Glucose oxidase-assisted extraction of resveratrol from Japanese knotweed (Fallopia japonica)
Abstract
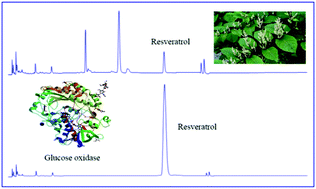
Resveratrol or trans-3,5,4′-trihydroxystilbene, is a natural polyphenolic compound present in several plants, including Japanese knotweed (Fallopia japonica), and has a wide spectrum of pharmacological properties. In the present study, enzyme-assisted extraction of resveratrol from F. japonica roots was examined. Fourteen commercial enzymes were screened, and glucose oxidase was found to offer the highest enhancement of extraction yields of resveratrol compared to other enzymes tested. The glucose oxidase-assisted extraction process was further optimized by varying different processing parameters. When 50% methanol was used as the solvent, the optimal extraction conditions were: temperature 50–60 °C, pH 6.5–7.5, treatment time 5 d and ratio of enzyme to raw material 6 : 100. At the optimal conditions, the extraction yields of resveratrol achieved 24.2 mg g−1 in glucose oxidase-treated samples, which increased more than 400% compared to untreated samples. Using model compounds to probe possible mechanisms of glucose oxidase catalysed glycoside bond cleavage reaction revealed that the enzyme only worked on O-glucoside bond, not on C- or S-glucosides. Furthermore, the enzyme was found to selectively act on glucose bonded glycoside, not on other sugars or disaccharides containing glucose. Glucose oxidase probably catalyzed cleavage lactone bond of glucose skeleton preferentially, then cleavage the glucosidic bond. After this procedure, sugar-based fragments were likely to combine into glucose.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...