Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Correction: A proteomic study of Shengmai injection's mechanism on preventing cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury via energy metabolism modulation
Shuyu
Zhan
ac,
Xiaohui
Fan
a,
Feng
Zhang
a,
Yi
Wang
a,
Liyuan
Kang
b and
Zheng
Li
*b
aPharmaceutical Informatics Institute, College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310058, China
bState Key Laboratory of Modern Chinese Medicine, Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin 300193, China. E-mail: lizheng1@gmail.com; Fax: +86-571-88208426; Tel: +86-571-88208427
cDepartment of Pharmaceutics, Medical College of Jiaxing University, Jiaxing 314001, China
First published on 16th December 2015
Abstract
Correction for ‘A proteomic study of Shengmai injection's mechanism on preventing cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury via energy metabolism modulation’ by Shuyu Zhan et al., Mol. BioSyst., 2015, 11, 540–548.
In a recent internal review of the data related to this paper, we found a mistake in calculating the relative intensity of the protein spots in the 2D-gel and western blot while comparing Sham, IR, and IR + SMI groups. The relative intensity (% to sham) was incorrectly calculated by comparing individual rats in a pairwise way. Now it has been corrected by comparing to the mean value of the Sham group. Therefore, related figures in the paper and tables in the ESI have been corrected. All the major results and conclusions in the paper remain unaffected by this mistake.
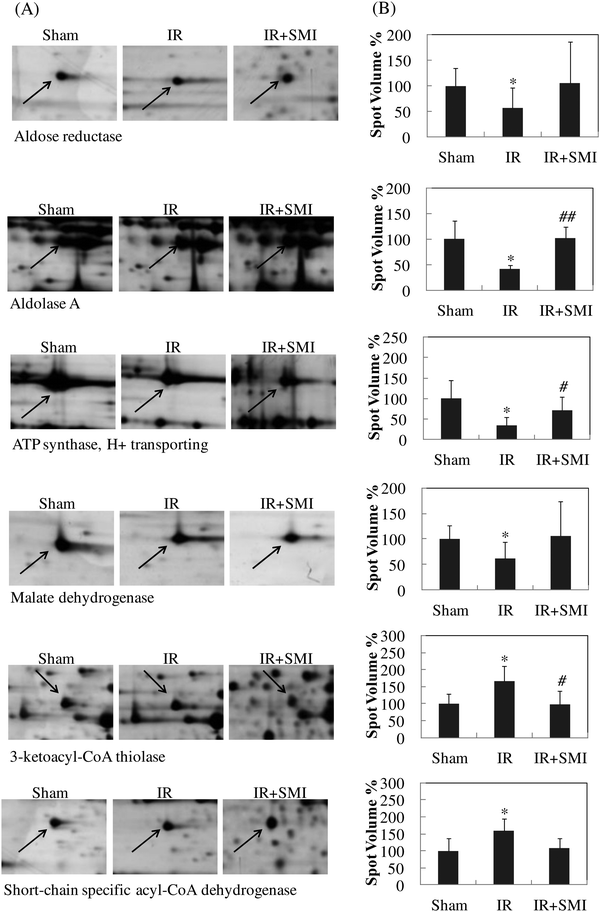
1. Fig. 3(B) on page 543 has been corrected to the following.
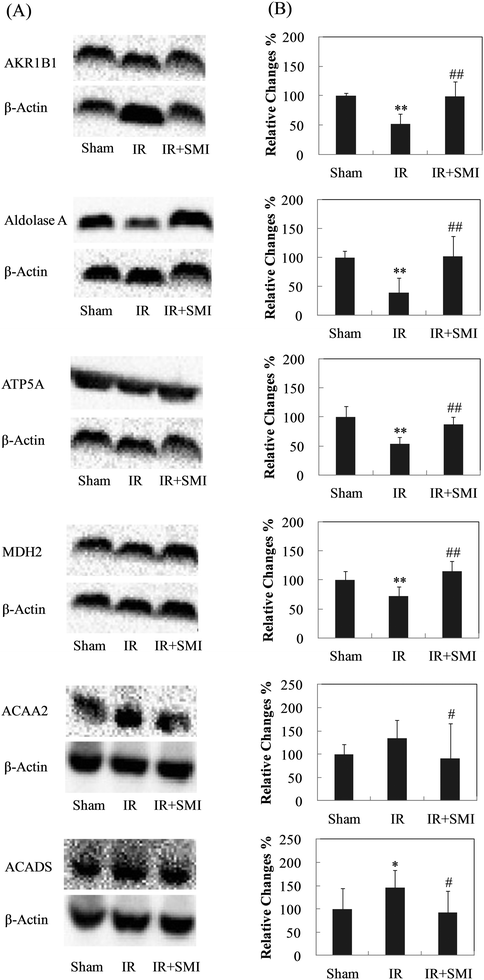
2. Fig. 5(B) on page 545 has been corrected to the following.
3. The description of the results on page 545, paragraph 2, line 9–11, “Compared with the IR group, 14 protein spots were found to be significantly altered in the SMI treated group. Out of these proteins indicated by the arrows in Fig. 2(A), 11 proteins were up-regulated and 3 proteins were down-regulated.” has been restated as:
“Compared with sham group, 14 protein spots were found to be significantly altered in the IR group and with matched protein identity from MALDI-TOF-MS/MS analysis. Out of these proteins indicated by the arrows in Fig. 2(A), 11 proteins were down-regulated and 3 proteins were up-regulated. By further checking these 14 proteins in the SMI treated group, 8 proteins were reversely regulated with p < 0.05 and the other 6 proteins also showed reverse trending, indicating the involvement of these proteins in the therapeutic mechanisms of SMI against IR induced injury.”
4. The relative intensity values in Table 2 of the ESI file have also been corrected, DOI: 10.1039/C4MB00161C.
The Royal Society of Chemistry apologises for these errors and any consequent inconvenience to authors and readers.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 |