Preparation of polydopamine sulfamic acid-functionalized magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles with a core/shell nanostructure as heterogeneous and recyclable nanocatalysts for the acetylation of alcohols, phenols, amines and thiols under solvent-free conditions
Abstract
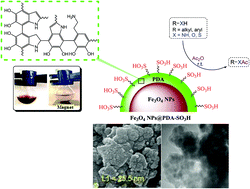
A convenient method for the loading of sulfonic acid groups on the surface of polydopamine (PDA)-encapsulated Fe3O4 nanoparticles is proposed to fabricate a core–shell Fe3O4@PDA-SO3H nanocatalyst. Such surface functionalization of magnetic particles is an elegant way to bridge the gap between heterogeneous and homogeneous catalysis. The as-prepared nanocatalyst was characterized using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), wavelength-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (WDX), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), a vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and back titration. The Fe3O4@PDA-SO3H nanoparticles have been used as an efficient catalyst for the acetylation of a wide range of alcohols, phenols, amines and thiols with acetic anhydride in good to excellent yields under solvent-free conditions. Furthermore, the recovery and reuse of the catalyst was demonstrated 12 times without a detectible loss in activity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...