s, H-25), 0.82 (H-1), 0.78 (s, H-24), 0.68 (H-5). 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ: 150.6 (C-20), 135.9 (CH![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) ), 115.9 (
), 115.9 (![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 109.6 (C-29), 86.3 (C-3), 70.6 (OCH2), 55.9 (C-5), 50.5 (C-9), 49.9 (C-18), 47.3 (C-19), 46.7 (C-17), 42.5 (C-14), 41.0 (C-8), 38.9 (C-4), 38.6 (C-1), 37.1 (C-10), 37.1 (C-13), 35.4 (C-22), 34.3 (C-7), 30.7 (C-16), 30.0 (C-21), 28.8 (C-28), 28.1 (C-23), 27.2 (C-15), 25.1 (C-12), 23.1 (C-2), 21.0 (C-11), 20.4 (C-28a), 19.4 (C-30), 18.3 (C-6), 16.3 (C-24), 16.1 (C-26), 16.1 (C-25), 14.9 (C-27), 4.1 (SeCH3). 77Se NMR (CDCl3, 114.4 MHz) δ: 93.4. HR-MS (ESI) calc. for C35H58OSe [M]+: 574.3653. Found: 574.3662. Anal. Calcd for C35H58OSe (573.81): C, 73.26; H, 10.19. Found: C, 72.97; H, 10.28.
CH2), 109.6 (C-29), 86.3 (C-3), 70.6 (OCH2), 55.9 (C-5), 50.5 (C-9), 49.9 (C-18), 47.3 (C-19), 46.7 (C-17), 42.5 (C-14), 41.0 (C-8), 38.9 (C-4), 38.6 (C-1), 37.1 (C-10), 37.1 (C-13), 35.4 (C-22), 34.3 (C-7), 30.7 (C-16), 30.0 (C-21), 28.8 (C-28), 28.1 (C-23), 27.2 (C-15), 25.1 (C-12), 23.1 (C-2), 21.0 (C-11), 20.4 (C-28a), 19.4 (C-30), 18.3 (C-6), 16.3 (C-24), 16.1 (C-26), 16.1 (C-25), 14.9 (C-27), 4.1 (SeCH3). 77Se NMR (CDCl3, 114.4 MHz) δ: 93.4. HR-MS (ESI) calc. for C35H58OSe [M]+: 574.3653. Found: 574.3662. Anal. Calcd for C35H58OSe (573.81): C, 73.26; H, 10.19. Found: C, 72.97; H, 10.28.
Acknowledgements
This work was financed by grants from the National Science Centre, Poland (no. 2012/07/B/ST5/00823) and by the Czech Ministry of Education grant from the National Program for Sustainability I (LO1204) and grant GAČR 14-19590S. We thank Olga Hustáková for excellent technical assistance.References
- (a) Y. Xie, M. D. Short, P. B. Cassidy and J. C. Roberts, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2001, 11, 2911–2915 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) S. V. Madhunapantula, D. Desai, A. Sharma, S. J. Huh, S. Amin and G. P. Robertson, Mol. Cancer Ther., 2008, 7, 1297–1308 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) E. Dominguez-Alvarez, D. Plano, M. Font, A. Calvo, C. Prior, C. Jacob, J. A. Palop and C. Sanmartin, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2014, 73, 153–166 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) Q. Guan, F. Yang, D. Guo, J. Xu, M. Jiang, Ch. Liu, K. Bao, Y. Wu and W. Zhang, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2014, 87, 1–9 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) P. Arsenyan, E. Paegle, I. Domracheva, A. Gulbe, I. Kanepe-Lapsa and I. Shestakova, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2014, 87, 471–483 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (f) V. Calcatierra, O. Lopez, J. G. Fernandez-Bolanos, G. B. Plata and J. M. Padron, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2015, 94, 63–72 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (g) M. Zhou, S. Ji, Z. Wu, Y. Li, W. Zheng, H. Zhou and T. Chen, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2015, 96, 92–97 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (h) I. L. Martins, C. Charneira, V. Gandin, J. L. Farreira da Silva, G. C. Justino, J. P. Telo, A. J. S. C. Vieira, C. Marzano and A. M. M. Antunes, J. Med. Chem., 2015, 58, 4250–4265 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) H.-J. Quan, J. Koyanagi, K. Ohmori, S. Uesato, T. Tsuchido and S. Saito, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2002, 37, 659–669 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) L. L. Romero-Hernández, P. Merino-Montiel, S. Montiel-Smith, S. Meza-Reyes, J. L. Vega-Báez, I. Abasolo, S. Schwartz Jr., O. López and J. G. Fernández-Bolaños, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2015, 99, 67–81 CrossRef PubMed.
- (a) D. Plano, C. Sanmartin, E. Moreno, C. Prior, A. Calvo and J. A. Palop, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2007, 17, 6853–6859 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) E. Ibanez, D. Plano, M. Font, A. Calvo, C. Prior, J. A. Palop and C. Sanmartin, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2011, 46, 265–274 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) E. Moreno, D. Plano, I. Lamberto, M. Font, I. Encio, J. A. Palop and C. Sanmartin, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2012, 47, 283–298 CrossRef PubMed.
- Sh. H. Abdel-Hafez, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2008, 43, 1971–1977 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) G. Mugesh and H. Wolf-Walther du Mont Sies, Chem. Rev., 2001, 101, 2125–2179 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) C. W. Nogueira, G. Zeni and J. B. T. Rocha, Chem. Rev., 2004, 104, 6255–6285 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) M. Piętka-Ottlik, H. Wójtowicz-Młochowska, K. Kołodziejczyk, E. Piasecki and J. Młochowski, Chem. Pharm. Bull., 2008, 56, 1423–1427 CrossRef.
- P. Cmoch, A. Korda, L. Rárová, J. Oklešťková, M. Strnad, R. Luboradzki and Z. Pakulski, Tetrahedron, 2014, 70, 2717–2730 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Sidoryk, A. Korda, L. Rárová, J. Oklešťková, M. Strnad, P. Cmoch, Z. Pakulski, K. Gwardiak, R. Karczewski and R. Luboradzki, Tetrahedron, 2015, 71, 2004–2012 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Sidoryk, A. Korda, L. Rárová, J. Oklešťková, Z. Pakulski, M. Strnad, P. Cmoch, K. Gwardiak and R. Karczewski, Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2016, 373–383 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) S. A. Sadek, S. M. Shaw, W. V. Kessler and G. C. Wolf, J. Org. Chem., 1981, 46, 3259–3262 CrossRef CAS; (b) H. J. Quan, J. Koyanagi, F. Komada and S. Saito, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2005, 40, 662–673 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) M. Ibrahim-Ouali, Tetrahedron Lett., 2009, 50, 1607–1609 CrossRef CAS; (d) O. E. D. Rodrigues, D. de Souza, L. C. Soares, L. Dornelles, R. A. Burrow, H. R. Appelt, C. F. Alves, D. Alves and A. L. Braga, Tetrahedron Lett., 2010, 51, 2237–2240 CrossRef CAS; (e) M. Ibrahim-Ouali, E. Romero and H. Bouleghlem, Tetrahedron, 2011, 67, 3668–3676 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) R. Benhaddou, S. Czernecki and D. Randriamandimby, Synlett, 1992, 967–968 CrossRef CAS; (b) C. Mukherjee, P. Tiwari and A. K. Misra, Tetrahedron Lett., 2006, 47, 441–445 CrossRef CAS; (c) P. Tiwari and A. K. Misra, Tetrahedron Lett., 2006, 47, 2345–2348 CrossRef CAS; (d) S. Valerio, A. Iadonisi, M. Adinolfi and A. Ravida, J. Org. Chem., 2007, 72, 6097–6106 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) S. Mehta, J. S. Andrews, B. D. Johnston and B. M. Pinto, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1994, 116, 1569–1570 CrossRef CAS; (b) H. Abe, S. Shuto and A. Matsuda, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2001, 123, 11870–11882 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) S. S. Weng, C. L. Li, C. S. Liao, T. A. Chen, C. C. Huang and K. T. Hung, J. Carbohydr. Chem., 2010, 429, 29–440 Search PubMed.
- (a) G. Stork, H. S. Suh and G. Kim, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1991, 113, 7054–7056 CrossRef CAS; (b) S. Mehta and B. M. Pinto, Tetrahedron Lett., 1991, 32, 4435–4438 CrossRef CAS; (c) K. C. Nicolaou, H. J. Mitchell, K. C. Fylaktakidou, R. M. Rodriguez and H. Suzuki, Chem. – Eur. J., 2000, 6, 3116–3148 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) S. C. Ennis, I. Cumpstey, A. J. Fairbanks, T. D. Butters, M. Mackeen and M. R. Wormald, Tetrahedron, 2002, 58, 9403–9411 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) A. Düffels and S. V. Ley, J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1, 1999, 375–378 RSC; (b) T. Bamhaoud, S. Sanchez and J. Prandi, Chem. Commun., 2000, 659–660 RSC; (c) A. Düffels, L. G. Green, S. V. Ley and A. D. Miller, Chem. – Eur. J., 2000, 6, 1416–1430 CrossRef; (d) H. Abe, S. Shuto and A. Matsuda, J. Org. Chem., 2000, 65, 4315–4325 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) M. Aloui, D. J. Chambers, I. Cumpstey, A. J. Fairbanks, A. J. Redgrave and C. M. P. Seward, Chem. – Eur. J., 2002, 8, 2608–2621 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) S. Mehta, J. S. Andrews, B. D. Johnston, B. Svensson and B. M. Pinto, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1995, 117, 9783–9790 CrossRef CAS; (b) K. C. Nicolaou, R. M. Rodriguez, H. J. Mitchell, H. Suzuki, K. C. Fylaktakidou, O. Baudoin and F. L. Van Delft, Chem. – Eur. J., 2000, 6, 3095–3115 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) K. C. Nicolaou, K. C. Fylaktakidou, H. J. Mitchell, F. L. Van Delft, R. M. Rodriguez, S. R. Conley and Z. Jin, Chem. – Eur. J., 2000, 6, 3166–3185 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. H. Furneaux, Z. Pakulski and P. C. Tyler, Can. J. Chem., 2002, 80, 964–972 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Gauthier, J. Legault, M. Lebrun, P. Dufour and A. Pichette, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2006, 14, 6713–6725 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Cmoch, A. Korda, L. Rárová, J. Oklešťková, M. Strnad, K. Gwardiak, R. Karczewski and Z. Pakulski, Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2014, 4089–4098 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Fugedi, in The Organic Chemistry of Sugars, ed. D. E. Levy and P. Fugedi, CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2006, ch. 4 Search PubMed.
- H. C. Braga, A. D. Wouters, F. B. Zerillo and D. S. Lüdtke, Carbohydr. Res., 2010, 345, 2328–2333 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Krief, W. Dumont and C. Delmotte, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2000, 39, 1669–1672 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) P. Dowd and P. Kennedy, Synth. Commun., 1981, 11, 935–641 CrossRef CAS; (b) A. Krief, M. Trabelsi and W. Dumont, Synthesis, 1992, 933–935 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) B. G. Bag and S. S. Dash, Nanoscale, 2011, 3, 4564–4566 RSC; (b) B. G. Bag and S. S. Dash, Langmuir, 2015, 31, 13664–13672 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) K. Bock, I. Lundt and C. Pedersen, Tetrahedron Lett., 1973, 14, 1037–1040 CrossRef; (b) K. Bock and C. Pedersen, J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. II, 1974, 293–297 RSC; (c) K. Bock and C. Pedersen, Acta Chem. Scand., Ser. B, 1975, 29, 258–264 CrossRef; (d) I. Tvaroska, Adv. Carbohydr. Chem. Biochem., 1995, 51, 15–61 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. B. Sinclair and R. T. Sleeter, Tetrahedron Lett., 1970, 833–836 CrossRef CAS.
- Agilent, CrysAlis PRO, Agilent Technologies, Yarnton, England, 2011 Search PubMed.
- G. M. Sheldrick, Acta Crystallogr., Sect. A: Fundam. Crystallogr., 2008, 64, 112–122 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Copies of 1H and 13C NMR spectra of the synthesized compounds. CCDC 1422676. For ESI and crystallographic data in CIF or other electronic format see DOI: 10.1039/c6ob01938b |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 |