Enhancing the hepatic protective effect of genistein by oral administration with stachyose in mice with chronic high fructose diet consumption†
Abstract
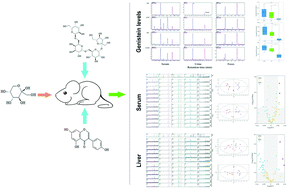
Dietary supplementation of soy stachyose or genistein is known to be of hepatoprotective health interest. This study showed that co-administration of genistein and stachyose caused stronger inhibition on abnormal weight gain and liver fat accumulation by decreasing fatty acid synthetase expression and balancing disorderly lipid metabolism than that of genistein or stachyose alone in high-fructose (HF) diet-fed mice. Furthermore, the production of malonaldehyde and carbonyl derivatives of proteins was also more effectively inhibited by co-treatment of genistein and stachyose, and thereby glutathione peroxidase and superoxide dismutase activities were elevated in HF-fed mice. Moreover, genistein in combination with stachyose was more effective to reduce the impact of HF on the serum markers of liver damage by inhibiting inflammatory cytokine release than stachyose or genistein alone in mice. The potential mechanism was that stachyose enhanced absorption of genistein in HF-fed mice by oral supplementation of genistein together with stachyose. These findings indicate that co-ingestion of stachyose and genistein may serve as a novel strategy for hepatic protection.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...