Quantitative analyses of Mn, V, and Si elements in steels using a portable laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy system based on a fiber laser
Abstract
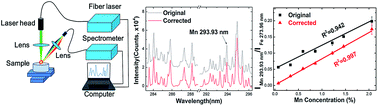
A portable laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) system based on a fiber laser was developed and employed to quantitatively analyze manganese (Mn), vanadium (V), and silicon (Si) elements in steels. After background removal, the coefficients of determination (R2 factors) of the calibration curves for Mn, V, and Si elements reached 0.997, 0.991 and 0.992, respectively, obvious improvements compared to those of the original spectra. The leave-one-out cross-validation (LOOCV) method was used to test the system. The root-mean-square error of cross-validation (RMSECV) for Mn (0.072–2.06 wt%), V (0.009–0.821 wt%), and Si (0.099–1.85 wt%) elements were 0.037, 0.041 and 0.079 wt%, respectively. The average relative errors (AREs) for Mn elements reached 7.6%. These results are comparable with those of the conventional LIBS which refers to utilizing the traditional flash-lamp-pumped laser as a laser source. However, compared to conventional LIBS, a fiber laser LIBS (FL-LIBS) is more compact, robust, and cost effective. The FL-LIBS, coupling a compact fiber laser and spectrometer, is a convenient approach to providing a portable solution for real-time and in situ detection in industry, especially in harsh environments.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2015 Asia Pacific Winter Conference on Plasma Spectrochemistry, Xiamen, China

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...