Glabridin-chalcone hybrid molecules: drug resistance reversal agent against clinical isolates of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus†‡
Abstract
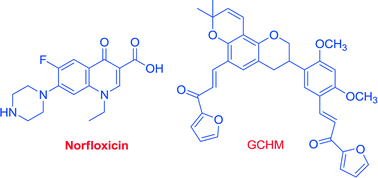
A novel series of glabridin-chalcone hybrid molecules (GCHMs) were synthesized and evaluated for their antibacterial and resistance reversal activity against clinical isolates of a methicillin-resistant strain of Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) alone and in combination with norfloxacin. Glabridin showed significant anti-staphylococcal activity against various MRSA clinical isolates with MICs of 12.5 μg ml−1. However, all its synthesized derivatives displayed moderate to weak activity (MICs ranging from 12.5 to >100 μg ml−1). Among all the synthesized hybrid molecules, compounds 6f, 6h, 8f and 8h along with glabridin were chosen for combination study with norfloxacin. Among all tested compounds, 8h exhibited marked synergism and up to 16-fold reduction in MICs with norfloxacin (FICI range from 0.312 to 0.375). In a systemically infected Swiss albino mice model, compound 8h significantly (p < 0.01, p < 0.05) lowered the systemic bacterial load in blood, liver, kidney, lung and spleen tissues. The present study reports the potential use of GCHMs in the development of economical anti-infective combinations for the treatment of infection caused by clinical MRSA isolates.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...