Self-assembly, structural order and mechanism of γ-Fe2O3@SiO2 ellipsoids induced by magnetic fields
Abstract
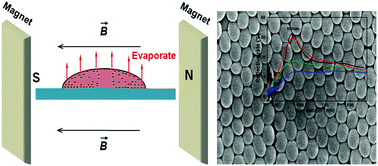
Monodispersed γ-Fe2O3@SiO2 ellipsoids are prepared by the three-step approach of hydrothermal synthesis, reduction–oxidation and SiO2 coating. The magnetic field induced self-assembly processes are designed and carried out in different conditions. Influences of magnetic field strength, solvent, temperature, concentration and substrate are carefully investigated and evaluated by SEM and reflective spectra. The optimal self-assembly conditions of γ-Fe2O3@SiO2 ellipsoid ordered structures are confirmed to be dispersed in ethanol at 0.06 mol L−1 followed by evaporation on a glass substrate in a magnetic field of strength 5000 Oe at 35 °C. Finally, an air–liquid interfacial mechanism is suggested to understand the self-assembly processes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...