Synthesis, characterization and anti-diabetic assay of diorganotin(iv) azo-carboxylates: crystal structure and topological studies of azo-dicarboxylic acid ligand and its cyclic tetranuclear dimethyltin(iv) complex†
Abstract
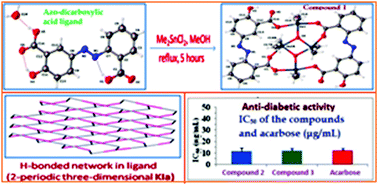
Diorganotin(IV) complexes with (E)-5-((2-carboxyphenyl)diazenyl)-2-hydroxy benzoic acid [H3L] were synthesized by reacting the sodium salt of the azo-dicarboxylic acid ligand [Na2HL] with an appropriate diorganotin(IV) dichloride [R = 1 (Me), 2 (Bu) and 3 (Ph)] in anhydrous methanol. The complexes were characterized using elemental analysis, UV, IR, NMR and mass spectrometry. 119Sn NMR study of complexes 1 and 2 indicates the presence of exo-and endo-cyclic tin atoms in the complexes and both the tin atoms are suggested to have 5-coordinate geometry in solution; in complex 3, a single 119Sn-resonance was observed in the range specified for a 4-coordinate structure. The molecular structure of H3L and its dimethyltin(IV) complex {[Me2SnHLSnMe2]O}2 (1) were determined using X-ray crystallography. The structure of 1 reveals that the compound is a centro-symmetric cyclic tetranuclear tin complex which contains a Sn2O4 core. In the structure, the central Sn2O2 ring is connected to two exo-cyclic tin atoms by two μ3-oxo oxygen atoms. Each exo- and endo-cyclic tin atom exhibited a five coordinate distorted trigonal bipyramidal geometry and suggested that the five coordinate structure of the complex in the solid state is also retained in solution. Topological studies of the azo-dicarboxylic acid ligand [H3L] and its cyclic tetranuclear dimethyltin(IV) complex were also carried out. The H-bonding network in H3L has been topologically classified as 2-periodic three-dimensional KIa. For the molecular packing in 1, a multilevel topological description is provided. Finally, the complexes have been screened for α-glucosidase enzyme inhibition assay as an indicator for their anti-diabetic properties and the results of the tests showed that they had better anti-diabetic activity than the standard drug acarbose.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...