Performance of field-effect transistors based on NbxW1−xS2 monolayers†
Abstract
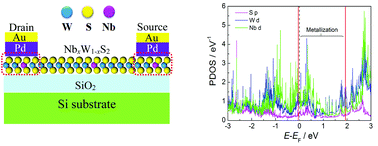
The Schottky barrier has been detected in many field-effect transistors (FETs) based on transition metal dichalcogenide (TMD) semiconductors and has seriously affected the electronic properties of the devices. In order to decrease the Schottky barrier in WS2 FETs, novel Nb doping in WS2 monolayers has been performed and p-FETs based on Nb-doped WS2 (NbxW1−xS2) monolayers as the active channel have been fabricated for the first time. The monolayer Nb0.15W0.85S2 p-FET has a drain current of 330 μA μm−1, an impressive ION/IOFF of 107, and a high effective hole mobility of ∼146 cm2 V−1 s−1. The novel Nb doping in monolayer WS2 has eliminated the ambipolar behavior and reduced the Schottky barrier in WS2 FETs. The reduction of the Schottky barrier is ascribed to the hybridization between W 5d, Nb 4d and S 3p states near the EF and to the enhancement of the metallization of the contact between the Pd metal and monolayer NbxW1−xS2 after Nb doping.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...