Abstract
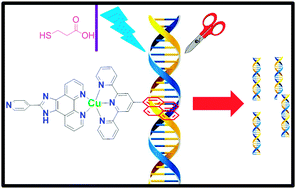
A series of heteroleptic Cu(II)–polypyridyl complexes with terpyridine (3N)/imidazole (2N) backbones and appended with pyridyl, 2-naphthyl, 9-anthryl and 1-pyrenyl groups are synthesized and evaluated for their photonuclease activity. An array of techniques viz. UV-vis, fluorescence, circular dichroism and thermal denaturation established strong DNA binding affinity (Kb = ∼104–106 M−1) and the binding modes were correlated with molecular docking studies. Photonuclease efficiency exceeded 90% for all the complexes under identical conditions. Interestingly, DNA binding propensity and photonuclease efficiency followed the increasing size, planarity, aromaticity, π-Stacking ability and hydrophobicity of the peripheral moiety.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Nitrogen Ligands

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...