Enzymatic processing of natural fibres: white biotechnology for sustainable development
Abstract
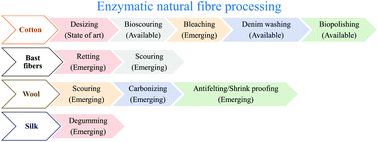
Industrial biotechnology has the potential to fulfil many key criteria of greener textile production. This review outlines the current research and future directions of the emerging applications of enzymatic technology in the sustainable production and processing of textiles. The state-of-the-art industrial enzymes in textile processing include amylases for desizing of cotton and cellulases for denim-washing and biopolishing. Aside from these established processes, emerging enzymatic processes such as cotton scouring and bleaching, bast fiber retting/degumming, wool scouring and shrink-proofing, silk degumming, bio-dye production and enzyme-assisted dyeing and finishing are at various stages of development. To illustrate the state-of-the-art, representative examples of enzymes in the processing of various types of textile substrates are discussed and evaluated in this article. The major limitations of the large scale implications of textile biotechnology are lack of sufficient research efforts to make it an economically viable option and issues related to technological glitches. The limitations of existing approaches will be highlighted and the requirements of continuous improvement to overcome current obstacles will be demonstrated by critical assessment.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...